Patents
Literature
105 results about "APAO" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
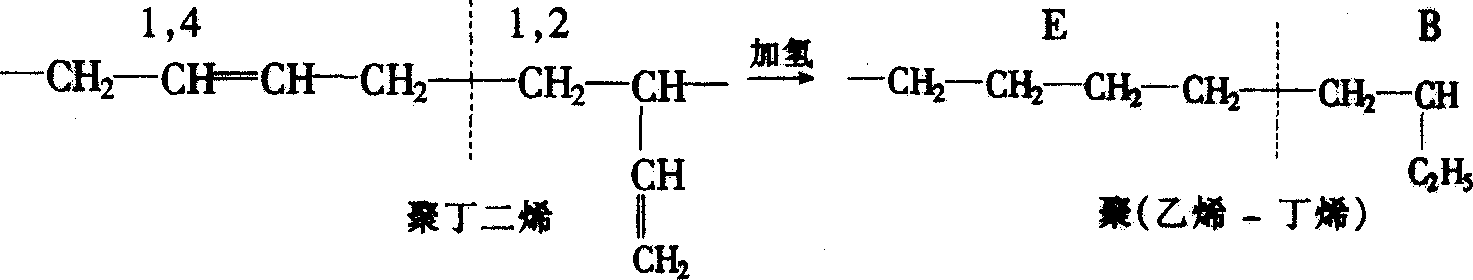
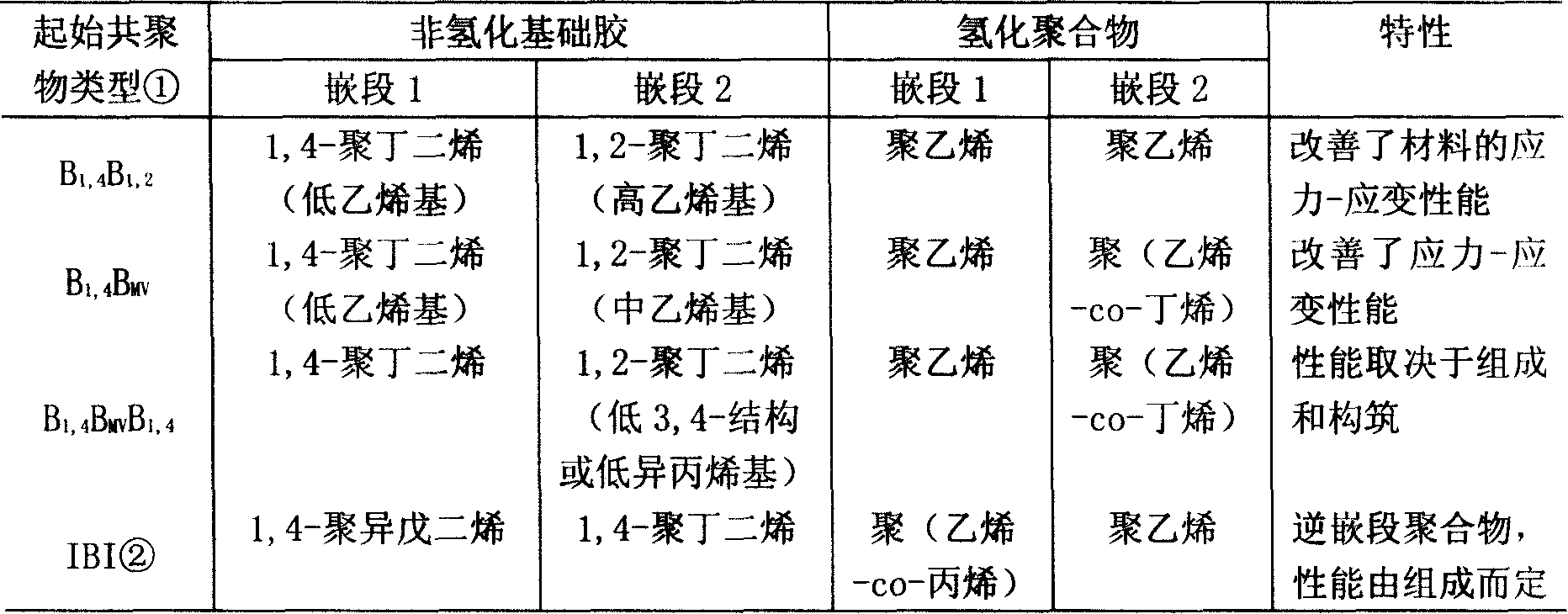
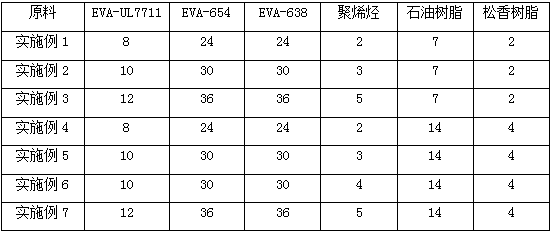
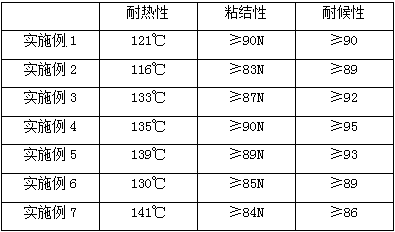
Amorphous Poly-alpha-olefins (APAO) are produced by (co-) polymerisation of α-olefins, e.g. propylene or 1-butene with Ziegler-Natta catalysts. The (co-)polymers have an amorphous structure which makes them useful for the production of hot melt adhesives.
