Method for identifying bull breeds with genetic markers of mononucleotides of Y chromosomes of Bos taurus
A Y-chromosome, single-nucleotide technology, applied in the field of molecular marker-assisted identification in introduction and breeding, can solve problems such as inability to distinguish varieties finely
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
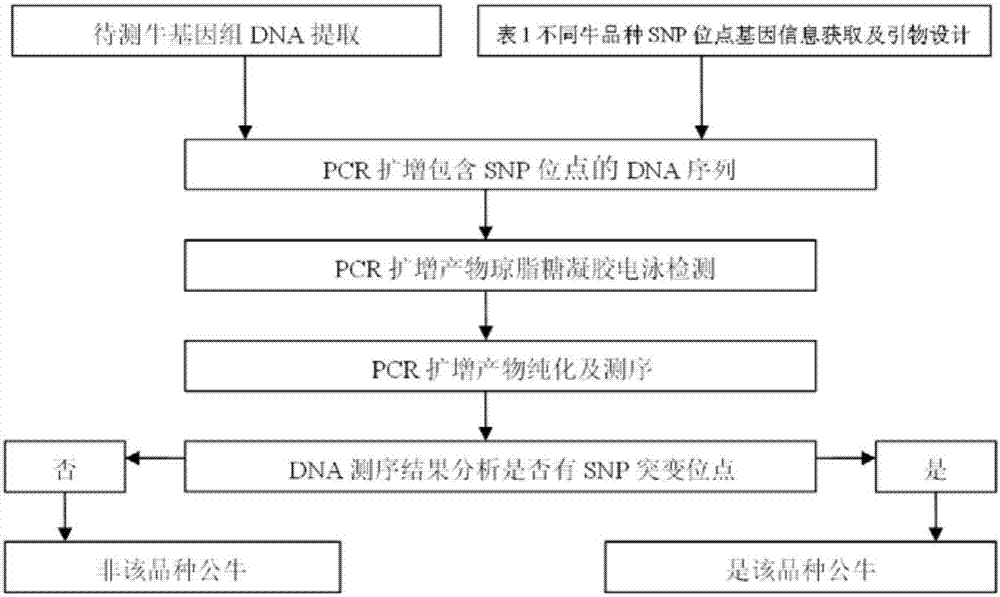
[0030] Example 1. The method of identifying bull breeds using the common bovine Y chromosome single nucleotide genetic marker (SNP): DNA sequencing method
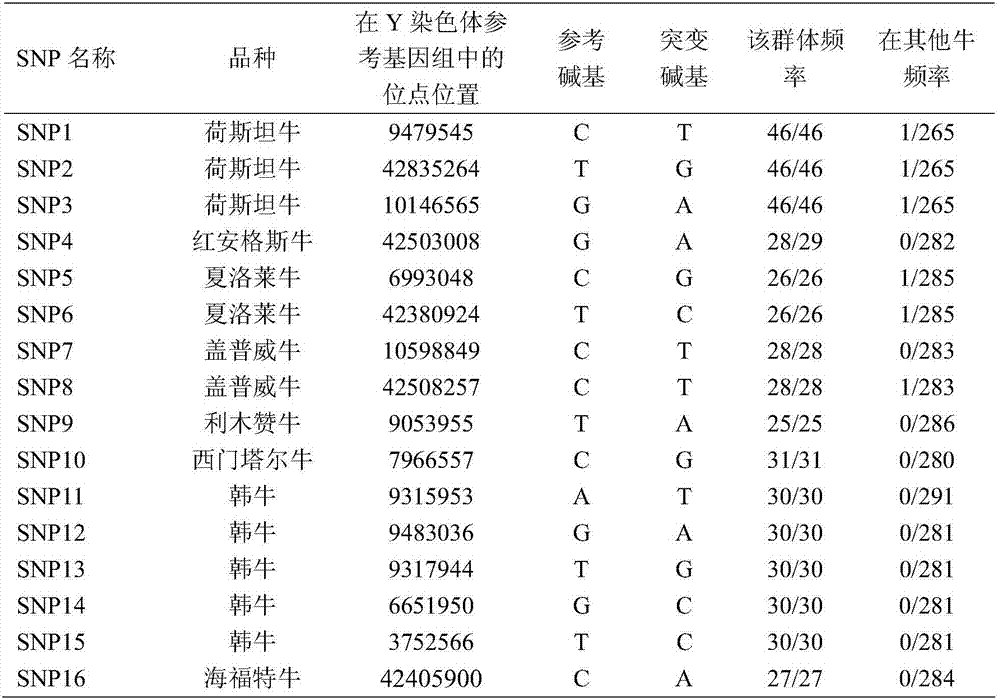
[0031] Taking the identification of Holstein bulls as an example, using the bovine Y chromosome reference genome sequence, select one or more of SNP1, SNP2 and SNP3, and extend a certain length on both sides, and use this as a template to design PCR amplification primers. Using the genomic DNA of the bull to be tested as a template and the DNA of a cow as a recessive control, PCR amplification was performed, and the amplified products were sequenced. Then use DNASTAR software to compare the sequencing results with the reference genome sequence to confirm whether the selected SNP site is a reference base or a mutation base. If it is a mutation base, the cow is a Holstein bull, otherwise it is not a Holstein bull. The specific steps are as follows , see figure 1 :
