Built-in permanent magnet vibration reduction and noise reduction synchronous motor
A synchronous motor, built-in technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit static parts, magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc. Durability, reduction of concealment and safety, etc., to improve the air gap magnetic field waveform, improve radial electromagnetic force, and reduce vibration and noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
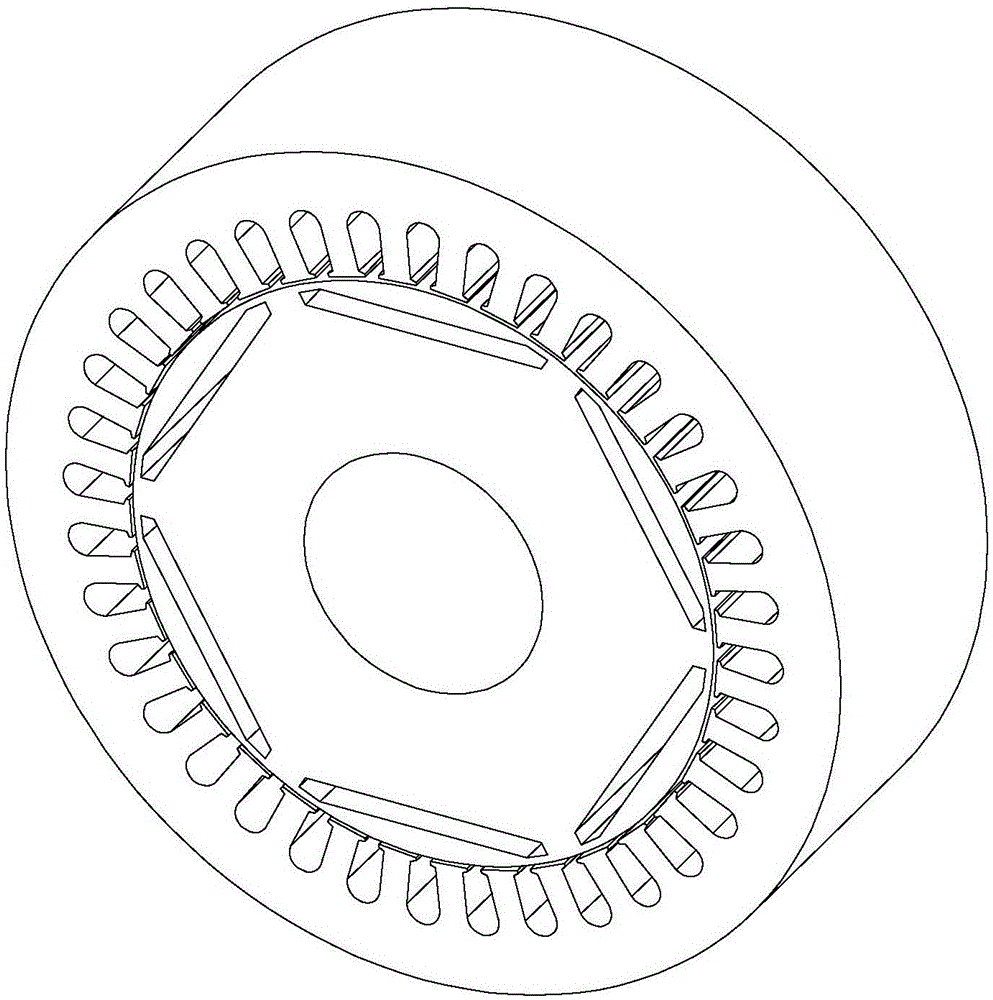
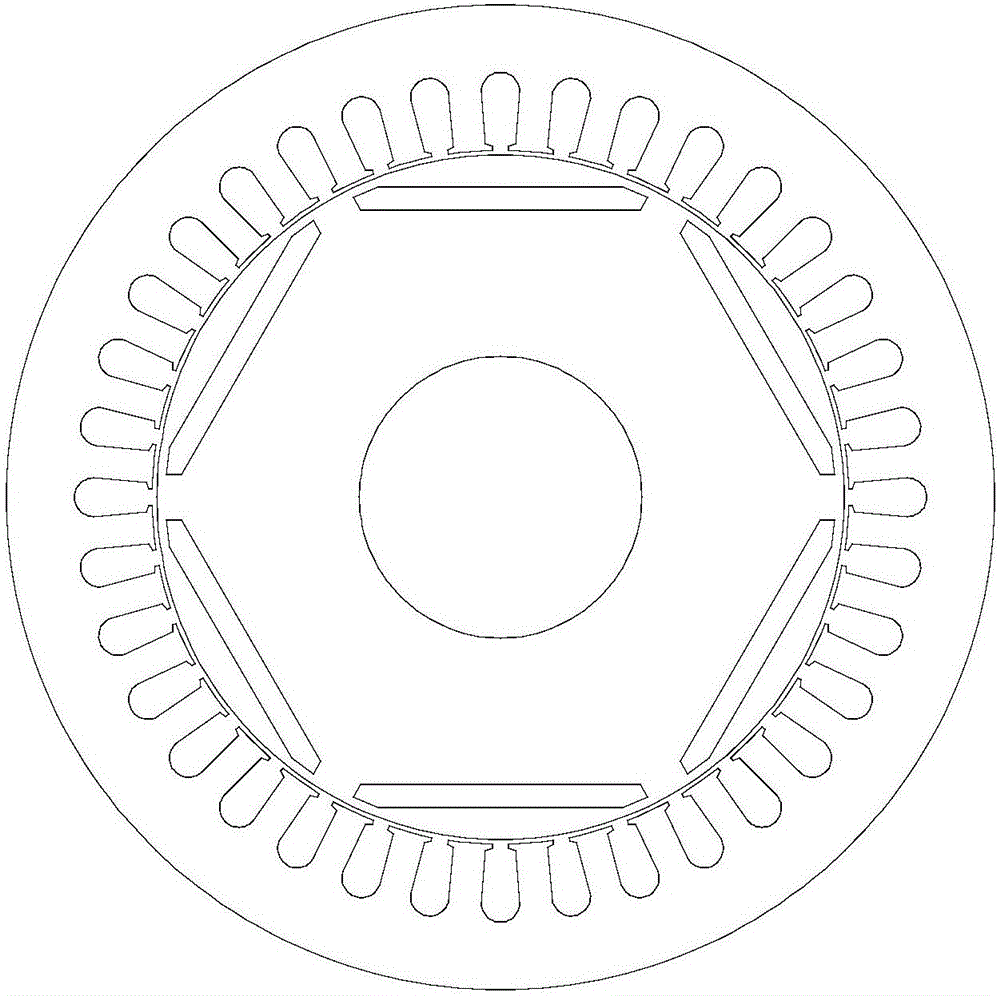
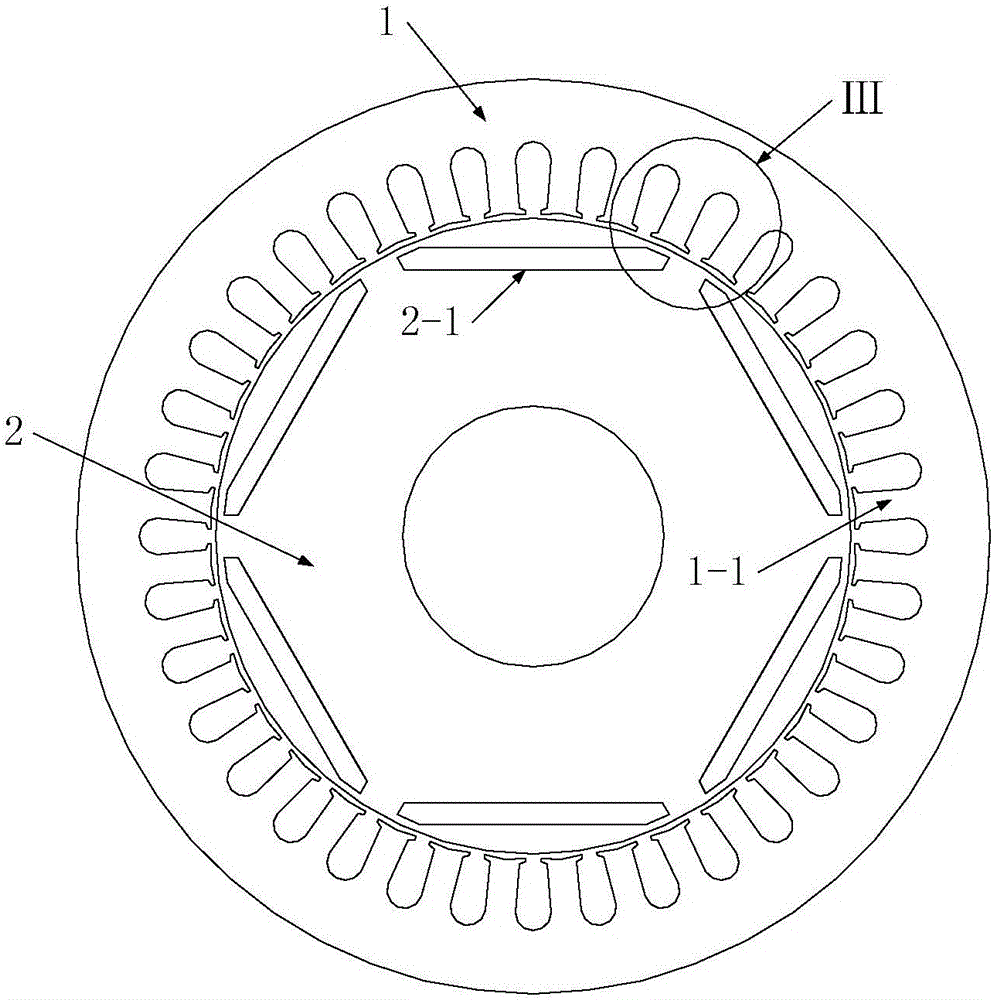
[0028] Specific implementation mode one: see image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment, the built-in permanent magnet vibration reduction and noise reduction synchronous motor described in this embodiment includes a stator 1 and a rotor 2, the stator 1 is set on the outside of the rotor 2, the two are coaxial, and between the two There is an air gap, and the addendum arc corresponding to each tooth portion 1-1 on the stator 1 is divided into two parts by the radial centerline of the tooth portion 1-1, and the two parts addendum arc The corresponding positions are respectively defined as: the front