Fast mainlobe shape-preserving adaptive beamforming method with arbitrary shape pattern
An adaptive beam, arbitrary shape technology, applied in the directions of radio wave measurement systems, instruments, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in controlling gain fluctuation in the main lobe, difficulty in selecting the loading amount, and difficulty in selecting the direction that needs to be constrained. Achieve the effect of high linear constraint efficiency, low computational complexity, and good shape retention performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
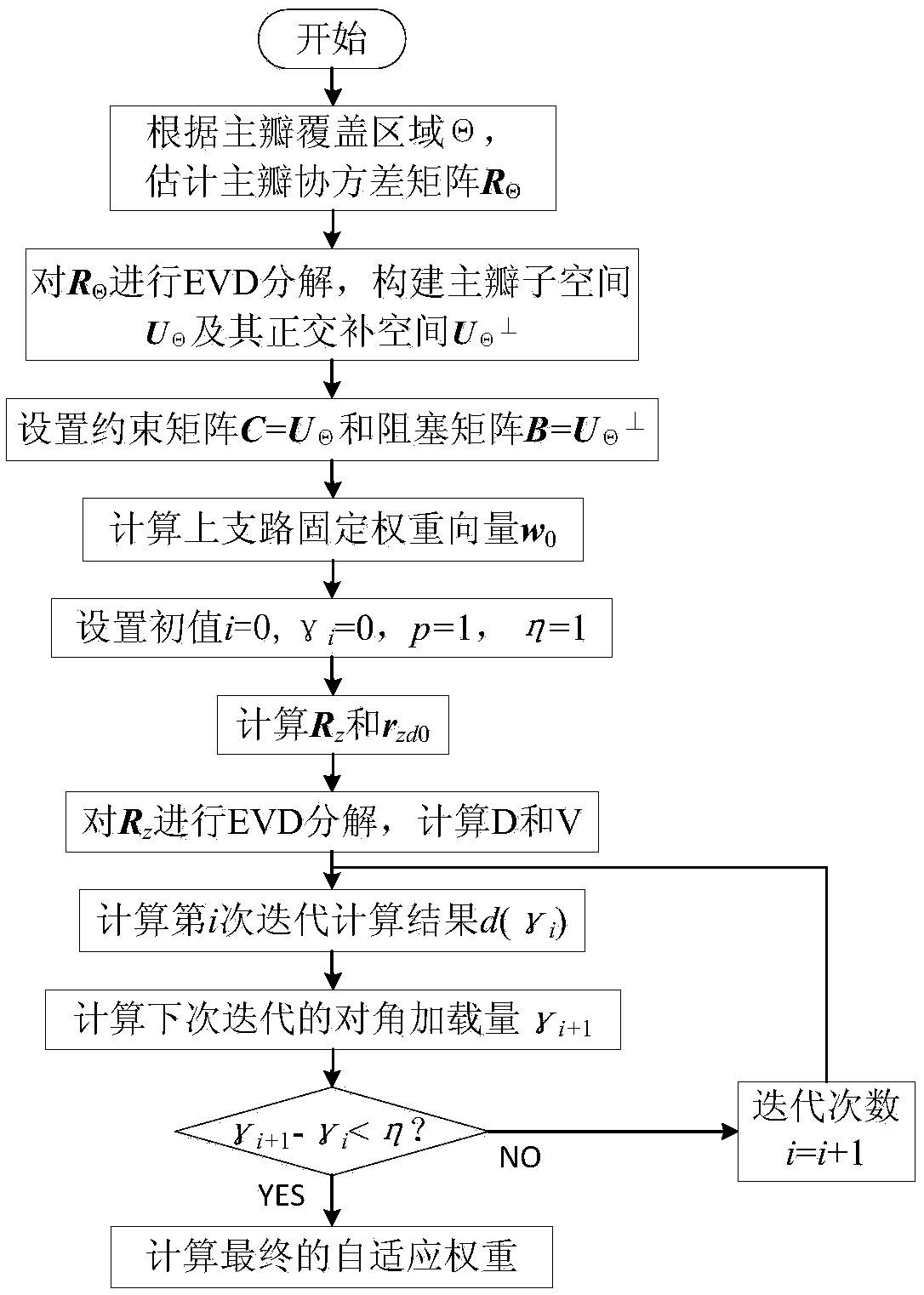
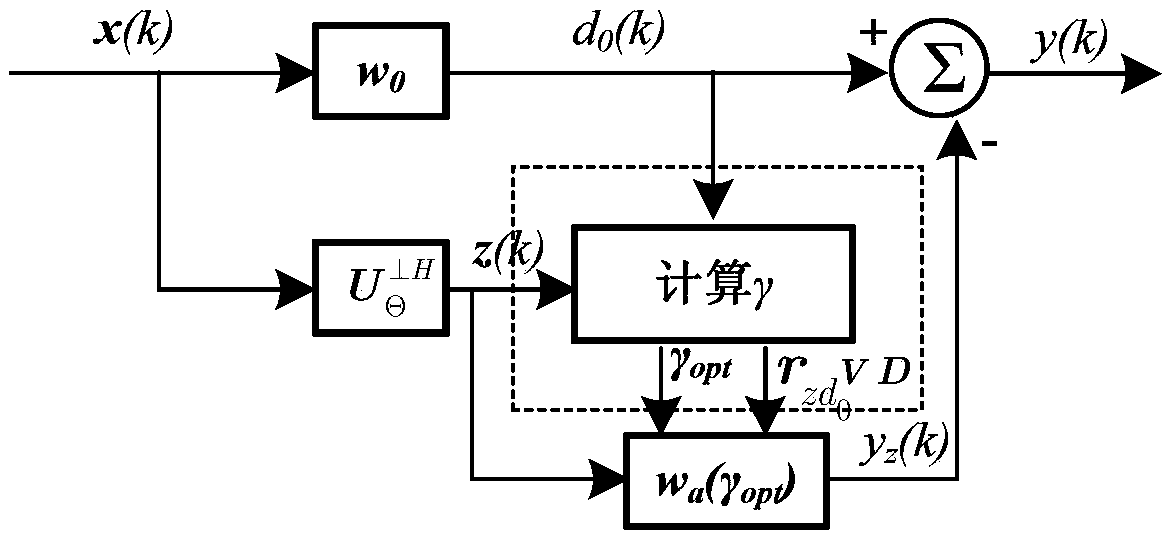
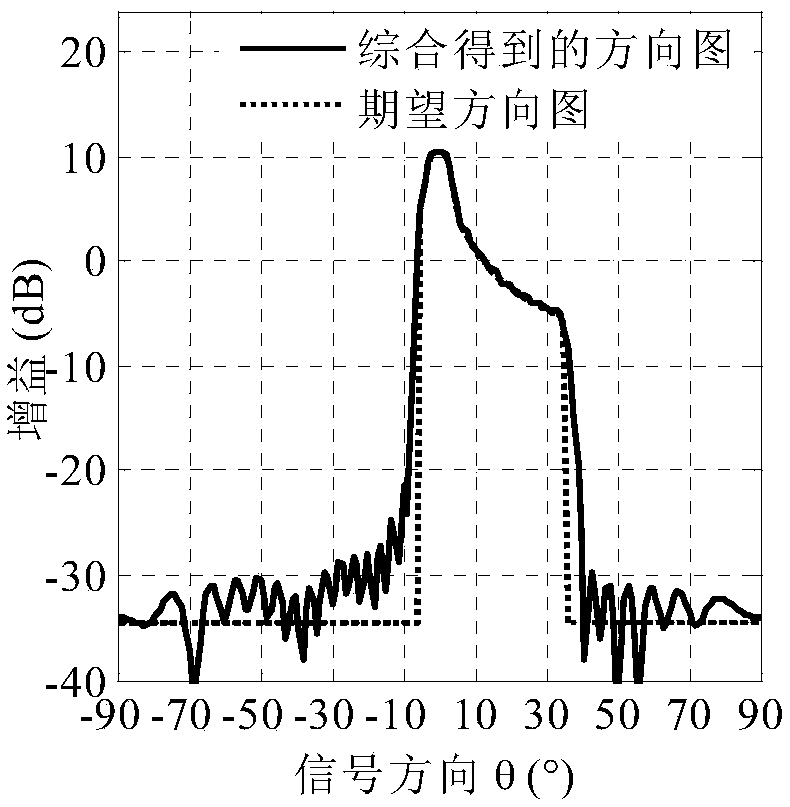
[0123] The invention is a high-precision control pattern main lobe area gain and static direction under the GSC (Generalized Sidelobe Canceler) framework. Figure 1 Based on the consistent basis, the method of adaptively suppressing the interference in the side lobe area does not need to estimate the angle of the interference source. For the method flow, see figure 1 , the algorithm implementation model under the GSC architecture can be found in figure 2 . This embodiment adopts a linear array with 32 array elements, a uniform linear array with an element spacing of half a wavelength, and an omnidirectional antenna as an element antenna. The desired static pattern main lobe area satisfies the cosecant square pattern characteristic, and the beam forming area is from -5° to 35°. The side lobe is about -30dB, and the jitter in the main lobe area is less than 0.2dB. The static cosecant square pattern is obtained comprehensively as follows image 3 shown.
[0124] The realiza...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com