Method for selecting wire after single-phase grounding of ungrounded system
A single-phase grounding and grounding system technology, applied in the direction of fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, etc., can solve problems such as TV fuse blown, bus short circuit, power cable explosion, etc. The method is simple and convenient, reduces faults, and improves fault detection efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
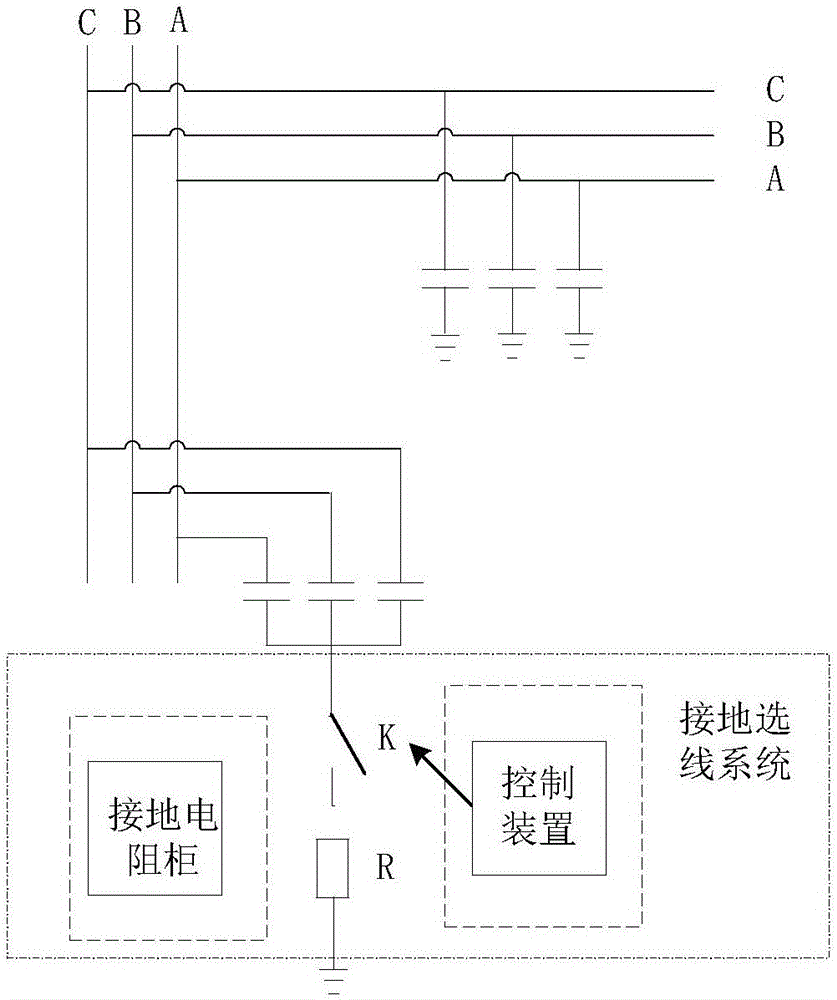
[0021] The method for line selection after a single-phase grounding occurs in an ungrounded system of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0022] A) In the substation system where the neutral point is not grounded, a control switch and a control switch are installed between the neutral point of the capacitor and the ground
[0023] A resistor with a resistance value of 100 ohms, in normal operation, the control switch is in the minute position;
[0024] B) According to the change of the bus voltage to judge whether there is a single-phase grounding of the line, the criterion is that the zero-sequence voltage is greater than 50V, and at the same time, when the voltage of a certain phase of the three-phase voltage drops less than 30V, and the voltage of the other two phases rises greater than 70V, It is judged that a single-phase ground fault has occurred;
[0025] C) After judging that it is single-phase grounding, close the control switch immediately and put...
Embodiment 2
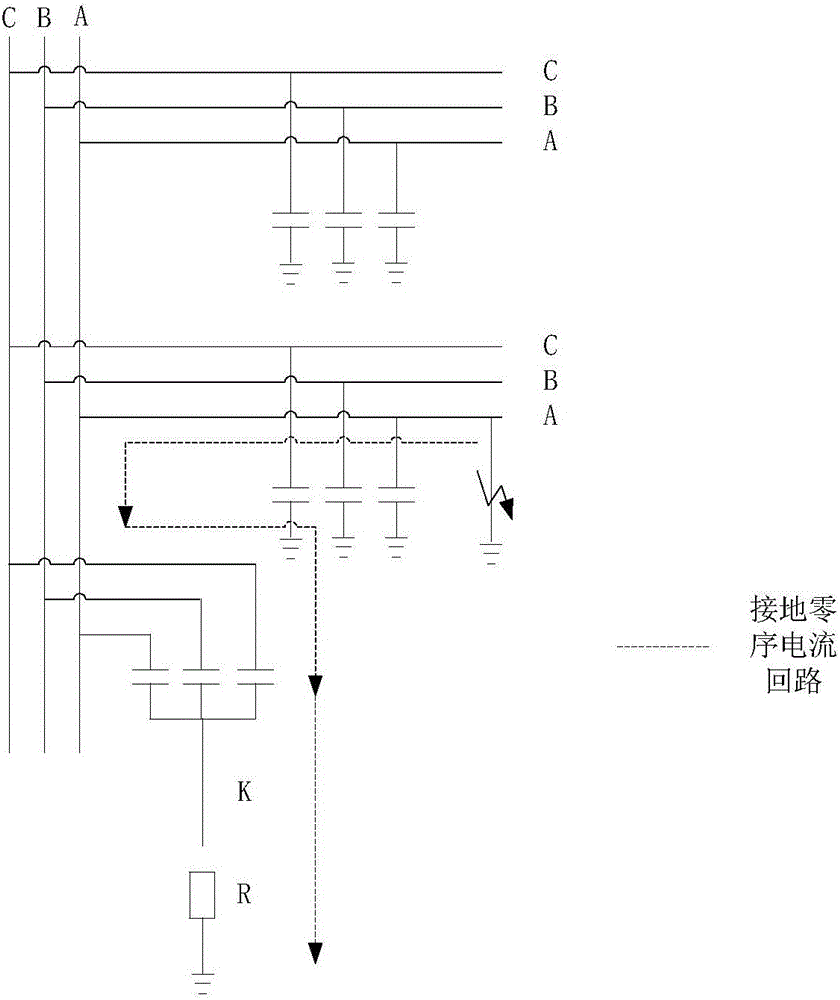
[0029] The method for line selection after a single-phase grounding occurs in an ungrounded system of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0030] A) In a substation system where the neutral point is not grounded, a control switch and a resistor with a resistance value of 100 ohms are installed between the neutral point of the capacitor and the ground. During normal operation, the control switch is in the position;
[0031] B) According to the change of the bus voltage to judge whether there is a single-phase grounding of the line, the criterion is that the zero-sequence voltage is greater than 50V, and at the same time, when the voltage of a certain phase of the three-phase voltage drops less than 30V, and the voltage of the other two phases rises greater than 70V, It is judged that a single-phase ground fault has occurred;
[0032] C) After judging that it is single-phase grounding, close the control switch immediately and put the resistor into it. At this t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com