Method for determining orbit of spacecraft by using relative position increment
A technology of relative position vector and relative position, which is applied in the direction of integrated navigator, navigation calculation tool, etc., to achieve the effect of simple orbit determination method, improved autonomy and easy realization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
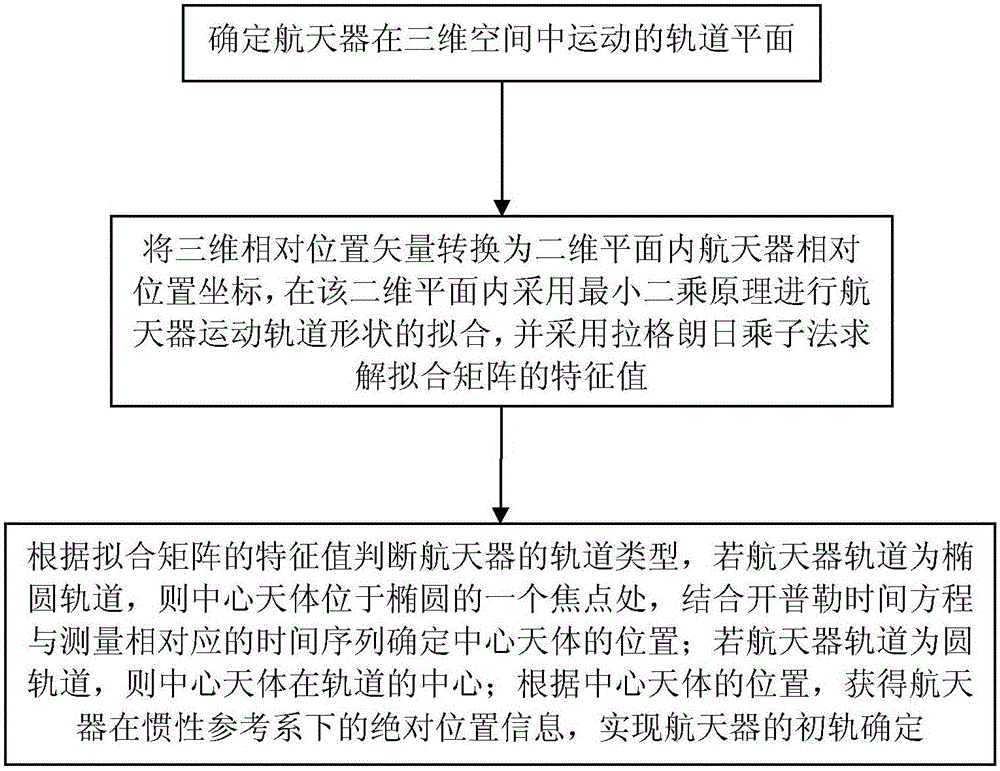
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: refer to image 3 Specifically illustrate the present embodiment, the relative position incremental orbit determination method of the spacecraft described in the present embodiment, the method is:
[0013] First, determine the orbital plane of the spacecraft moving in three-dimensional space;
[0014] Then, transform the three-dimensional relative position vector into the relative position coordinates of the spacecraft in a two-dimensional plane, use the least square principle to fit the shape of the orbit of the spacecraft in the two-dimensional plane, and use the Lagrangian multiplier method to solve the eigenvalues of the fitted matrix;
[0015] Finally, the orbit type of the spacecraft is judged according to the eigenvalues of the fitting matrix. If the orbit of the spacecraft is an ellipse, the central celestial body is located at one focus of the ellipse, and the central celestial body is determined by combining the Kepler ti...
