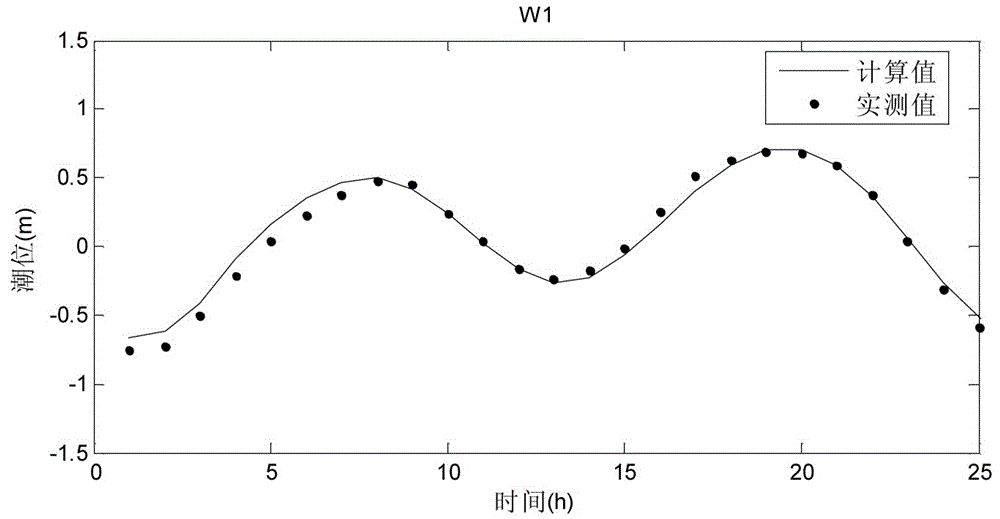
Near-far zone coupling numerical simulation method suitable for thermal drainage and deepwater discharge in nuclear power plant
A numerical simulation and temperature drainage technology, which is applied in CAD numerical modeling, general water supply saving, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems that the near area and far area cannot be simulated at the same time, so as to ensure the conservation of water flow quality and improve the simulation accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
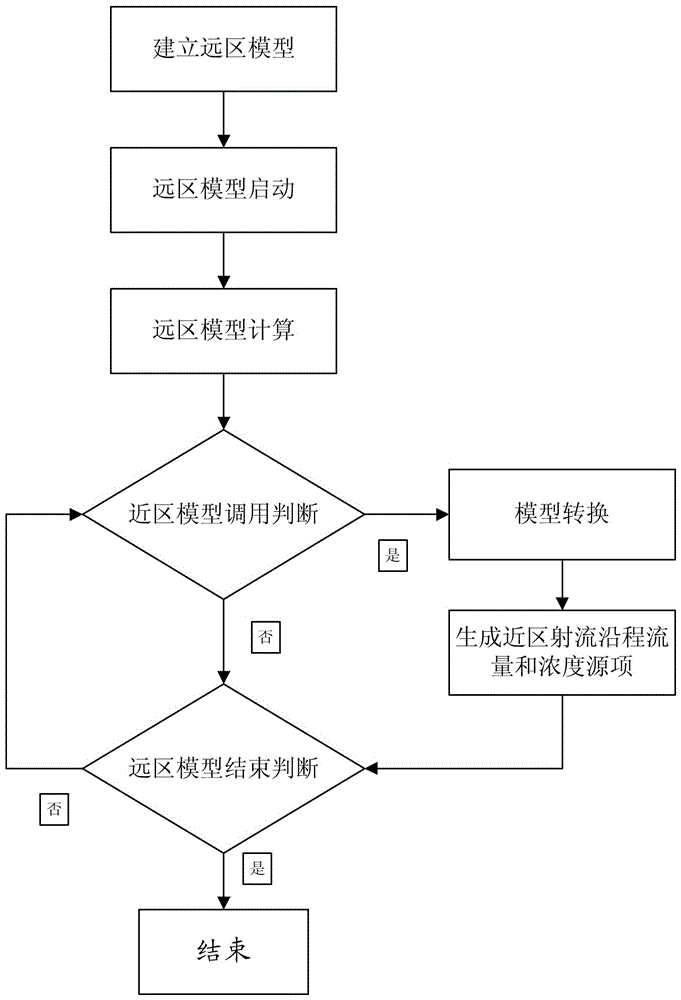
[0039] This embodiment is a near-far area coupling simulation method for power plant thermal drainage and deep water discharge. The process is as follows figure 1 shown. This embodiment is an algorithm process that can be compiled as a computer program, and the hardware used for calculation can be a general computer workstation or other electronic digital computing systems with digital storage and computing capabilities.
[0040] In this embodiment, different models are used to simulate the jet dilution process in the near area of warm water and the environmental flow dilution process in the far area. The jet integral model is used in the near area, and the three-dimensional hydrodynamic mathematical model is used in the far area. The calculation environment parameters in the far area transfer parameters to the near area, and the near area transfers the parameters to the far area through the form of source terms, and realizes the dynamic coupling simulation of the dilution a...
Embodiment 2
[0079] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and it is a refinement of the model in the first embodiment. The near zone model described in this embodiment is a Corjet model, and the far zone model is a Delft3D three-dimensional hydrodynamic model.
[0080] The Corjet model obtains the jet trajectory and the dilution along the jet by solving the integral equation of the jet in infinite water. For the outflow of a single nozzle, it is easier to obtain the distribution of dilution along the near-zone model; for the outflow of multiple nozzles, since each nozzle has its own trajectory at the initial outflow, there is cross influence after a certain distance. Generally, there are two processing methods for area simulation: one is to ignore the jets that do not intersect with each other, and the outflow is equivalent to a line source outflow, which is suitable for the case of small momentum and large density difference; the other is to discharge multiple jets I...
Embodiment 3
[0082] This embodiment is an improvement of the above-mentioned embodiment, and is a refinement of the model of the above-mentioned embodiment. The solution time step of the far zone model described in this embodiment is 15 seconds, and the calling time interval of the near zone model is 5 minutes.
[0083] The time step for solving the far zone model is the discrete step length in time when the model equation is solved, which is a parameter to ensure the stability and accuracy of the numerical solution. If the time step is too large, the calculation may diverge, and if the time step is too small, the calculation cost will increase. The calling time interval of the near-area model is the length of the interval for the near-area model to solve the source item and transmit it to the far-area model. This interval reflects the impact of changes in far-area environmental parameters on the calculation of the near-area model. The capture of time-varying characteristics of parameters ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com