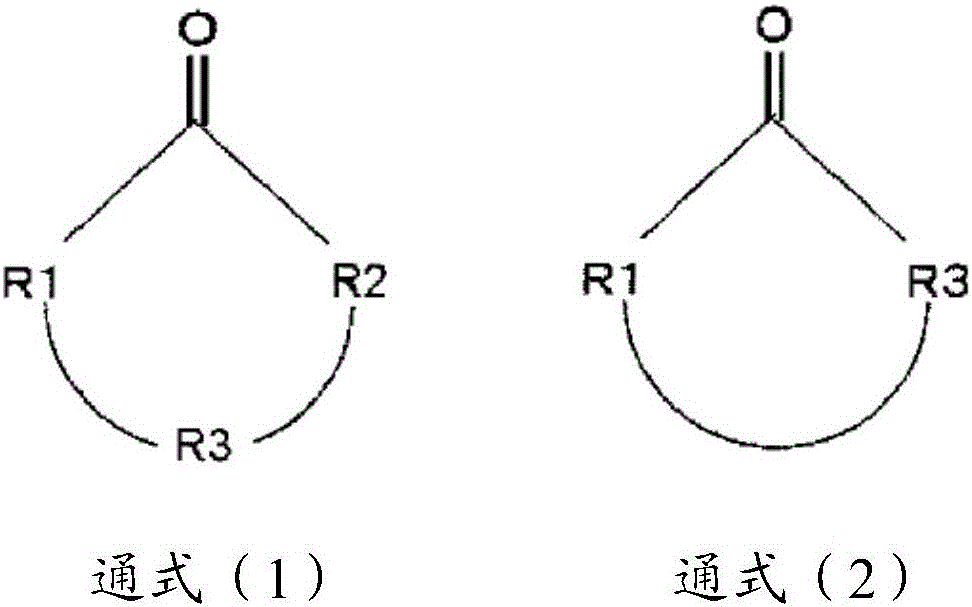
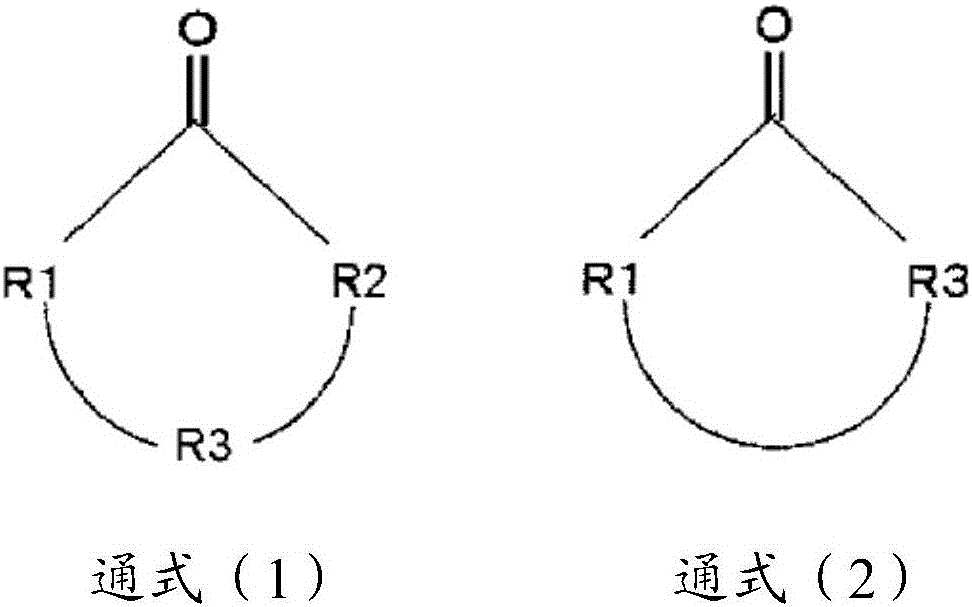
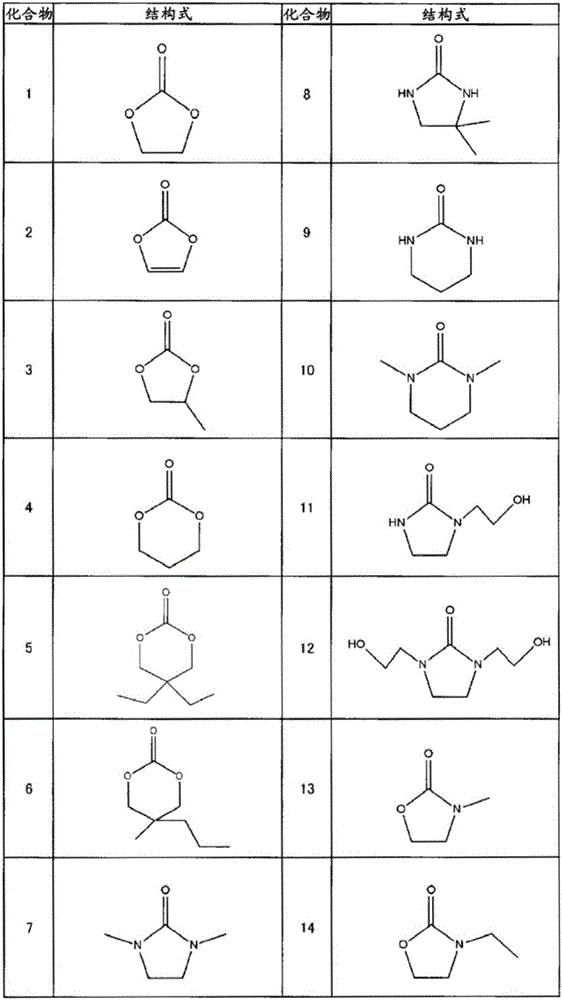
Active energy ray-curable inkjet ink
A technology of active energy rays and inkjet inks, applied in ink, printing, copying/marking methods, etc., can solve the problems that hinder the low viscosity of inkjet inks, and achieve excellent adhesion, excellent curing, and spit out stability high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~31、37 and comparative example 1~7
[0157] Preparation of transparent ink
[0158] Table 2 shows the raw materials used to prepare the clear ink. According to the compounding described in Tables 3-6, a polymerizable monomer, a photopolymerization initiator, a polymerization inhibitor, and an organic solvent were slowly added to a reaction container, and the obtained liquid mixture was stirred. Next, after adding a surface tension adjusting agent to the above-mentioned mixed liquid, it was shaken by a shaker for 6 hours to prepare an ink. The obtained ink was filtered through a PTFE filter with a pore diameter of 0.5 microns to remove dust and coarse particles, and used as an evaluation ink. In addition, the addition and mixing order of the raw material for obtaining the said mixed liquid may differ.
Embodiment 32~35
[0160] Modulation of color ink
[0161] 15 parts by weight of the organic pigment, 7.5 parts by weight of the pigment dispersant, and 77.5 parts by weight of DPGDA were stirred with a high-speed mixer or the like until they became uniform. Next, the obtained mill base was dispersed for about 1 hour with a horizontal sand mill to prepare a pigment dispersion.
