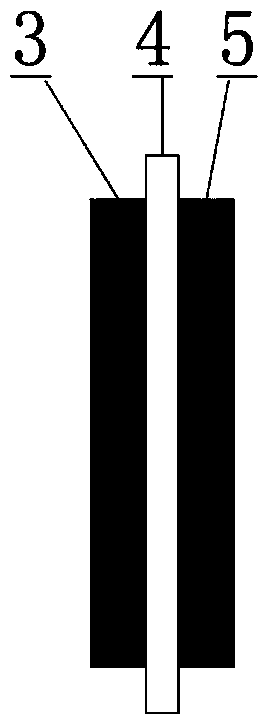A high temperature fuel cell stack
A fuel cell stack and high temperature technology, applied in fuel cells, fuel cell additives, solid electrolyte fuel cells, etc., can solve problems such as difficult water discharge and flooding, reduce corrosion, increase battery life, and improve stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0019] Specific implementation methods include:
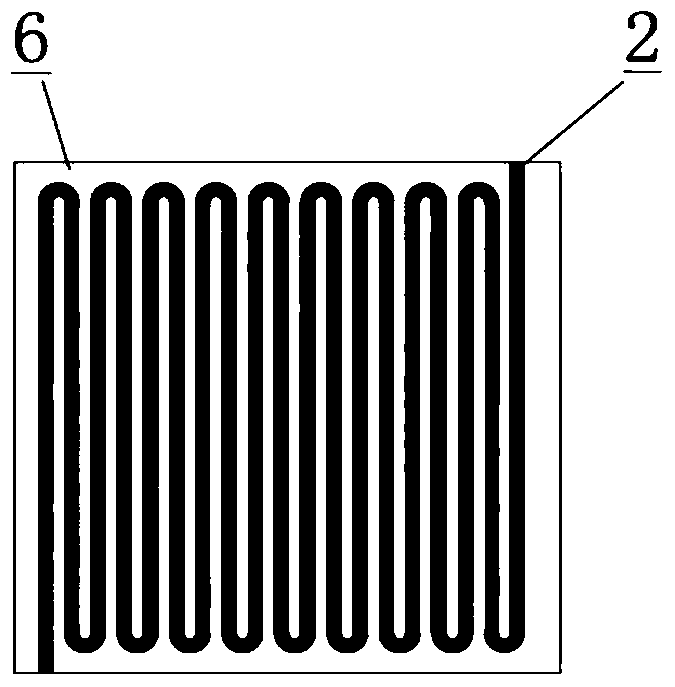
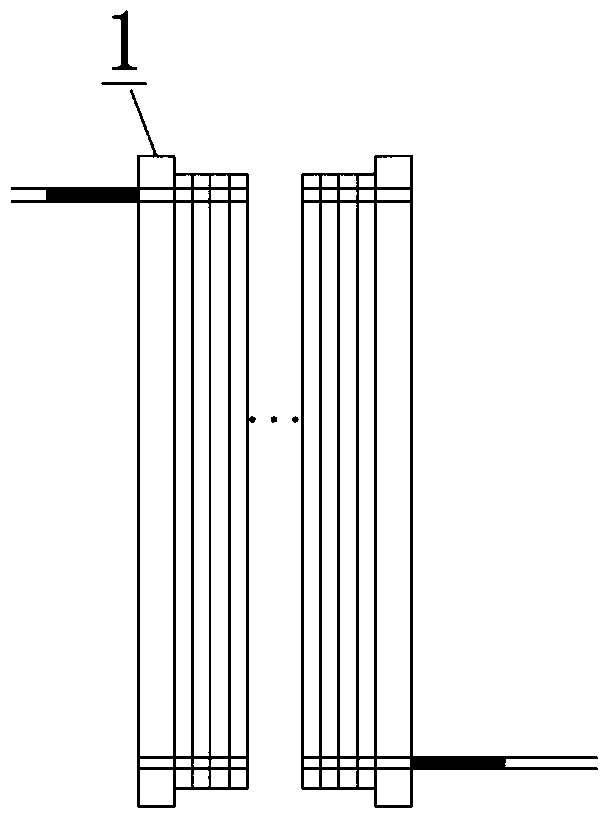
[0020] End plate 1, used for fluid distribution and current collection; Molecular sieve coating 2, removes water during battery startup and shutdown; Anode catalyst layer 3, Catalyzes the oxidation reaction of fuel; Proton exchange membrane 4, Transports protons, isolates cathode and anode reactants ; The cathode catalytic layer 5 catalyzes the reduction reaction of oxygen; the bipolar plate 6 distributes the fluid of the cathode and anode reactants. working principle:
[0021] The molecular sieve coating 2 is coated on the flow channel of the end plate 1 and the bipolar plate 6, the anode catalytic layer 3, the proton exchange membrane 4 and the cathode catalytic layer 5 together form a membrane electrode assembly MEA, and the MEA is assembled with the end plate and the bipolar plate and between the bipolar plates.
[0022] High-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells use PBI membranes, and their proton transport doe...
Embodiment approach 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, 20 single cells are placed between two end plates to form a high-temperature fuel cell stack, and the inner surface of the end plate near the single cell and the surfaces on both sides of the bipolar plate are coated with 3A molecular sieve coating. Layer, the thickness of the molecular sieve membrane is 0.005mm.
[0025] The high-temperature fuel cell stack assembled in this way did not find obvious decline in battery performance after continuous start and stop 100 times, while the high-temperature fuel cell stack coated with the molecular sieve membrane was tested under the same conditions as the above-mentioned high-temperature fuel cell stack After 73 times of starting and stopping, there was an obvious decline in battery performance due to flooding. Through the comparison of the two methods, it is found that the above method can effectively improve the flooding phenomenon caused by the high-temperature fuel cell stack during start-...
Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: In this embodiment, 20 single cells are placed between two end plates to form a high-temperature fuel cell stack, and the inner surface of the end plate near the single cell and the surfaces on both sides of the bipolar plate are coated with 5A molecular sieve coating Layer, the thickness of the molecular sieve membrane is 0.01mm.
[0027] The high-temperature fuel cell stack assembled in this way did not find obvious decline in battery performance after continuous start and stop 100 times, while the high-temperature fuel cell stack coated with the molecular sieve membrane was tested under the same conditions as the above-mentioned high-temperature fuel cell stack After 73 times of starting and stopping, there was an obvious decline in battery performance due to flooding. Through the comparison of the two methods, it is found that the above method can effectively improve the flooding phenomenon caused by the high-temperature fuel cell stack during start-up...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com