Application of rice base rot antibiotic zeamines in plant disease control
A technology for rice base rot pathogens and plant diseases, applied in the direction of chemicals, applications, biocides, etc. for biological control, can solve problems that have not been reported, and achieve the effect of solving resistance problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The preparation of embodiment 1 zeamines
[0021] OD 600 =1.0 D. zeae seed solution was inserted into the toxin-producing medium (LS medium), 25 o C. After culturing at 180rpm for 36 hours, collect the supernatant of the fermentation culture solution of rice base rot pathogen D. zeae by centrifugation. The obtained fermentation broth was stored in a 2L Erlenmeyer flask sealed and protected from light until the next step of extraction.
[0022] The present invention adopts the conventional compound separation and extraction method to separate and extract the antibacterial active substances in the fermentation broth. The pH value of the fermentation broth was adjusted up to 10 with 5M NaOH, and then the supernatant of the fermentation broth with a pH of 10 was concentrated to 1 / 10 of the original volume using a rotary evaporator. Extract twice with three volumes of organic solvent (n-butanol: ethyl acetate = 2:1). After the organic solvent was evaporated to dryness wi...
Embodiment 2
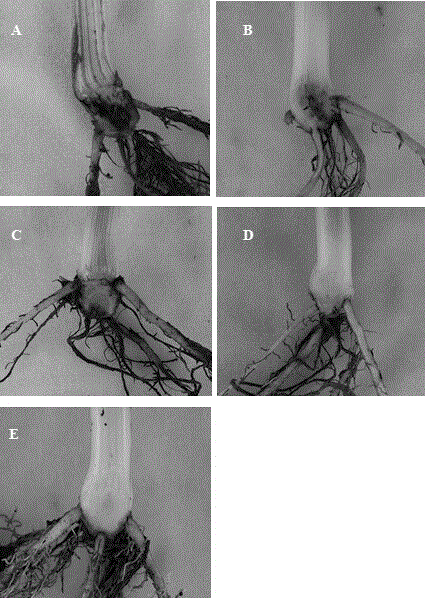
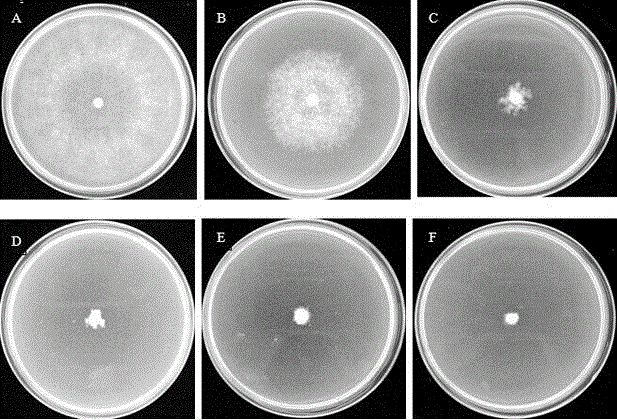
[0023] Example 2 Inhibitory effect of zeamines on Peronophythora Chen.
[0024] Use 10% methanol as a solvent to dissolve the extract, and then configure it with CDA (carrot medium) medium to form a medium with zeamines, and use the mycelial growth rate method to determine the inhibitory effect of different concentrations of extracts on the mycelial growth of Pythora lychee . The specific operation is:
[0025] Mycelia growth rate method: use 10% methanol as a solvent to configure zeamines into a certain concentration of the test agent, and accurately add a certain amount of zeamines solution to 50 oIn the melted CDA medium, the final concentrations of zeamines in the medium were 0.5 μg / mL, 1 μg / mL, 2 μg / mL, 4 μg / mL, and 8 μg / mL, and each concentration was poured into three replicate culture plates. The same volume of 10% methanol was used as a control. After being cultivated for 5 days on a medium plate with a diameter of 9 cm for the tested pathogenic bacteria Pyrosophtho...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3: Inhibitory effect of zeamines on Peronophythora Chen.
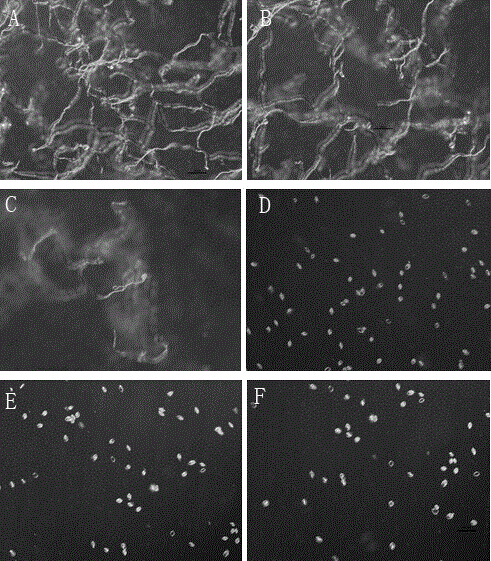
[0027] Using glass slides to measure (Fang Zhongda, 1998), the sporangia of Peronospora lychee cultured on CDA medium for 6 days were washed with sterile water, the sporangia solution was prepared, and the concentration of sporangia was adjusted to each visual field (10 ×10 times) about 40~60 sporangia. Add different amounts of zeamines solutions to the sporangia suspension, so that the final concentrations are 0.5 μg / mL, 1 μg / mL, 2 μg / mL, 4 μg / mL, and 8 μg / mL. Take 50 μL of spore suspension and drop it on the concave glass slide, then place the concave glass slide in a 9cm petri dish with a piece of filter paper, and drop a small amount of sterile water on the filter paper to keep it moist, cover the petri dish, and place it at 28 o After culturing in the dark for 6 hours, the sporangia germination was observed under an optical microscope. Experimental results such as figure 2 As shown, the experime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com