Buried ballastless track structure
A ballastless track, buried technology, used in tracks, roads, buildings, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to completely block the accumulation of wind and sand, and achieve the effect of stable and reliable placement, avoiding the accumulation of wind and sand, and avoiding displacement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
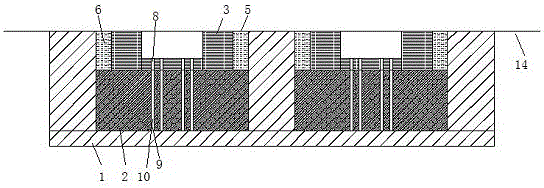
[0029] refer to figure 1 as well as Figure 8 as shown, figure 1 A schematic cross-sectional view of a buried ballastless track structure provided by the present invention, Figure 8 It is a schematic diagram of the track bed structure provided by the present invention. This embodiment provides a buried ballastless track structure, including a ballast bed 1, a track slab 2, and a sleeper 3, the sleeper 3 is erected on the track slab 2, and the ballast bed 1 has a concave pit 4. Both the track plate 2 and the sleeper 3 are arranged inside the pit 4, and the top surface of the sleeper 3 and the top surface of the ballast bed 1 are arranged on the same plane; The track bed 1 is seamlessly connected to form a whole, and the two sides of the sleeper 3 and the middle of the track bed 1 form a buffer zone 5, and shock-absorbing cotton 6 is filled in the buffer zone 5.
[0030] Wherein, there are two dimples 4 in the ballast bed 1, and two track plates 2 and sleepers 3 placed in t...
Embodiment 2
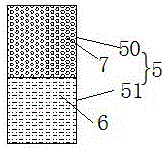
[0034] refer to figure 2 as shown, figure 2 The structure diagram of the first buffer belt provided by the present invention, specifically, this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that in this embodiment, the buffer belt 5 is composed of the first buffer belt 50 and the second buffer belt 50. The buffer zone 51 is formed, the second buffer zone 51 is filled with the shock-absorbing cotton 6 , and the first buffer zone 50 is formed by pouring elastic concrete 7 . The installation direction of the first buffer belt 50 and the second buffer belt 51 is that the first buffer belt 50 is arranged on the upper side of the second buffer belt 51, and the buffer belt 5 is divided into an upper half and a lower half. That is, the upper half of the buffer belt 5 is a first buffer belt 50 poured with elastic concrete 7, and the lower half is a second buffer belt 51 filled with shock-absorbing cotton 6. The elastic concrete The top surface of the ...
Embodiment 3
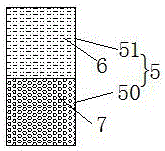
[0036] refer to image 3 as shown, image 3 The structure diagram of the second buffer belt provided by the present invention, specifically, this embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment, the difference is that in this embodiment, the buffer belt 5 is composed of the first buffer belt 50 and the second buffer belt 50. The buffer zone 51 is formed, the second buffer zone 51 is filled with the shock-absorbing cotton 6 , and the first buffer zone 50 is formed by pouring elastic concrete 7 . The setting direction of the first buffer strip 50 and the second buffer strip 51 is that the first buffer strip 50 is arranged on the lower side of the second buffer strip 51, and the buffer strip 5 is divided into an upper half and a lower half. That is, the lower half of the buffer belt 5 is the first buffer belt 50 formed by pouring elastic concrete 7, and the upper half is the second buffer belt 51 filled with shock-absorbing cotton 6. The shock-absorbing The top surface...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com