Hot melt adhesive composition based on a random copolymer of isotactic polypropylene and a secondary polymer
InactiveUS7262251B2Broad processibilityImprove thermal stabilityOther chemical processesFilm/foil adhesivesWaxPlasticizer
Owner:ATO FINDLEY
Hot melt sealant and foam-in-place gasketing material
ActiveUS20070042193A1Good balance of propertyImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesPolymer scienceSealant
A hot melt sealant and foam-in-place gasket composition based on a rubber such as ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and / or ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) and at least one semicrystalline olefinic polymer. The hot melt composition includes the rubber or a blend of rubbers in an amount of 5% to 50% by weight, at least one semicrystalline olefinic polymer in an amount of 5% to 40% by weight, at least one amorphous poly-α-olefin (APAO) polymer in an amount of 0% to 70% by weight, a compatible tackifier in an amount of 0% to 50% by weight, and a plasticizer in an amount of at least 30% by weight. The composition is particularly useful for foamed gasket applications as a replacement for pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA) coated foam tape.
Owner:BOSTIK INC
Hot melt adhesive composition based on a random copolymer of isotactic polypropylene
InactiveUS7067585B2High bond strength retentionGood adhesionOther chemical processesFilm/foil adhesivesWaxPlasticizer
A hot melt adhesive composition is based on an isotactic polypropylene random copolymer (RCP). The composition contains about 4%–50% by weight of the RCP copolymer, about 20%–65% by weight of a compatible tackifier, about 0%–40% by weight of a plasticizer, about 0%–3% by weight of a stabilizer, about 0%–40% by weight of a wax, and optionally about 0%–60% by weight of an atactic poly-α-olefin (APAO). The adhesive composition may be used in a number of applications such as, for example, in disposable nonwoven hygienic articles, paper converting, flexible packaging, wood working, carton and case sealing, labeling and other assembly applications.
Owner:BOSTIK INC
High-polymer modified pitch, its water-proof roll material and use thereof
ActiveCN101070434AImprove standardsHigh standard waterproof functionOther chemical processesRoof covering using flexible materialsPolymer modifiedCrack resistance
The invention provides a polymer modified asphalt, and the weight of the components comprising as follows :45-55% matrix asphalt, 4 - 8% blend oil, 12 - 14% of SBS ,5-9 % APAO, 2-7% of High-temperature improvement and 15-20% filler. It also offers polymer modified asphalt, which made of waterproof membrane and the railway bridge, highway bridge deck waterproofing project applications. The invention of these waterproofing membrane have a high standard of waterproof function, it can withstand high intensity of railway bridge and particularly high stress dynamic load .It also have excellent performance on water-resistance, high and low temperature resistance, adhesion, crack resistance, fatigue resistance and other aspects .it can be used for railway bridge and the road deck waterproofing works.
Owner:JINZHOU DONGFANG YUHONG BUILDING MATERIALS +1
Bitumen modifier for traffic tracking resistance and modified bitumen and mixer thereof
ActiveCN101063000AGood storage stabilityReduce energy consumptionIn situ pavingsBuilding insulationsPolyolefinThermoplastic elastomer
The invention discloses a pitch modifier for traffic anti-rut, modified asphalt and bituminous mixture, which is characterized by the following: allocating 20-200 wt thermoplastic elastomer ethenyl aromatic hydrocarbon-conjugated diene block copolymer and 5-950 wt polyolefin; setting the thermoplastic elastomer ethenyl aromatic hydrocarbon-conjugated diene block copolymer as SBS, SIS, SEBS and or SEPS; setting the polyolefin as PE, PP, EVA, APP, APAO, POE, HDPE, LDPE and or LLDPE; setting the mass percent of adding basic pitch at 1%-7%; increasing high-temperature behavior and anti-rut ability distinctively; modifying anti-water damage and anti-low temperature property. This craft is simple, which avoids the problem of bad stability of modified asphalt storage.
Owner:深圳前海海川新材料科技有限公司
High-polymer modified asphalt waterproof roll for road and bridge and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106739310AGuaranteed thicknessHigh temperature shear resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationBituminous waterproofingEngineering
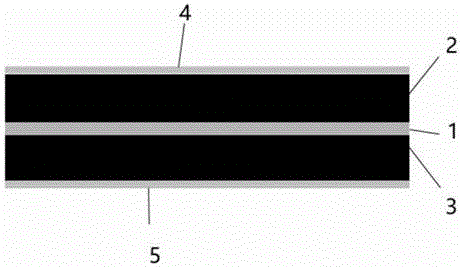
The invention relates to a high-polymer modified asphalt waterproof roll for roads and bridges. The high-polymer modified asphalt waterproof roll is manufactured in the way that a bank base layer (1) is used; modified asphalt coating and covering layers (2) and (3) are respectively bonded on the upper and lower surfaces of the bank base layer (1); an isolation layer (4) covers the upper surface of the modified asphalt coating and covering layer (2); an isolation layer (5) covers the lower surface of the modified asphalt coating and covering layer (3); each modified asphalt coating and covering layer is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 38 to 44 percent of 90# asphalt, 11 to 17 percent of 200# asphalt, 5 to 8 percent of polypropylene, 1 to 3 percent of SBS, 4 to 6 percent of APAO, 2 to 3 percent of high-temperature modifiers, 15 to 17 percent of modification powder and 10 to 15 percent of filling materials. The product of the high-polymer modified asphalt waterproof roll has the advantages that the high-temperature resistant and low-temperature cracking resistant capability is high; the anti-aging capability is high; the joint deformation capability is high; the high-standard waterproof function is provided; meanwhile, the construction performance of the waterproof roll for roads and bridges is improved; the high-polymer modified asphalt waterproof roll is mainly used for pavement of cast asphalt concrete mixtures.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIENTAL YUHONG WATERPROOF TECH
Traffic anti-track asphalt modifier and its modified asphalt and asphalt mixture
ActiveCN101165102AGood storage stabilityReduce energy consumptionIn situ pavingsBuilding insulationsPolyolefinThermoplastic elastomer
The present invention discloses one kind of rut resisting road asphalt modifier, and its modified asphalt and asphalt mixture material. The rut resisting road asphalt modifier consists of thermoplastic elastomer of vinyl arene-conjugated diene block copolymer 20-200 weight portions, polyolefin 5-950 weight portions and lignocellulose 30-60 weight portions. The thermoplastic elastomer of vinyl arene-conjugated diene block copolymer is SBS, SIS, SEBS and / or SEPARATES; and the polyolefin is PE, PP, EVA, APP, APAO, POE, HDPE, LDPE and / or LLDPE. The present invention also discloses the preparation process of the asphalt modifier. The asphalt modifier can raise the high temperature performance and rut resisting performance of asphalt mixture material obviously, and can also raise its water damage resistance, low temperature cracking performance, etc.
