Quantitative on-demand-distribution method and device for scattered articles and difference compensation distribution method
An on-demand distribution and discrete technology, applied in the direction of transportation and packaging, conveyor objects, etc., can solve the problems of slow conveyor speed, capacity bottlenecks, errors, etc., and achieve the effect of fast output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
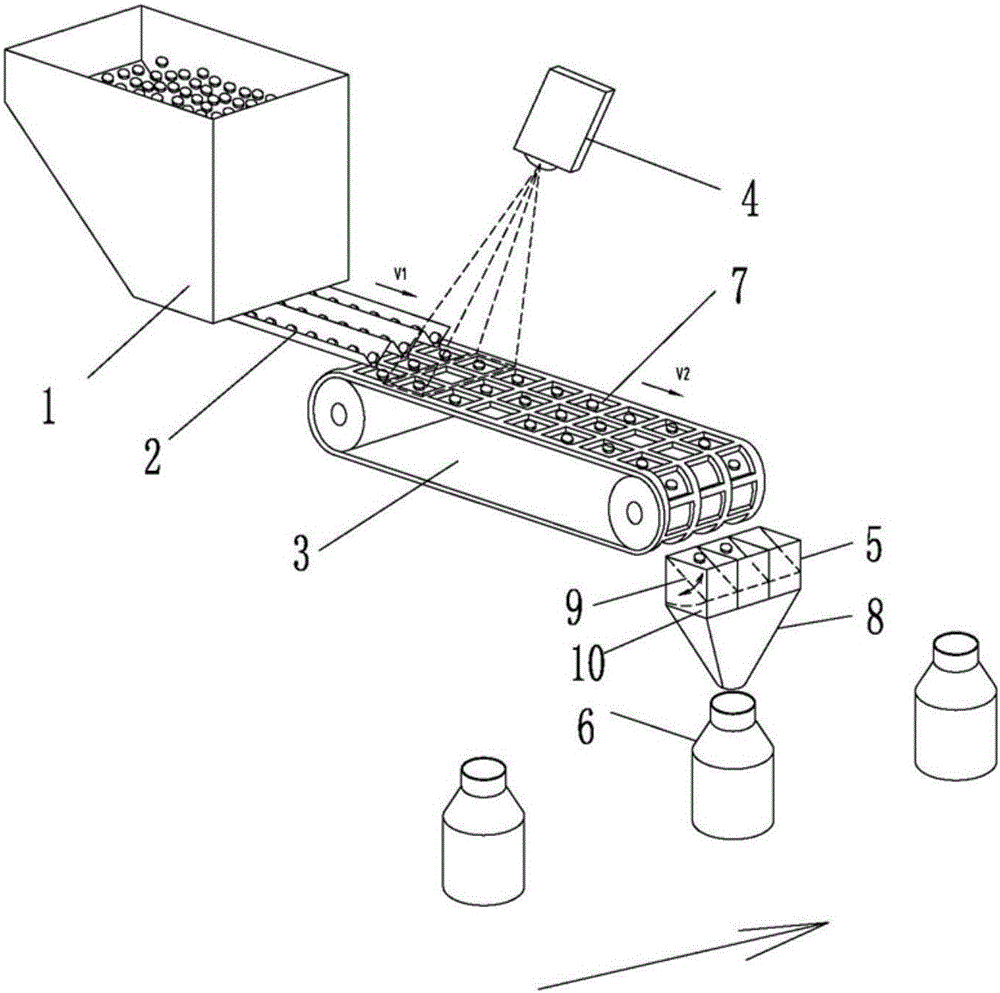
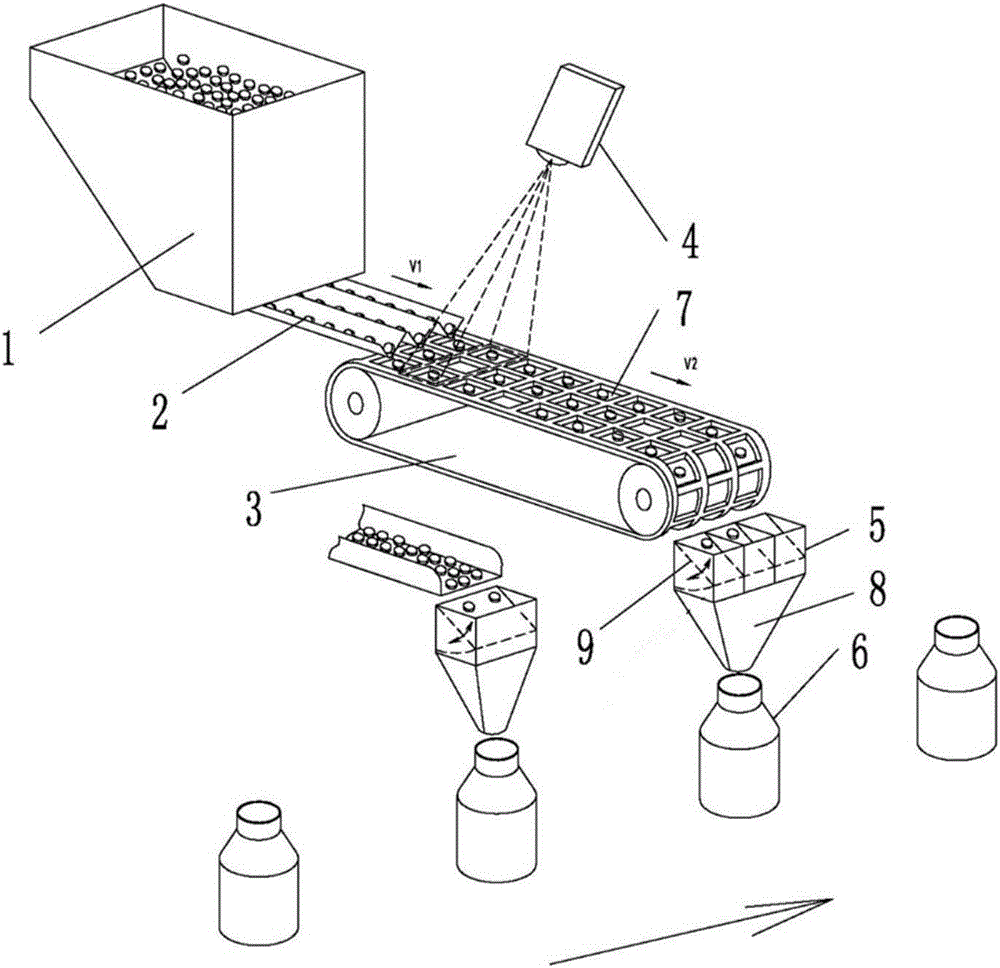
[0041] A quantitative on-demand distribution method for discrete items, such as figure 1 , figure 2 shown,
[0042] In step 1, the feeder 1 continuously supplies articles to the first conveyor 2, and the first conveyor 2 divides the articles into at least one single-layer distributed article row, and outputs them to the second conveyor 3,
[0043] Step 2: The second conveyor 3 is provided with a column of counting compartments 7 corresponding to each article row, and the articles in each article row are outputted by the first conveyor 2 and fall into the counting score of the column corresponding to the surface of the second conveyor 3 . Grid 7, the number of items in each counting grid 7 is 1 or 0;
[0044] Step 3, accurately counting the items in the counting compartment 7 on the surface of the second conveyor 3;
[0045] Step 4: Allocate the items in the counting compartment 7 to the storage 6 according to the required quantity.
[0046] In the present invention, the a...