half teeth 1-1-1 and the second half teeth 1-1-2, the front half teeth 1-1-1 and the rear half teeth 1-1-2 are arranged counterclockwise in turn, the front half teeth The arc of the addendum of the tooth 1-1-1 is different from the arc of the addendum of the rear half tooth 1-1-2.
[0029] In this embodiment, the built-in permanent magnet vibration reduction and noise reducti...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific implementation mode two: see image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the built-in permanent magnet noise-reduction synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1 is that when the rotation direction of the rotor 2 is counterclockwise, the tooth tip of the first half tooth 1-1-1 The radian of the arc is greater than the arc of the addendum arc of the rear half tooth 1-1-2.
[0032] In this embodiment, when the rotation direction of the rotor 2 (that is, the positive direction of the magnetic field rotation) is counterclockwise, along this direction, in each tooth portion 1-1 on the stator, there are always the first half teeth 1-1- 1 is in contact with the magnetic field first, so when the magnetic field turns over a tooth 1-1 of the stator, the front half tooth 1-1-1 of the stator is subjected to the air gap magnetic field for a longer time than the second half tooth 1-1-2, so the front half tooth 1-1-1 is The a...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the built-in permanent magnet noise reduction synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1 is that when the rotation direction of the rotor 2 is in the clockwise direction, the addendum of the first half tooth 1-1-1 The radian of the arc is smaller than the arc of the addendum arc of the rear half tooth 1-1-2.
[0034] In this embodiment, when the rotation direction of the rotor 2 (that is, the positive direction of the magnetic field rotation) is clockwise, along this direction, in each tooth portion 1-1 on the stator, there are always the rear half teeth 1-1 -2 is in contact with the magnetic field first, so when the magnetic field turns over a tooth portion 1-1 of the stator, the second half tooth 1-1-2 of the stator is subjected to the air gap magnetic field for a longer time than the front half tooth 1-1-1, so the rear half tooth 1-1-2 will The radian of the addendum arc of the half tooth 1-1-2 is designed to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com