Owner:SHENZHEN OCEANPOWER NEW MATERIALS TECH
Environment protection type colourful flashing hot-melt adhesive
InactiveCN101289605AProportionally largeLow costPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesRosin adhesivesPolymer scienceSolvent
The invention relates to environment-friendly colorized flash hot-melt adhesive, which comprises main body resin, tackifying resin, a diluent agent, flash powder, pigment and solvent, wherein the main body resin is selected from one sort or a plurality of sorts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer EVA, ethylene-butyl acrylate copolymer EMA, ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer EAA, ethylene-ethyl acrylic acid copolymer EEA, styrene-isoprene copolymer SIS, styrene-butadiene copolymer SBS and amorphous alpha-olefin polymer APAO; and the tackifying resin is selected from one sort or a plurality of sorts of rosin, polymerized rosin, 145 resin, 138 resin, terpene resin, petroleum resin or hydrogenant petroleum resin. The environment-friendly colorized flash hot-melt adhesive adopts the nontoxic flash powder which has excellent suspension property and is cheap, environment-friendly, unprecipitated and easy to be dispersed evenly as filler; moreover, the usage amount of the tackifying resin is increased, thereby substantially reducing product cost and improving product bonding strength and performance.
Owner:金尔升
Hot melt adhesive composition based on a random copolymer of isotactic polypropylene
A hot melt adhesive composition is based on an isotactic polypropylene random copolymer (RCP). The composition contains about 4%-50% by weight of the RCP copolymer, about 20%-65% by weight of a compatible tackifier, about 0%-40% by weight of a plasticizer, about 0%-3% by weight of a stabilizer, about 0%-40% by weight of a wax, and optionally about 0%-60% by weight of an atactic poly-alpha-olefin (APAO). The adhesive composition may be used in a number of applications such as, for example, in disposable nonwoven hygienic articles, paper converting, flexible packaging, wood working, carton and case sealing, labeling and other assembly applications.
Owner:ATO FINDLEY
Method of reducing frictional losses in oil and gas well drilling
InactiveUS20160024369A1Reduce frictionReduce dragFlushingDrilling compositionHydrocarbon solventsWell drilling
Fluids for use within a wellbore are provided, comprising amorphous polyalphaolefins (APAO), copolymers of alphaolefins and styrene (APAO-S), terpolymers of alphaolefins and styrene and butadiene (APAO-SB) and / or amorphous polyisobutylene (APIB) and copolymers of polyisobutylene and styrene (APIB-S) and terpolymers of polyisobutylene and styrene and butadiene (APIB-SB) in an oil-based hydrocarbon solvent. Novel properties of such fluids are described, and the fluids may be used, for example, during drilling or fracturing operations.
Owner:MIRZAEI AMIR A +1
Water-based disposable medical packaging hot melt glue and production process
InactiveCN107722876AAvoid limitationsAvoid complexityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesWax adhesivesWater basedPolymer science
The invention discloses water-based disposable medical packaging hot melt glue and a production process. The water-based hot melt glue is prepared by adopting water-based acrylate emulsion, vinyl-acryl emulsion, vinyl-acetate emulsion, amorphous polypropylene (APAO) emulsion, polyethylene wax emulsion and paraffin emulsion, adding an anion emulsifier and a non-ionic emulsifier as stabilizers, andadding methyl silicone oil, vinyl silicone oil and the like by virtue of a compounding process. The hot melt glue is suitable for paper-film, paper-coated paper, and paper-paper packaging products, and can avoid the limitation and complexity of the existing hot melt glue preparation field.
Owner:东莞市中凌包装材料有限公司
Attapulgite hot-melt adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105219298ALow costHigh viscosityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAlpha-olefinButadiene-styrene rubber
The invention provides an attapulgite hot-melt adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The attapulgite hot-melt adhesive is characterized by comprising 20 to 50% of matrix resin, 20 to 50% of tackifying resin, 10 to 30% of a diluent, 2 to 40% of attapulgite and 0.1 to 1% of an anti-oxidant, wherein the matrix resin is any one or a composite of more selected from the group consisting of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), ethylene-butyl acrylate copolymer (EBA), ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer (EAA), ethylene-ethyl-acrylic acid copolymer (EEA), styrene-isoprene copolymer (SIS), styrene-butadiene copolymer (SBS) and amorphous alpha-olefin polymer (APAO), the tackifying resin is selected from the group consisting of rosin, polymerized rosin, resin 145, resin 138, terpene resin, petroleum resin and hydrogenated petroleum resin, the diluent may be paraffin, ceresine, polyethylene wax or Fischer-Tropsch wax, the attapulgite may be raw attapulgite or modified attapulgite like viscous attapulgite, brightened attapulgite and acidified attapulgite, the anti-oxidant is 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol, i.e., 264, or pentaerythritol tetrakis[beta-(3',5'-di-t-butyl-4'-hydroxyphenyl)propionate], i.e., 1010, and the matrix resin has VA% of 5 to 40 and a melt index of 15 to 400.
