One-tube reaction type DNA molecule clone splicing method
A technology of DNA molecules and reactions, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of low efficiency, failure to realize the standardization and reuse of DNA fragments, and the existence of DNA tail sequence modification, so as to avoid costs and improve the efficiency of ligation reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
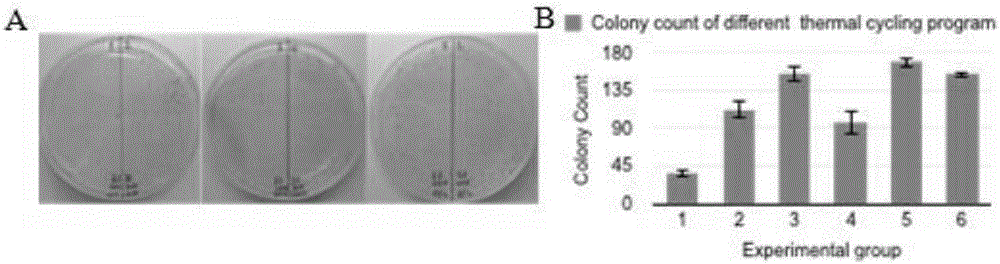
[0052] The optimization of embodiment 1 thermocycling program
[0053] The six different thermal cycle programs described in Table 3 are used for the method of gene splicing described in the present invention (except that the thermal cycle program is different, all the other experimental materials and methods are the same), the results show that: longer reaction time, more The number of reaction cycles, lower annealing temperature and reaction temperature are beneficial to the experiment. There was no significant difference in the results of two-step thermocycling adjustments and three-step cycling conditions (Table 3, figure 1 ). Therefore, in conjunction with the PCR reaction, three-step thermal cycle conditions, longer reaction time, and more reaction cycles are used to improve reaction efficiency.
[0054] table 3
[0055] group Reaction conditions; number of cycles number of transformants 1 55C 15s, 65C 45s; 20 times 36 2 55C 15s, 65C 45s; 30...
Embodiment 2
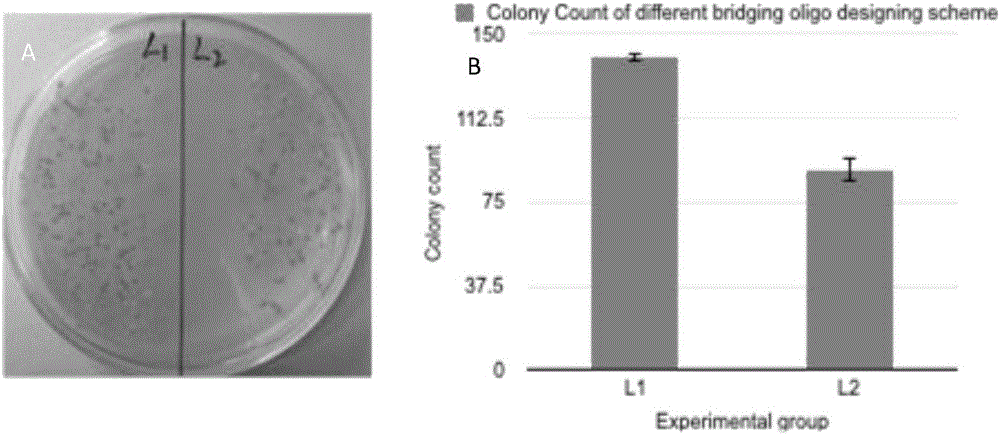
[0061] The optimization of embodiment 2 bridging primers
[0062] 1. Design optimization of bridging primers
[0063]The bridging primer of the present invention is composed of two half bridging primers (bridge primer 1 and bridging primer 2), wherein bridging primer 1 is complementary to the 5' phosphorylated end of a target DNA; bridging primer 2 is complementary to the 3' phosphorylated end of another target DNA The phosphorylated ends are complementary, and the bridging primer 1 and bridging primer 2 form a continuous bridging primer. The present invention sets up two groups for the design of bridging primers, and the first group is to design bridging primer 1 and bridging primer with the same Tm value 2; The second group is to design bridging primer 1 and bridging primer 2 with the same length, and use these two groups to carry out the method for gene splicing of the present invention (except that the bridging primer design is different, the rest of the experimental mater...
Embodiment 3
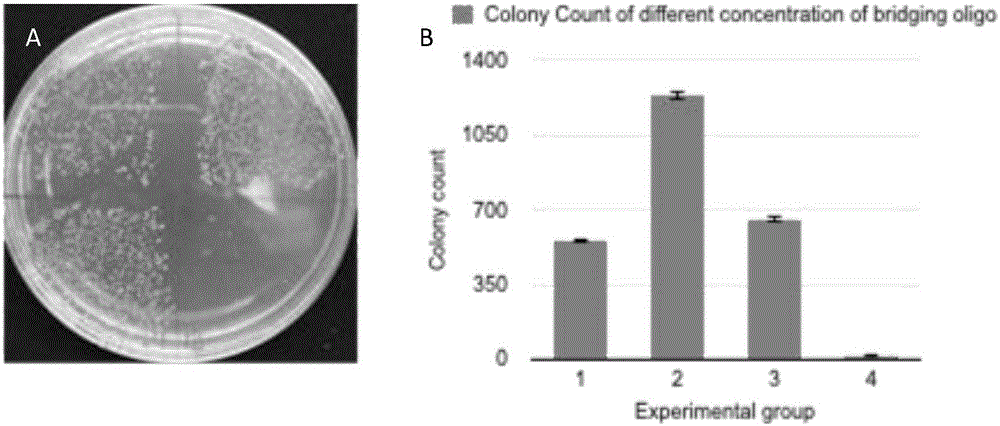
[0068] The optimization of embodiment 3 reaction buffer components
[0069] The thermal cycle conditions used in the experiment are the conditions shown in Table 4, and the reaction system is shown in Table 5.
[0070] Table 5 reaction system
[0071]
[0072] 1. Since one tube reaction contains two enzymes, Taq ligase and T4 polynucleotide kinase, different enzymes will use different buffer components. This experiment takes into account the combination of two different enzyme components The formed buffer components (20X) were added to the final reaction system; other experimental groups were Taq ligase buffer, T4 polynucleotide kinase buffer or pure water.
[0073] After testing, it was found that the effect caused by different buffers is very obvious. Except for the experimental group in which the two buffers were simply mixed, the buffers used in the other experimental groups resulted in the final number of transformants being 0 (such as Figure 5 , during the experim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com