Dickeya zeae-resistant japonica rice breeding method
A basal rot and bacterial technology, which is applied in the breeding field of japonica rice with bacterial basal rot resistance greatly shortened breeding cycle, can solve the problems of low screening efficiency, shortened breeding cycle and long breeding cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] (2.1) Preparation of crude toxin: Select the highly pathogenic toxin-producing strain Ech7 of bacterial root rot as the source of crude toxin, inoculate the strain in protein-free culture medium, and shake and culture at 30°C for 24 hours, then inoculate the bacterial culture at 4 Centrifuge at 10000×g for 15 min at ℃, and the obtained yellow supernatant is the crude toxin of rice bacterial root rot;
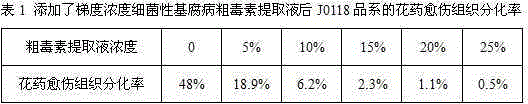
[0040] (2.2) Identify the crude toxin tolerance concentration of the selected japonica rice materials to be improved: respectively in the differentiation medium (the formula is: MS inorganic salt + MS organic matter + 3% sucrose + 0.6% plant gel + KT2.0mg / L + NAA0 .5mg / L+ hydrolyzed protein 1g / L, pH value 6.0), add a certain gradient concentration of crude toxin extract, and then transfer the anther callus induced by the japonica rice material selected in step (1) into the Differentiation medium, the callus differentiation rate was counted after 30 to 40 days of induction...
Embodiment
[0049] From 2010 to 2013, we selected the indica rice material Boyou 713 as the source of resistance to bacterial root rot, and the breeding main line J0118 as the japonica rice material to be improved, and adopted the technical route of the present invention to carry out breeding for bacterial root rot resistance. Three floriculture families with excellent agronomic traits and improved resistance to bacterial root rot were obtained. The specific operation procedures are as follows:
[0050] (1) Screening J0118 and Boyou 713 respectively as japonica rice materials to be improved and indica rice resistance sources to bacterial root rot:
[0051] Many years of breeding practice have found that the main breeding line J0118 has excellent agronomic traits, high yield, good rice quality, and early maturity, but is more susceptible to bacterial root rot. In the main season of 2010, the anthers of J0118 were inoculated on the indica rice medium for induction culture , it was found tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com