Owner:蒋寿悟
APAO hot melt adhesive and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103351835AIncrease working temperatureHave affinityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesPetroleum resinPolyamide
The invention discloses an APAO hot melt adhesive and a preparing method thereof, which includes the following materials in weight percentage: 10-25% of naphthenic oil, 1-5% of white mineral oil, 20-50% of APAO resin, 1-50% of APP resin, 35-60% of C5 hydrogenization petroleum resin, 0.5-1% of antioxygen 1010, and 0.5% of antiager A. According to the invention, the bonding strength is higher, the working temperature of hot melt adhesive finished product is greatly increased, so that the requirements for bonding technology of textures such as shoe linings, sponge, toe puffs, non-woven fabrics and leather are completely met; besides, the APAO hot melt adhesive has special affinity and bonding force for materials of PE and PP with low surface energy and difficulty in adhesion; a simple and practical blending preparation technology is adopted, and the chemical preparation methods such as crosslinking and copolycondensation of most former polyamide hot melt adhesive are avoided, so that the technological process is greatly simplified, the energy consumption is reduced, and better economic benefit and industrial production prospect are achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHENG JUEQI FUJIAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
Water sealing hot melt adhesive for cable and application thereof
InactiveCN104715830ATo achieve the effect of preventing water penetrationImprove reliabilityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesUnderwaterRosin
The invention relates to water sealing hot melt adhesive for a cable and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of cables. The water sealing hot melt adhesive for the cable is composed of, by mass, 30% to 60% of APAO, 15% to 45% of petroleum resin, 5% to 20% of rosin resin, 5% to 10% of PB and 5% to 10% of quartz powder. The hot melt adhesive is applied to production of the water tightness cable. Due to the fact that the application purpose is achieved through the developed longitudinal water tightness cable, it can be guaranteed that the cable still can work normally at the depth of 1000 m underwater, and seawater can not seep into equipment or cabins along the cable even when the cable is broken.
Owner:SHANGHAI JUNXIN SHIP TECH
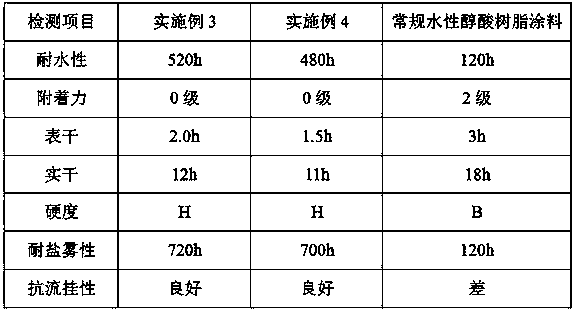
APAO-modified water-based alkyd resin and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to APAO-modified water-based alkyd resin and a preparation method thereof. The APAO-modified water-based alkyd resin is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 20.0-35.0 parts of vegetable oil fatty acid, 5.0-10.0 parts of maleic anhydride grafted APAO, 20.0-42.0 parts of a polyacid, 25.0-60.0 parts of a polyol, 10.0-20.0 parts of xylene, 2.5-5.0 parts of n-heptanoic acid, 3.5-7.0 parts of dimethylolpropionic acid, 4.0-12.0 parts of a neutralizing agent, and 100.0-150.0 parts of deionized water. The APAO modified water-based alkyd resin prepared by the method has the characteristics of good adhesion, water resistance, good fullness, and good sagging resistance, can be used for interior and exterior wall coatings, water-based industrial coatings, water-based floor coatings, water-based wood coatings and the like, and has huge application potential.
Owner:UNION FOSHAN CHEM +1
Anti-sagging APAO-modified alkyd resin water-based functional coating
ActiveCN110776815AGood anti-sag performanceImprove adhesionPolyester coatingsPolymer scienceVegetable oil
The invention relates to an anti-sagging APAO-modified alkyd resin water-based functional coating. The coating comprises, by weight, 50.0-70.0 parts of APAO-modified water-based alkyd resin, 15.0-30.0parts of silicon-modified waterborne alkyd resin, 3.0-6.0 parts of an anti-freezing agent, 0.3-0.8 part of a thickener, 0.0-25.0 parts of a pigment filler, 0.0-0.8 part of a dispersing agent, 3.0-8.0parts of a coalescing agent, 0.1-0.4 part of an antifoaming agent, 0.2-0.5 part of a leveling agent, 0.1-0.5 part of a wetting agent and 8.0-20.0 parts of deionized water, wherein the APAO-modified waterborne alkyd resin is prepared from vegetable oil fatty acid, maleic anhydride-grafted APAO, polybasic acid, polyhydric alcohol, n-heptanoic acid, dimethylolpropionic acid and a neutralizer througha reaction. The anti-sagging APAO-modified alkyd resin water-based functional coating prepared by the invention has the characteristics of good sagging resistance, good adhesion, high hardness, goodmechanical properties, high crosslinking density, good water resistance and the like.
