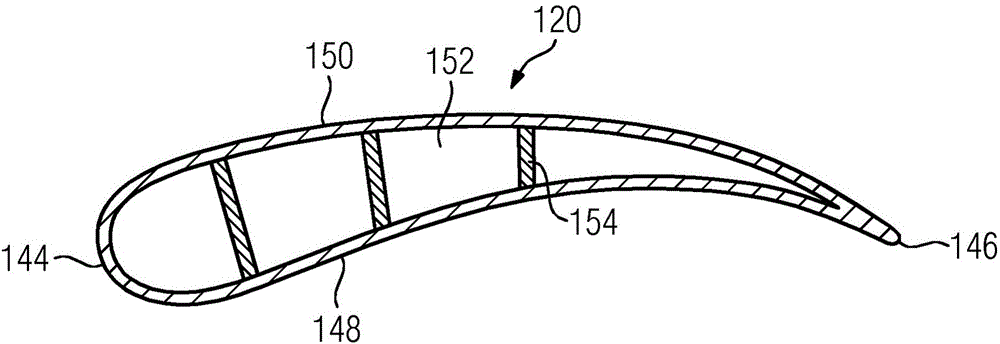
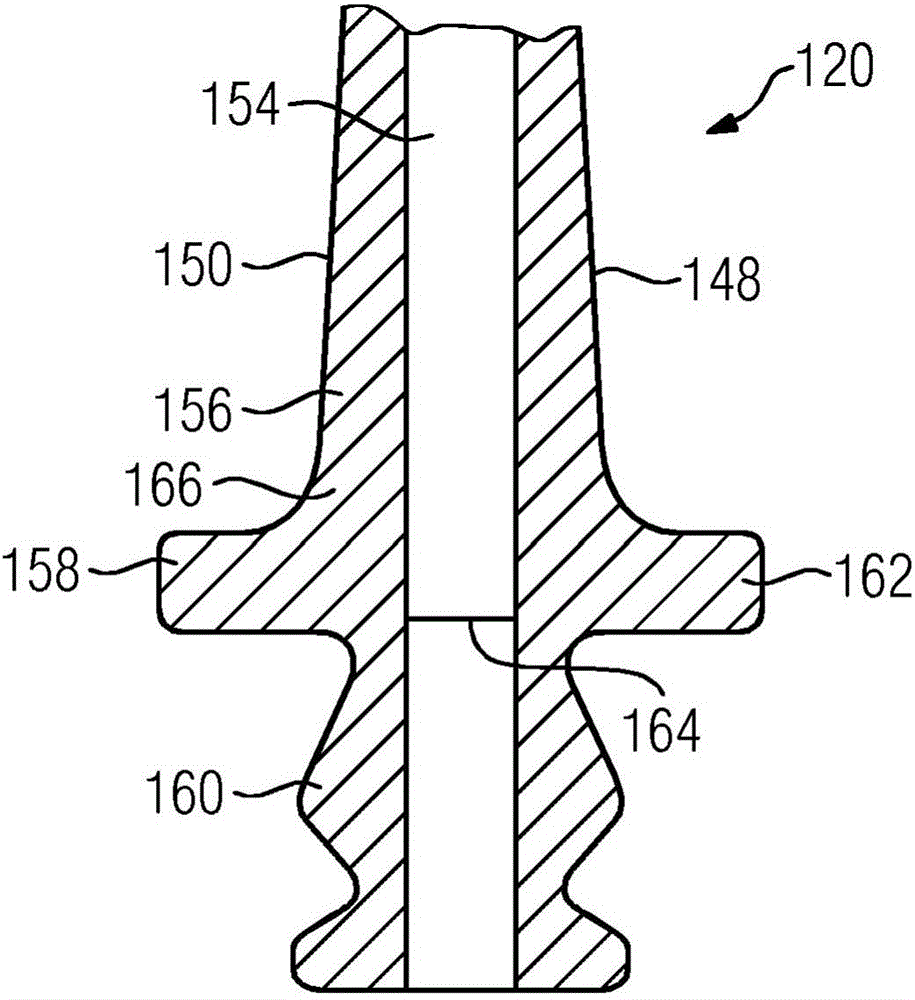
Turbine blade
A technology of turbine blades and turbines, applied in the direction of blade support components, air transportation, engine functions, etc., can solve the problems of poor cooling air guidance, etc., and achieve the effects of increased service life, low stress load, and reduced decoupling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
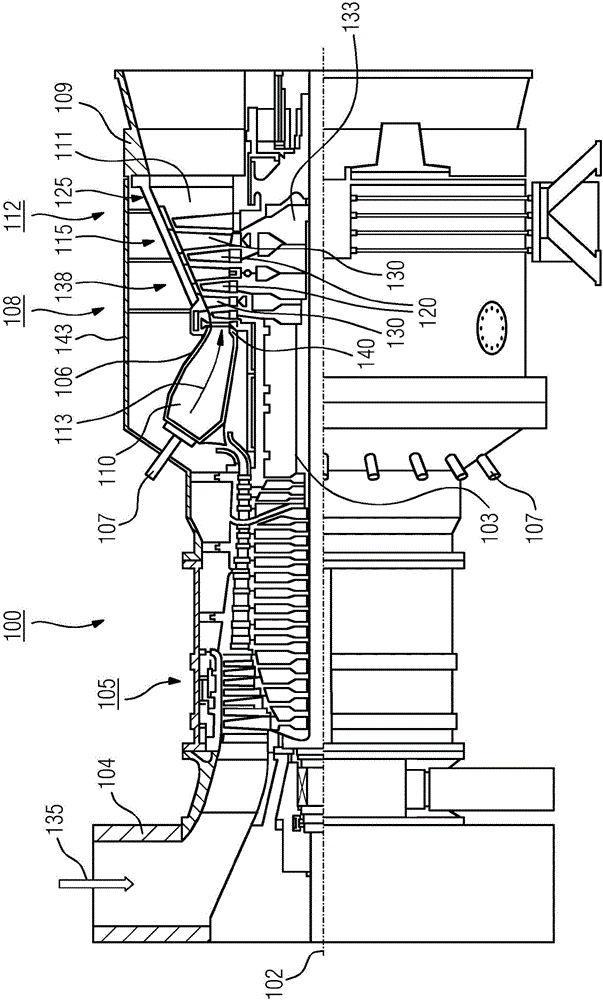
[0025] figure 1 The turbine 100 , here a gas turbine, is shown in longitudinal partial section. The turbine 100 is a fluid machine that converts the internal energy (enthalpy) of a flowing fluid (liquid or gas) into rotational energy and ultimately into mechanical drive energy.
[0026] The gas turbine 100 has internally a rotor 103 mounted such that it can rotate about an axis of rotation 102 (axial direction), which is also named turbine rotor. Along the rotor 103, the intake housing 104, the compressor 105, the torus-like combustion chamber 110, in particular the annular combustion chamber 106 with a plurality of coaxially arranged burners 107, the turbine 108 and the exhaust gas The housings 109 are arranged sequentially.
[0027] The annular combustion chamber 106 communicates with the annular hot gas passage 111 . There, for example, four turbine stages 112 connected one behind the other form the turbine 108 . Each turbine stage 112 is formed by two rings of blades. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com