Allelic gene GL/gl pair for controlling haired/hairless property of cucumis melo
A kind of gene, melon technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of positioning, cloning and the molecular mechanism of the formation of research gaps, stay and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
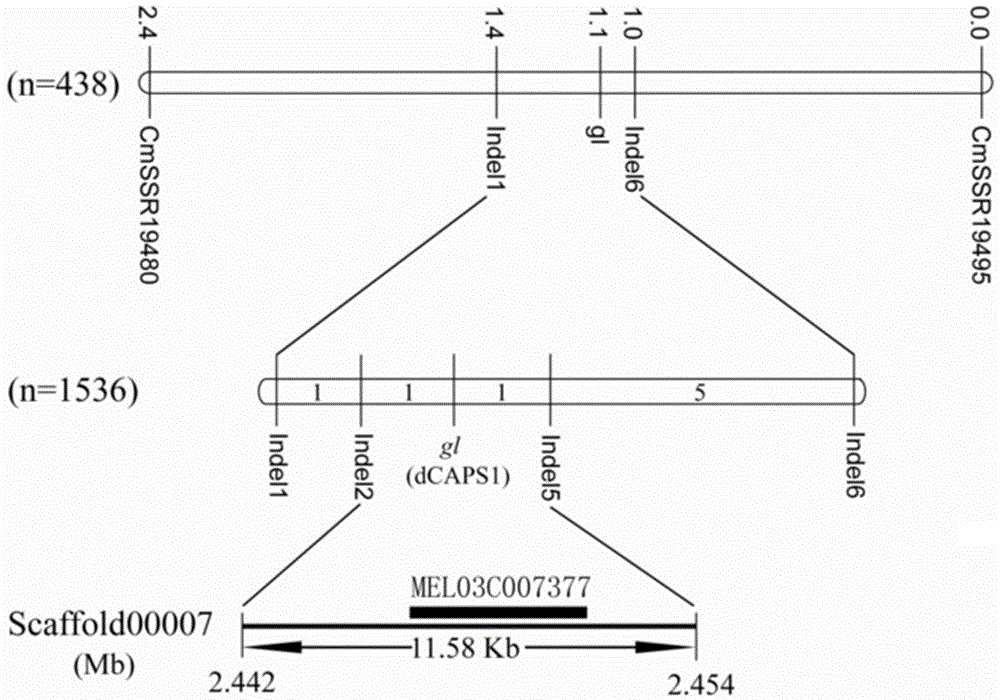
[0037] The analysis process of the hairy / hairless gene in melon in this application includes the construction of genetic segregation population, preliminary positioning, fine positioning and map-based cloning, and the positioning results are as follows: figure 1 As shown, the relevant experimental process is briefly introduced as follows:
[0038] 1. Construction of genetic segregation populations
[0039] The melon hairless material NSL73046 was used as the female parent, and the normal melon material M68 was used as the male parent (it should be explained that during the experiment, considering the availability of materials and the convenience of operation, the inventor used M68 as the male parent, and used other homozygous When there are hairy materials, related experiments can also be carried out), using these two parents to configure a hybrid combination, the results show that the obtained F 1 Progeny plants are normally hairy.
[0040] from F 1 Select 10 individual p...
Embodiment 2
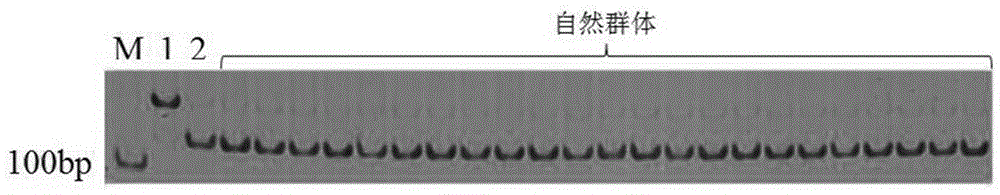
[0077] On the basis of the sequencing results of Example 1, based on GL and gl The exon TCA-TAA mutation site can be designed to identify Gl and gl The dCAPS molecular marker of the gene is named as dCAPS1. When the dCAPS1 molecular marker is used for PCR amplification, the primer sequence is:
[0078] dCAPS1-F: 5' GGTTGCGGGAGATGGGAATT 3'
[0079] dCAPS1-R: 5'TGAAACTCGTGAAGCTTCGGTTC 3';
[0080] Using this primer pair, the PCR amplification product in the hairless parent material is 124bp, and the base sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; the PCR amplification sequence in the hairy parent is 124bp long, and the base sequence is as in SEQ ID As shown in NO.4;
[0081] Comparing the sequences of SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4, the sequences of SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 have a base mutation at 21bp, so SEQ ID NO.4 has a mutation at 16-21bp The restriction site of EcoR1, that is, the sequence contains the restriction endonuclease EcoR1 restriction site 5'-GAATTC-3', so after...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com