[0162] To the previously prepared pigment dispersion, a mixed solution of a polymerizable monomer, a photopolymerization initiator, a polymerization inhibitor, and an organic solvent was slowly added so as to be formulated in Table 7, and the obtained mixed solution was stirred. The compounding amount of DPGDA described in Table 7 is a numerical value which also includes the amount of DPGDA in the pigment dispersion. Next, after adding a surface tension modifier to the above-mentioned mixed solution, it was shaken by a shaker for 6 hours to prepare a color ink. The obtained color ink was filtered through a PTFE filter ...
Embodiment 36
[0164] Preparation of white ink
[0165] As a pigment, 50 parts of Tipaque CR-60 (titanium oxide treated with aluminum, primary particle size 210 nm, manufactured by Ishihara Sangyo Co., Ltd.), 2.5 parts of pigment dispersant, and 47.5 parts of DPGDA were stirred with a high-speed mixer until uniform . Next, the obtained mill base was dispersed for about 2 hours with a horizontal sand mill to prepare a pigment dispersion.
[0166]A mixed solution of a polymerizable monomer, a photopolymerization initiator, a polymerization inhibitor, and an organic solvent was slowly added to the previously prepared pigment dispersion so that the formulation described in Table 7 was obtained, and the obtained mixed solution was stirred. The compounding amount of DPGDA described in Table 7 is a numerical value which also includes the amount of DPGDA in the pigment dispersion. Next, after adding a surface tension modifier to the above mixed liquid, it was shaken by a shaker for 6 hours to prep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com