Micro-CT (micro-computed tomography) based non-uniform Voxel grid discretization method for three-dimensional braided composite material
A composite material and three-dimensional weaving technology, applied in image data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as discrete grids, and achieve the effects of avoiding errors, reducing calculations, and reducing scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
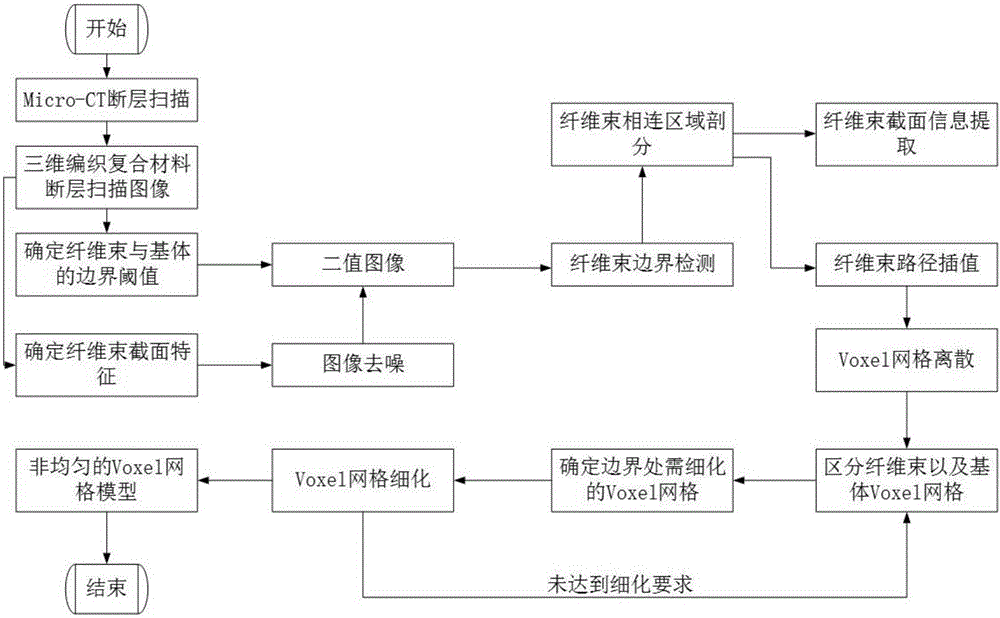
[0045] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 The non-uniform Voxel grid discretization method based on Micro-CT three-dimensional braided composite material in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0046] Step 1. Based on the micro-CT slice scanning of the internal weaving structure of the three-dimensional braided composite material, identify and scan the slice images of different gray levels. In the slice image, the gray scale of the fiber bundle and the matrix is very different. Through the gray scale slice According to the gray value of different fiber bundles and matrix materials in the layer image, the threshold histogram of fiber bundles and matrix is counted to determine the region segmentation threshold, and the binary image of the gray slice image is obtained according to the region segmentation threshold; among them, the scanned gray The sheet image is the image of the internal weaving structure of the three-di...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0070] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the gray values of the different fiber bundles and matrix materials in the gray-scale sheet image described in step 1 are specifically:
[0071] g ( j , j ) = 1 ... ... f ( i , j ) ≥ H 0 ... ... f ( i , ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0073] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that after the denoising process is performed on the binary image of the sheet image in step 2, the boundary between the smooth matrix region and the inner region of the fiber bundle will be smoothed The fiber bundle boundary is subjected to geometric vectorization processing, and the cross-sectional shape of the fiber bundle is determined by the polygon as follows:
[0074] Step 21, performing an opening operation and a closing operation on the binary image of the slice image to eliminate the long and narrow gaps and small holes in the binary image of the slice image;
[0075] Step 22: Denoise the interior of the matrix and the interior of the fiber bundles using image erosion and expansion techniques, that is, remove other pixels distributed in dots and dots inside the matrix and fiber bundles to obtain the denoised matrix area and fiber bundle area (i.e. smooth Matrix region and fiber bundl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com