Owner:UNION FOSHAN CHEM +1
Polypropylene foam particle and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a polypropylene foam particle and a preparation method thereof. The polypropylene foam particle comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of polypropylene, 5-10 parts of an amorphous state alpha-olefin copolymer (APAO) or petroleum resin, 0.1-3 parts of a nucleating agent, 1-20 parts of a fire retardant and 0.1-0.4 part of an antioxidant. The components are extruded by a mixing extruder, and are cooled by water, braced and cut into particles, so as to obtain small modified polypropylene particles; inorganic powder, the small modified polypropylene particles and a physical foaming agent are discharged at low pressure after being heated in a high-pressure kettle, and are foamed, so as to obtain the polypropylene foam particles. Inorganic powder adopted by the method disclosed by the invention can be recycled, so that the production cost is saved, the prepared polypropylene foam particle is non-sticky, good in performance, small in capacity, free of wastewater generated in the whole production process, free of environmental pollution, and applicable to industrial production, and the foam density is smaller than 0.2g / cm<3> in the foaming process.
Owner:武汉德冠新材料科技有限公司
APAO hot melt adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108587536AIncrease working temperatureHigh bonding strengthMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesWaxPolyolefin
The invention discloses an amorphous poly alpha olefin (APAO) hot melt adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The APAO hot melt adhesive comprises the following components in percentage by weight:25-60% of amorphous polyolefins, 30-60% of tackifying resin, 5-20% of wax, 0.1-1% of an antioxidant and 0.1-1% of an anti-aging agent. The APAO hot melt adhesive provided by the invention has good thermal stability and good solvent resistance, special adhesive using equipment is not needed, and the cost is low.
Owner:WUXI HAITE NEW MATERIAL RES INST
Ultralow-warpage high-strength long glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an ultralow-warpage high-strength long glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material and a preparation method thereof. The long glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material comprises the components by the weight percentage: 20 wt%-65 wt% of polypropylene, 20 wt%-60 wt% of long glass fibers, 5 wt% to 20 wt% of a cyclic polyolefin, 2 wt%-7 wt% of an amorphous polyolefin APAO, 0.2 wt% to 1 wt% of an antioxidant, 0.1 wt% to 0.5 wt% of a lubricant, 1 wt%-3 wt% of a compatilizer, and 0.5 wt%-1.5 wt% of a black master batch. Cyclic polyolefin and amorphouspolyolefin APAO are matched for use, the dosage of each component is controlled, and the long glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material is modified by using the compatilizer with high grafting rate, so that the warping problem caused by anisotropy of glass fiber orientation and polypropylene shrinkage can be remarkably reduced, and the strength of the material can be effectively improved. The composite material is easy to form and process, and can be used for manufacturing large-size thin-wall workpieces which are easy to warp, such as instrument board frameworks, rear tail doorsand the like.
Owner:绍兴纳岩材料科技有限公司
Polyolefin hot-melt glue having a low reactivation temperature and high heat stability and use thereof for vacuum deep-drawing lamination
ActiveUS20180251660A1Low reactivation temperatureImprove thermal stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsAdhesive processes with adhesive heatingPolyolefinPolymer science
A hot-melt glue composition, including a) at least one atactic poly-α-olefin (APAO) that is solid at 25° C.; b) at least one hydrocarbon resin having a softening point of at least 80° C., measured in accordance with the ring-and-ball method according to DIN EN 1238; and c) at least one maleic-anhydride-grafted wax having a softening point of not more than 150° C., measured in accordance with the ring-and-ball method according to DIN EN 1238, which is a maleic-anhydride-grafted polypropylene wax or a maleic-anhydride-grafted polyethylene wax, wherein the proportion of the at least one maleic-anhydride-grafted wax in the hot-melt glue composition is at least 3 wt %. The hot-melt glue composition is characterized by a low reactivation temperature, together with high heat resistance and good adhesion to ABS and nonpolar polyolefin materials. The hot-melt glue composition is well suited for film lamination by vacuum deep-drawing lamination, in particular for applications in automobile construction.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
APAO modified styrene-acrylic emulsion and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to APAO modified styrene-acrylic emulsion and a preparation method thereof. The modified styrene-acrylic emulsion comprises, by weight, 4.0-8.0 parts of APAO, 10.0-25.0 parts ofan acrylate hard monomer, 6.0-20.0 parts of an acrylate soft monomer, 2.0-5.0 parts of glycidyl acrylate, 20.0-35.0 parts of styrene, 1.5-4.0 parts of a crosslinking monomer, 2.5-5.0 parts of acrylicacid, 0.1-0.3 parts of ammonium persulfate, 0.5-1.0 parts of sodium bicarbonate, 2.5-6.0 parts of a neutralizing agent, 1.5-4.4 parts of an emulsifier, 5.0 to 10.0 parts of a cosolvent, and 100.0 to 160.0 parts of deionized water; the APAO modified styrene-acrylic emulsion provided by the invention has the advantages of good adhesive force and good anti-sagging performance, and an anti-sagging auxiliary agent does not need to be added. The APAO modified styrene-acrylic emulsion prepared by the invention has the properties of good adhesive force, acid and alkali resistance, water resistance, salt fog resistance, good sagging resistance, simplicity in construction and the like.
Owner:UNION FOSHAN CHEM +1
Hot melt adhesive as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107523235AImprove high temperature resistanceNo smellNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesWaxAntioxidant
The invention relates to a hot melt adhesive as well as a preparation method thereof, and also relates to application of the hot melt adhesive in automobiles. The hot melt adhesive is prepared from the following components by mass percent: 60-66% of amorphous poly alpha olefin (APAO), 3-6% of wax, 24-35% of tackifying resin and 0.5-1.5% of an antioxidant. The hot melt adhesive provided by the invention has an excellent high-temperature-resistant characteristic and does not emit odor at the room temperature, thus being especially suitable for being used as an automobile hot melt adhesive.
