Method for evaluating toxicity of pesticides on bee larva by the aid of laboratory artificial-breeding bee larva
A bee larvae and laboratory technology is applied in evaluating the toxicity of pesticides to honeybee larvae, and the use of artificially reared honeybee larvae in the laboratory to evaluate the toxicity of pesticides to honeybee larvae can solve the problems of increased test cost, damage to tested larvae, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc. Achieve strong practicability and scalability, accurate evaluation, and a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: the method for artificially raising honeybee larvae in the laboratory of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Preparation of bee larvae
[0044] During the spawning period of the queen bee, select three boxes of bee colonies that have not been treated for four weeks, are healthy, have known source and physiological state. Open the beehive cover and insert one empty spleen, fix the queen bee on the empty spleen with a queen partition to lay eggs, remove the queen partition after 24 hours to release the queen bee, and check the new oviposition situation. According to the fertility of the queen bee, the isolation time can be appropriately shortened to reduce the size and age differences among the larvae. The honeycomb containing bee eggs continues to remain in the beehive until hatching (the bee egg hatching period is generally 3 days).
[0045] (2) Laboratory rearing of bee larvae
[0046] The inserted honeycomb is taken out f...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: the present invention utilizes the method for artificially raising bee larvae in the laboratory to evaluate the toxicity of pesticides to bee larvae, comprising the following steps:
[0065] (1) Preparation of bee larvae
[0066] During the spawning period of the queen bee, select three boxes of bee colonies that have not been treated for four weeks, are healthy, have known source and physiological state. Open the beehive cover and insert one empty spleen, fix the queen bee on the empty spleen with a queen partition to lay eggs, remove the queen partition after 24 hours to release the queen bee, and check the new oviposition situation. According to the fertility of the queen bee, the isolation time can be appropriately shortened to reduce the size and age differences among the larvae. The honeycomb containing bee eggs continues to remain in the beehive until hatching (the bee egg hatching period is generally 3 days).
[0067] (2) Laboratory rearing of be...
Embodiment 3
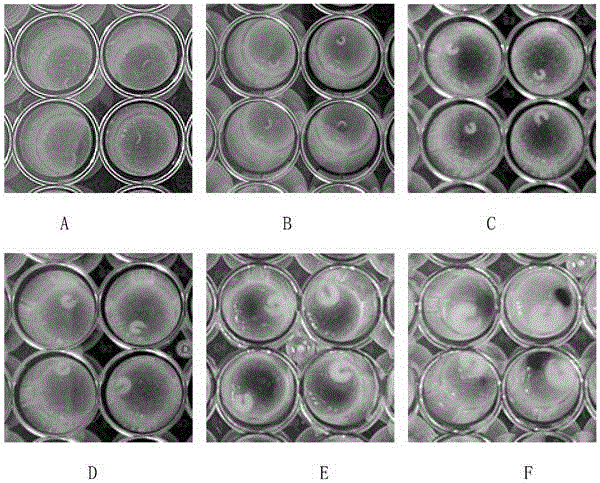
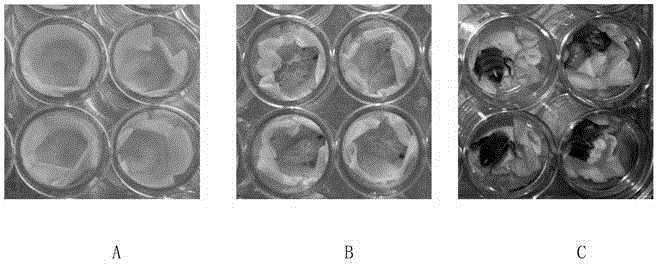
[0077] Using a method similar to Example 2, taking Italian honeybee larvae as the research object, and using imidacloprid, a typical neonicotinoid pesticide, as a representative, the toxicity research of pesticides on honeybee larvae was carried out. After the preparation of honeybee larvae was completed, on the first day of the experiment, 1-day-old late larvae were selected from three bee colonies, placed on a 48-well plate, fed with the same amount of basal diet, and adapted for three days (temperature 34±1°C) , Humidity 95%), health checks were carried out on the 4th day after the start of the test, abnormal, sick and injured larvae were removed, and then distributed to each treatment group. The experiment set up a blank control group (C1, always fed with basal diet), a solvent control group (C2, always fed with basal diet) and 5, 50, 500, 1000, 2000 and 3000mg·L -16 concentration treatment groups (add 1 μL of drug solution to the basal diet on the 4th, 5th and 6th days af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com