[0032] 1) extract the genomic DNA of the cattle to be tes...
example 2
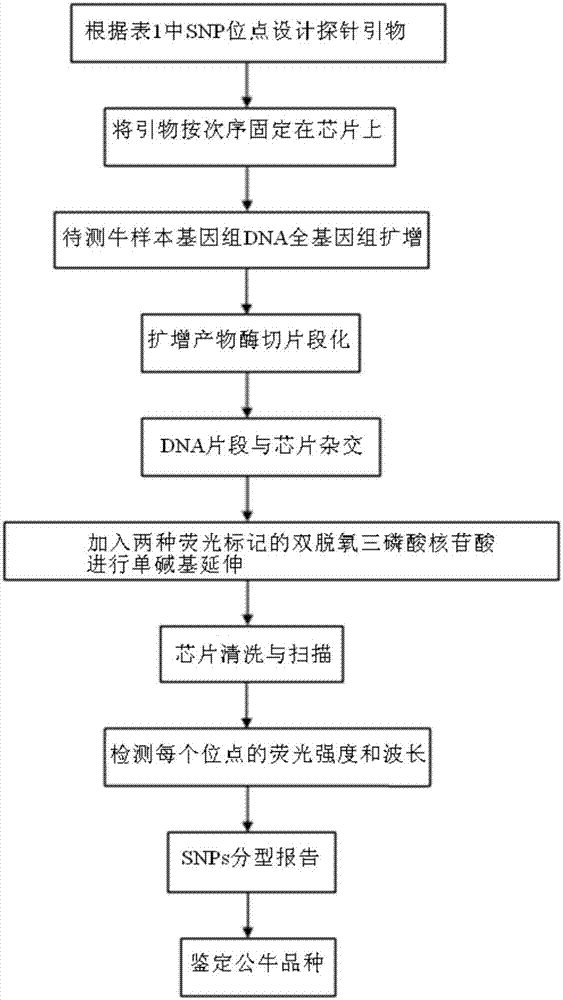
[0042] Example 2, the method of identifying bull breeds using the common bovine Y chromosome single nucleotide genetic marker (SNP): SNP chip method
[0043] see figure 2 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0044] 1) Design a 50bp single-stranded probe primer according to each SNP site in Table 1.
[0045] 2) Fix these primers on the chip in a certain order.
[0046] 3) The genomic DNA of the bovine sample to be tested is subjected to whole genome amplification.
[0047] 4) The amplified product is digested and fragmented with a random endonuclease.
[0048] 5) Hybridizing the DNA fragments with the chip, so that the genomic DNA digestion product can specifically bind to the probe.
[0049] 6) Two kinds of fluorescently labeled dideoxytriphosphate nucleotides (ddATP, ddGTP) are added for single base extension, and only the probes complementary to gDNA can be extended.
[0050] 7) The chip is scanned after cleaning.
[0051] 8) Detect the fluorescence intensity and wavelengt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com