Owner:VALENCE BONDING TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Amphiphilic ionomer enhanced healthy environment-friendly hot melt adhesive as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN111876098AIncrease melt viscosityImprove wettabilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsIonomerPolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of hot melt adhesives, and discloses an amphiphilic ionomer enhanced healthy and environment-friendly hot melt adhesive as well as preparation and application thereof. The amphiphilic ionomer reinforced healthy environment-friendly hot melt adhesive is prepared from the following raw material components in parts by weight: 35 to 45 parts of APAO resin,5 to 15 parts of SBS resin, 20 to 40 parts of tackifying resin, 10 to 20 parts of paraffin oil, 5 to 10 parts of amphiphilic polybutylene succinate ionomer and 0 to 10 parts of functional nanoparticles. The amphiphilic poly(butylene succinate) ionomer is added into the hot melt adhesive, so that the infiltration performance of the APAO resin on different polar surfaces can be remarkably improved,and the bonding performance on non-polar surfaces and the peel strength after curing are improved. In addition, by adding the functional nanoparticles, the hot melt adhesive can be endowed with a corresponding health function and reinforcing performance, and the quality and performance of the hot melt adhesive are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAIQIANG CHEM +1
High/low-temperature-resistant APAO hot melt adhesive for filter production and preparation method of high/low-temperature-resistant APAO hot melt adhesive
ActiveCN111995966AHigh strengthGood flexibilityMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAdhesive cementPolymer science
The invention relates to the technical field of adhesives, in particular to a high-and-low-temperature-resistant APAO hot melt adhesive for filter production and a preparation method thereof. The high-and-low-temperature-resistant APAO hot melt adhesive comprises the following preparation raw materials in parts by weight: 40 to 70 parts of a thermoplastic high polymer material, 30 to 60 parts of atackifier, 2 to 15 parts of a viscosity regulator, 0.01 to 0.05 part of an antioxidant and 0.5 to 2 parts of a plasticizer. The hot melt adhesive provided by the invention has excellent high-temperature resistance and low-temperature resistance, good adhesive layer flexibility, long opening time and high strength, is suitable for various special operation processes, and solves the problems of nohigh-temperature resistance and no low-temperature resistance of a common EVA hot melt adhesive in the prior art.
Owner:上海路嘉胶粘剂有限公司
Comprehensive integrated testing protocol for infant lung function
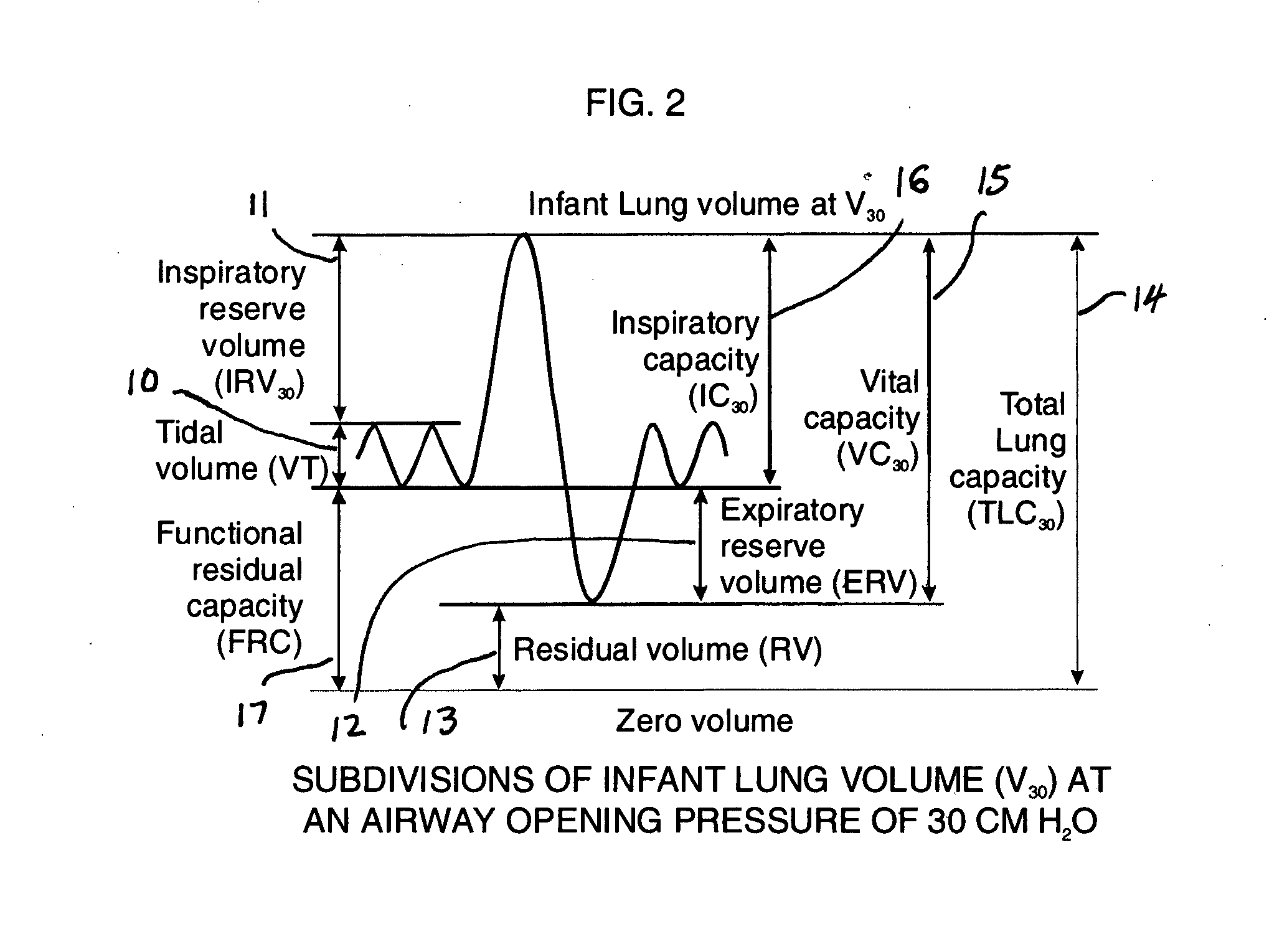
InactiveUS20090131811A1Highly repeatable robust measurementRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsNitrogen gasSlow vital capacity
A Comprehensive Integrated Testing Protocol (CITP) incorporates precise measurements of the dynamic and the static lung volumes and capacities at V30 for routine infant lung function testing. The static functional residual capacity (sFRC) in infants is measured after a short hyperventilation induces a post-hyperventilation apnea (PHA) that abolishes the infant's breathing strategies and creates a reliable volume landmark. A measurement of the sFRC is then obtained by inert gas washout; e.g., by measuring the volume of nitrogen expired after end-passive expiratory switching of the inspired gas from room air to 100% oxygen during the PHA. A true measurement of the total lung capacity (TLC) is obtained from the sum of (1) the passively exhaled gas volume from a Pao