specific Embodiment approach 2
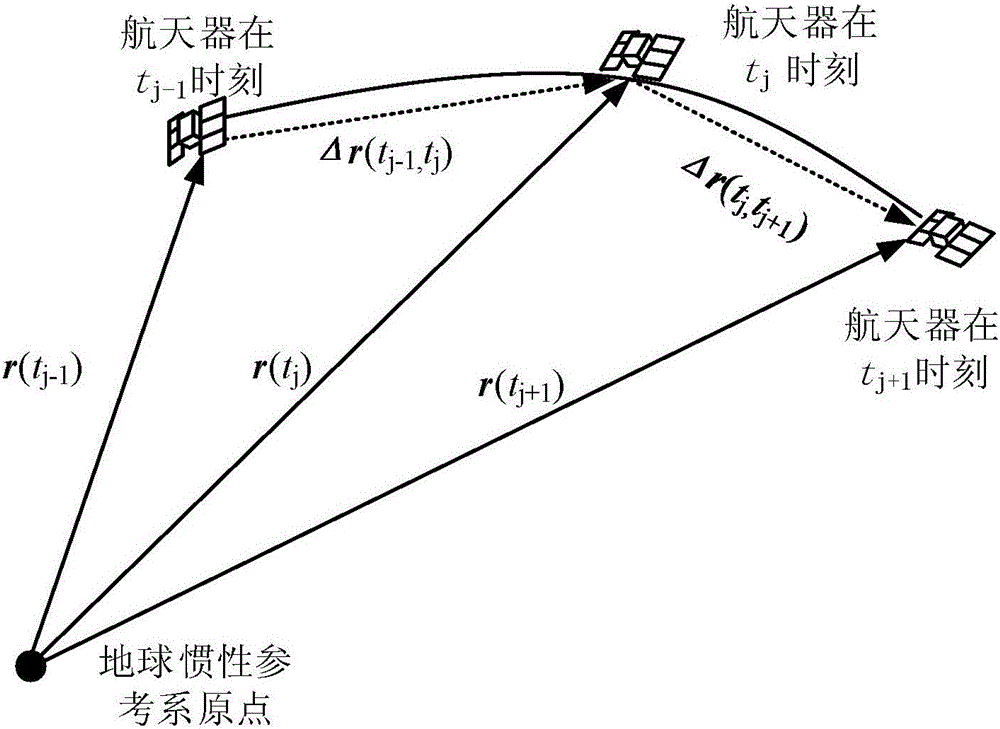
[0016] Specific implementation mode two: refer to figure 1 This embodiment is described in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the relative position incremental orbit determination method of the spacecraft described in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, the specific method for determining the orbital plane of the spacecraft moving in three-dimensional space for:
[0017] Measure the spacecraft at the epoch time t in the earth-centered inertial coordinate system j with t j-1 The relative position vector Δr(t j-1 ,t j ), and according to the relative position vector Δr(t j-1 ,t j ) to obtain the initial position of the spacecraft r(t 0 ), where j=1,2,3,...;
[0018] According to the relative position vector Δr(t j-1 ,t j ), using the principle of least squares to determine the unit angular momentum vector h;
[0019] Δr x ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
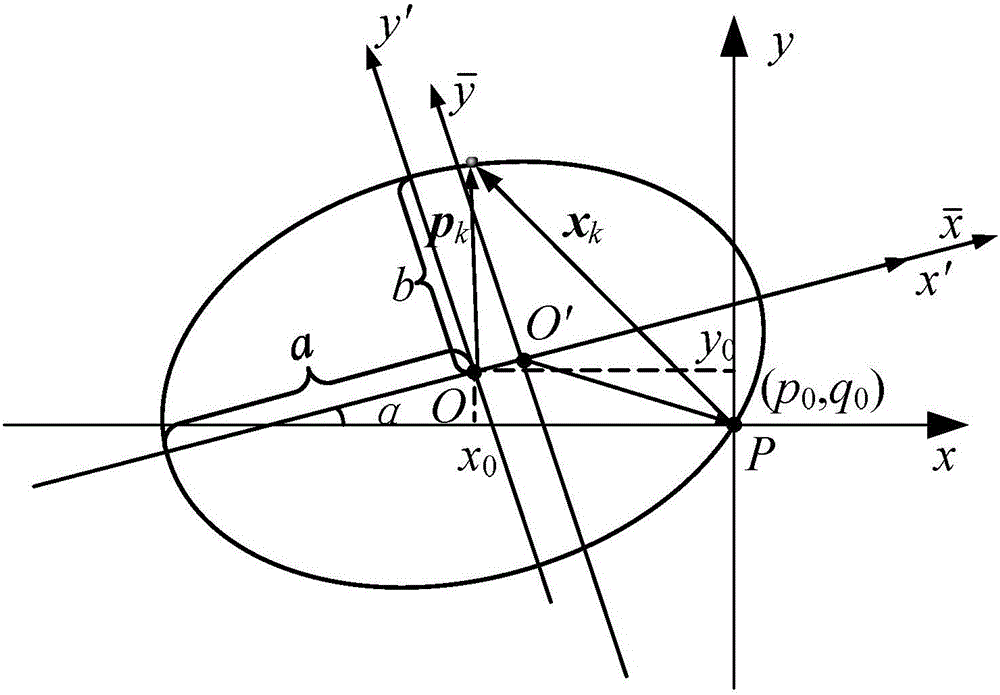
[0029] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is to further explain the relative position incremental orbit determination method of the spacecraft described in the second specific embodiment. In this embodiment, the three-dimensional relative position vector is converted into the relative position of the spacecraft in the two-dimensional plane The specific method of coordinates is:
[0030] Set reference frame P xyz Taking the initial position of the spacecraft as the origin, the z-axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane, and the x and y-axes are based on the coordinate transformation matrix Q of the Earth's J2000 reference system Xx get;
[0031] Obtain the relative position of the spacecraft in the reference frame P according to the orbital inclination i and the right ascension of the ascending node Ω xyz The vector x in k :
[0032] x k =Q Xx m k (4)
[0033] In the formula, is the vector of the spacecraft position relative to the initial position at time ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com