Embodiment 2
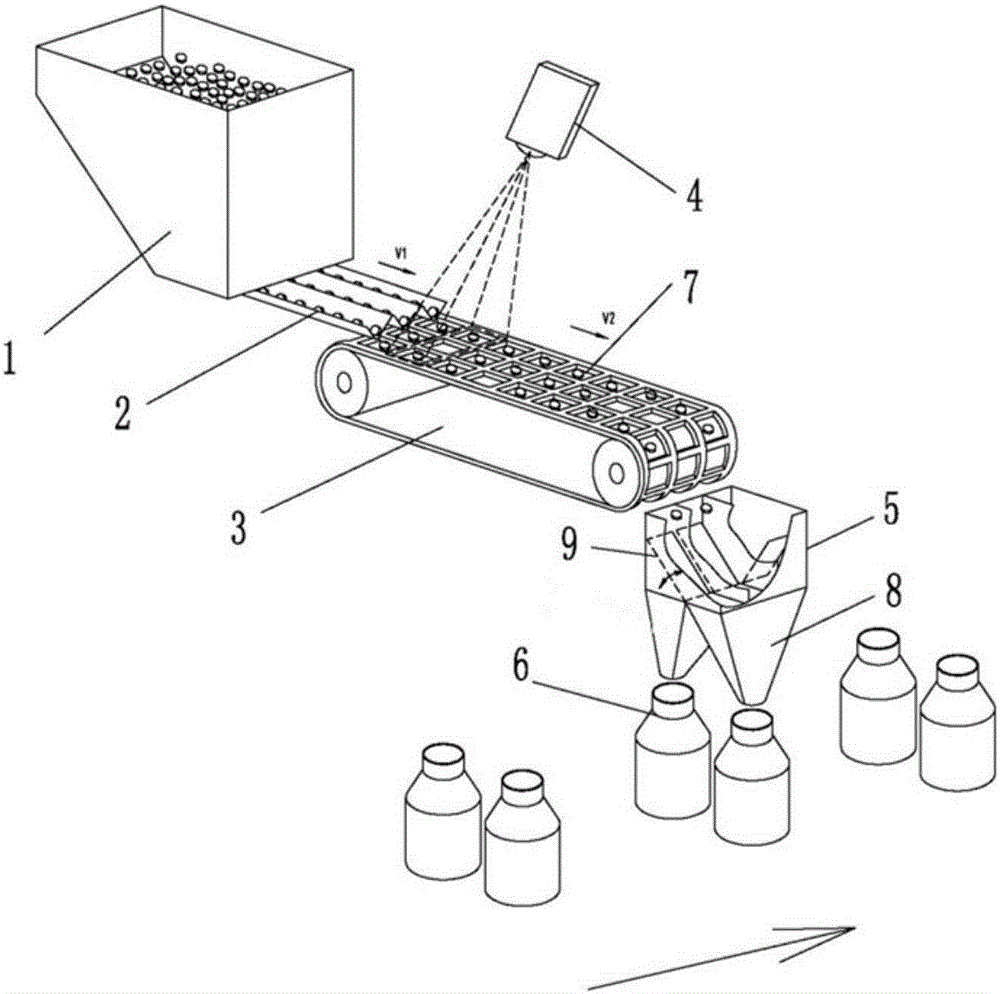
[0055] like image 3 , Figure 4 shown,
[0056] Another object of the invention of the present invention is to propose a kind of difference-complement allocation method applying this on-demand allocation method, which is realized in the following manner:
[0057] The method of the present invention according to the arbitrarily changed demand can be used for feeding, and the feeding method is as follows:
[0058] First, the storage 6 obtains the first distribution quantity that is lower than the target quantity, and then calculates the number of items whose first distribution quantity is different from the target quantity, generates a required quantity corresponding to the storage 6, and finally outputs the required quantity of items to the corresponding storage 6 .
[0059] In the current precise counting method, the first distribution is random, that is, the amount of the required feeding is also random, that is, when the storage 6 receives the first distribution, it will...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3, as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 shown,
[0061] A quantitative on-demand dispensing device for discrete items, comprising:
[0062] Feeder 1, supplies items to the first conveyor 2;
[0063] a first conveyor 2, the first conveyor 2 divides the articles into at least one single-layer distributed article row and conveys them to the second conveyor 3;
[0064] The second conveyor 3, the surface of the second conveyor 3 is provided with counting compartments 7 distributed in a matrix form, and each column of counting compartments 7 is arranged corresponding to an item row;
[0065] The counting mechanism 4 accurately counts the items in the counting compartment 7 on the surface of the second conveyor 3;
[0066] The central processing unit distributes the items in the counting compartment 7 to the storage 6 according to the required quantity of the storage 6
[0067] Storage 6, collect the items in the counting compartment 7.
[0068] Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com