plateau of 30 cm H2O through a pneumotachometer (PNT) by integrating the flow signal to produce volume, which is the inspiratory capacity (IC), and (2) the sFRC. From intrasubject TLC and residual volume (RV), the difference is a reliable estimate of the slow vital capacity (SVC). Similar measurements may be obtained with a fastened squeeze jacket for comparison. Actual airway opening pressure (aPao) is measured during a 0.20 s airway occlusion after halting the inflating airflow and prior to activating the jacket inflation. An open mouth is maintained during forced expiration in order to generate an oronasal instead of a forced expiration.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
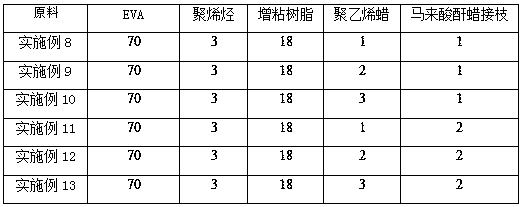
Furniture edge sealing glue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109096951AHigh viscosityGood weather resistanceMacromolecular adhesive additivesCartonEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of hot melt adhesives, and particularly relates to a furniture edge sealing glue and a preparation method thereof. The furniture edge sealing glue is prepared from, by mass ratio, 25 parts of EVA, 7 parts of APAO, 12 parts of POE, 34 parts of tackifying resin, 27 parts of fully hydrogenated C9 and 5 parts of fully hydrogenated rosin. The preparation method for the furniture edge sealing glue includes mixing the above-mentioned raw materials at 150 DEG C to obtain a colloidal mixture, and performing underwater pelleting production through a twin-screw extruder. The furniture edge sealing glue is good in aging resistance and yellowing resistance, has a fast curing speed, good toughness and good bonding performance at low temperature, and is suitable for causing a PE film wrapping a sucker to be bonded to a carton.
Owner:浙江固特新材料科技股份有限公司
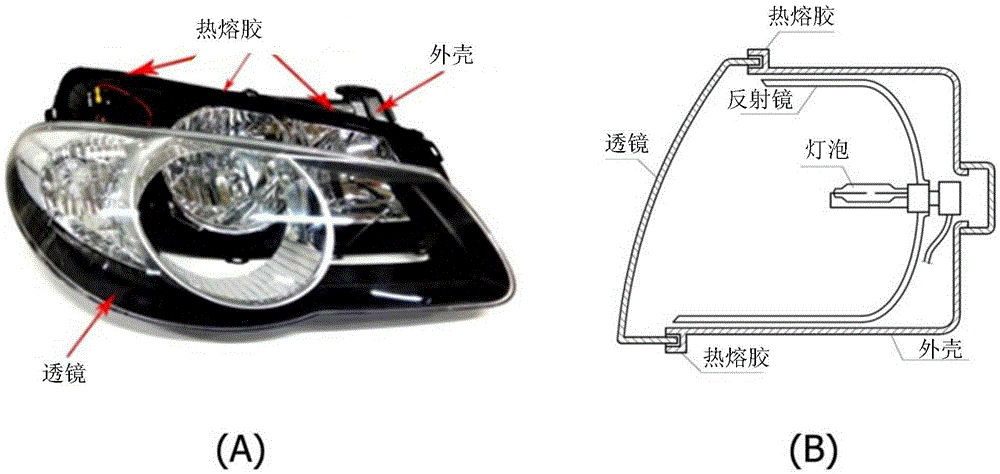
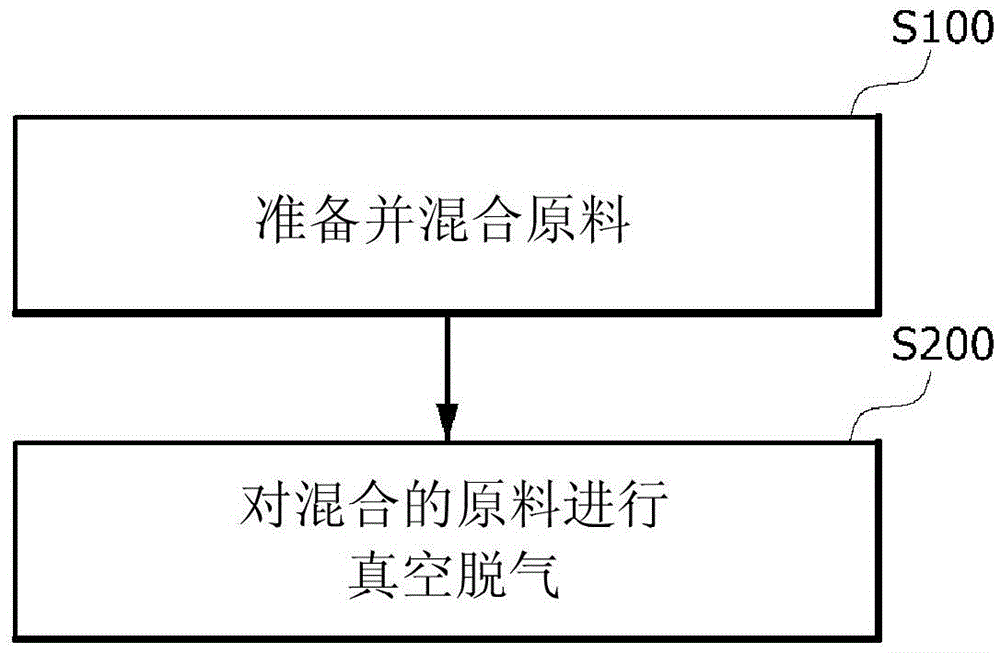
Method for preparing hot-melt adhesive composition and hot-melt adhesive composition prepared thereby
ActiveCN106256867AMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesHigh resistanceAlpha-olefin
Disclosed is a method for preparing a hot-melt adhesive composition and a hot-melt adhesive composition prepared thereby. The method comprises: preparing and mixing raw materials, including a butyl rubber, an ethylene propylene diene (EPDM) rubber, a styrene block copolymer, an amorphous poly-alpha-olefin (APAO) and a tackifier resin; and performing vacuum degassing of the mixed raw materials, wherein the styrene block copolymer comprises a styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) rubber. The hot-melt adhesive composition has high resistance in temperature cycles between low and high temperatures so as to maintain its physical properties, and thus has an excellent property of sealing a headlamp for a long period of time until the end of the lifespan of the headlamp. Also, the composition generates no gas in the sealed state of the headlamp, and thus does not create bubbles or voids and does not pose a water tightness problem.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD +1
Modified asphalt waterproof coiled material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111173149AReduce slippagePrevent agingSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsPolymer scienceBituminous waterproofing
