Polyolefin-based hot melt adhesives with improved processing and bonding performance
A technology of hot-melt adhesives and polyolefin elastomers, applied in the direction of polymer adhesive additives, non-polymer adhesive additives, adhesives, etc., can solve the problem of high fluidity, wettability, strong initial adhesion, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0089] raw material:
[0090] Nyflex 222B is a hydrotreated naphthenic process oil available from Nynas Corporation.
[0091] Escorez 5400 is a hydrogenated cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon resin with a softening point of 103°C. It is available from ExxonMobil Chemical Company.
[0092] Escorez 5615 is a hydrogenated aromatic modified cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon resin with a softening point of 115°C. It is available from ExxonMobil Chemical Company.
[0093] Vestoplast 508 is a butene-rich poly(1-butene-co-propylene) copolymer available from Evonik Industries. It has a Brookfield viscosity of 8,000 cP at 190°C and a Ring and Ring softening point of 84°C.
[0094] Pro-fax RP591V is a random propylene copolymer available from Basel Polymers. RP591V has a melt flow rate of 100 g / 10 min (230°C / 2.16 kg) and a density of 0.90 g / cc.
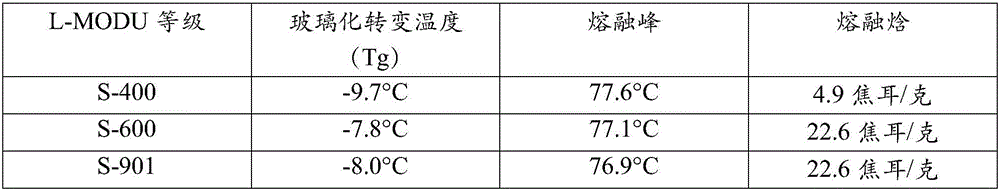
[0095] L-MODU S600 is a low modulus, controlled tacticity polypropylene available from Idemitsu. It is reported to have a Brookfield viscosity of 52,00...
example 1
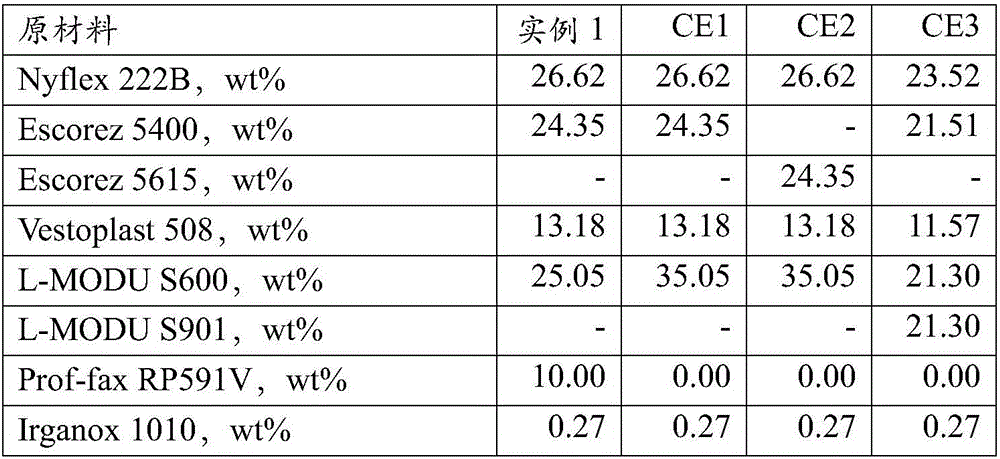
[0102] Example 1 (Ex 1) and comparative examples 1-3 (CE1, CE2 and CE3)
[0103] The formulations in Table 1 were produced as described above and screened for preset cold flow resistance. The first comparative example (CE1 in Table 1) produced using only the combination of L-MODU and APAO resulted in a material that showed a significant preset cold flow even after cooling. Such materials are expected to cause blocking in applications using porous substrates.
[0104] Example 1 (Ex 1) shows that replacing a portion of the L-MODU of CE 1 with a propylene copolymer results in an adhesive exhibiting zero preset cold flow by the quantitative test method. Nevertheless, qualitative ball tests show that under rapid cooling, limited flow is still seen nonetheless. This type of low but non-zero flow is proposed to provide the wet-out required for a strong bond without extensive penetration of the substrate which could lead to sticking and / or leakage.
example 2-6
[0112] Table 2. Examples 2-6 and Comparative Examples 4-10
[0113]
[0114]Examples 2-6 highlight the ability of the inventive adhesives to form strong initial and aged bonds without exhibiting blocking. Comparative Examples 4-6 help define the scope of the formulation space of the present invention as use of very low levels (less than 1 wt %) or complete omission of isotactic polypropylene Pro-fax 591V results in increased blocking in laminate applications. Comparative Examples 7-10, which used only high melting point waxes as the crystalline component, showed extremely high blocking in coating studies. These comparative examples further support the unique ability of the inventive formulations to resist blocking when applied to porous substrates such as nonwovens.
[0115] Table 3. Examples 2-6 and Comparative Examples 4-10
[0116]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| phase transition enthalpy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com