The invention relates to a modified asphalt waterproof coiled material and a preparation method thereof. The modified asphalt waterproof coiled material comprises an isolating layer, a lower surface modified asphalt layer, a padding layer, an upper surface modified asphalt layer and a particle layer. The lower surface modified asphalt layer is made from the following raw materials: asphalt 90#, butadiene styrene rubber, polymethyl silicone, APAO, vermiculite powder, cordierite micro powder, tetracosanoic acid, alkyl polyglucosides, DMHAC10, a softener and a stabilizer; and the upper surface modified asphalt layer is made from the following raw materials: asphalt 90#, butadiene styrene rubber, AEO, Carbomer, APAO, spodumene powder, vermiculite powder, cordierite micro powder, a softener, aplasticizer and a stabilizer. Different modified asphalt layers are arranged on the two sides of the padding layer of the waterproof coiled material to reduce the phenomenon that the waterproof coiledmaterial slips during the following using process after construction of a vertical wall and also avoid the phenomenon that the waterproof coiled material is aged due to long-time irradiation after construction of the vertical wall.
Owner:潍坊市宇虹防水材料(集团)有限公司
Hot melt adhesive and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN104745122AImprove adhesionFast dryingMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesRosin adhesivesForeign matterPolymer science
The invention belongs to a hot melt adhesive and a preparation process thereof. The hot melt adhesive is composed of naphthenic oil, white oil, EVA (Ethyleno Vinyl Acetale), APAO (Amorphous Poly Alpha Olefin), wax, rosin modified resin, petroleum resin, an antioxidant and an anti-aging agent. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing materials at a formula ratio; checking to confirm that no foreign matter exists in a reaction kettle, and starting a switch to heat conductive oil; and putting the naphthenic oil, the white oil, the wax, the antioxidant, the anti-aging agent and the like, heating for 25-35 minutes, putting APAO, EVA and the like after the temperature is increased to 65-75 DEG C, introducing nitrogen in the reaction kettle, heating and stirring for 1-3 hours, putting the rosin modified resin and the petroleum resin after the materials are completely melted, and vacuumizing and stirring until a colloid is uniform and free from bubbles so as to obtain the adhesive. The hot melt adhesive is mainly applied to adhering the materials, such as paper, artworks and coated films; and the hot melt adhesive prepared by the invention is high in adhesive force, high in drying speed, low in energy consumption, good in thermal stability, aging resistant and acid and alkali resistant, and is applied to automatic flow line producing and packaging requirements.
Owner:仙游县新势力新材料有限公司
Foaming hot melt adhesive and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN110951417AImprove antioxidant capacityFlame retardantMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The invention discloses a foaming hot melt adhesive and a preparation process thereof. The foaming hot melt adhesive comprises 40-60% of APAO random poly-alpha olefin, 1-12% of polyethylene wax, 0.1-1% of an antioxidant, 30-45% of a C5 petroleum resin, 2-5% of a foaming agent and 3-6% of a flame retardant. According to the invention, by selecting the APAO random poly-alpha olefin, the polyethylenewax, the antioxidant, the C5 petroleum resin, the foaming agent and the flame retardant as raw materials, the prepared foaming hot melt adhesive is convenient to store, long in service life and goodin foaming effect and has a certain flame retardant effect; and in the manufacturing process, the polyethylene wax and the C5 petroleum resin are deeply embrittled through liquid nitrogen so as to effectively improve the crushing effect of the polyethylene wax and the C5 petroleum resin, so that the melting effect among the raw materials can be improved during heating, and the bonding strength ofthe foaming hot melt adhesive is greatly improved.
Owner:广东台煜新材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com