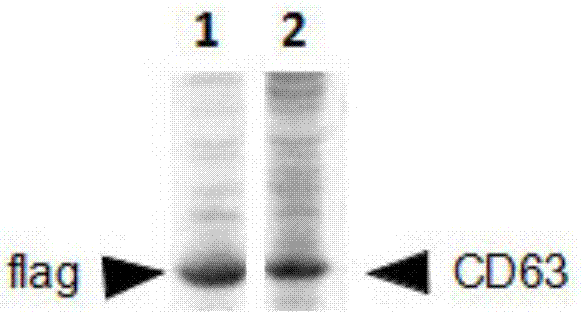
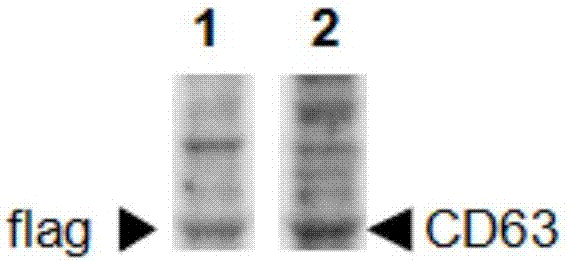
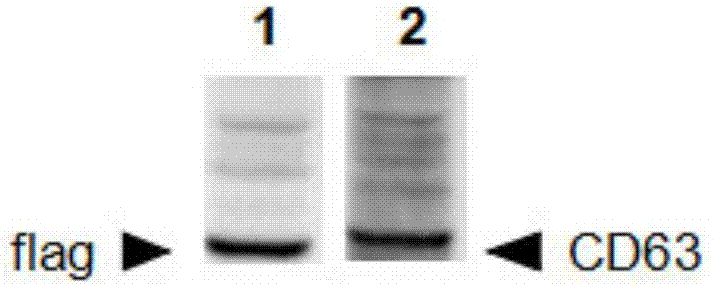
Method for separating exosomes
A separation method and technology of exosomes, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as quality reduction, vesicle damage, and time-consuming process, and achieve high yield, reduced centrifugation time, and good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] The construction of embodiment 1 plasmid
[0060] The plasmid pCDNA3.1 was digested with Nhe I endonuclease and restriction endonuclease Hind III, and a band with a vector size of 5.4kb was recovered; the primer CD63-F / R amplified the synthesized CD63 template to obtain a CD63 fragment; because 3flag-F / R are templates for each other, and the 3flag fragment is obtained by PCR amplification. The vector, CD63 fragment and 3flag fragment were added to the HB-infusion seamless cloning kit premix at a molar ratio of 1:3:3, and ligated to obtain the target plasmid pCD63-3*Flag.
[0061] Specific components of the medium in Table 1
[0062]
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2 Isolation of exosomes in 293 cells
[0064] 1) Cultivate 293 cells, and when the cell density reaches 70-80%, transfer pCD63-3*Flag into the cells by PEI method, and after culturing for 24 hours, use G418 to screen out the positive clone 293-CD63-3*Flag cells; 293-CD63-3*Flag cells were planted in a 100mm culture dish and cultured for 1 day using the aforementioned cell culture medium;
[0065] 2) Wash the cells with serum-free a-MEM, 5 times, 5ml each time;
[0066] 3) Culture with 10ml 10% a-MEM without exosomes FBS (fetal bovine serum) for 3 days, collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 1000g for 5min, and then centrifuge at 12000g for 30min at 4°C to remove broken cell debris and apoptotic bodies;
[0067] 4) After centrifugation, mix the supernatant with PBS at a volume ratio of 1:1;
[0068] 5) Add flag antibody-coated beads (magnetic beads) to the medium solution containing exosomes, incubate at 4°C for 15 minutes, and the magnetic beads bind to exosom...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3 Isolation of exosomes in Hela cells
[0075] 1) Cultivate Hela cells, and when the cell density reaches 70-80%, transfer pCD63-3*Flag into the cells by PEI method, and after culturing for 24 hours, use G418 to screen out the positive clone Hela-CD63-3*Flag cells; 2 *10^6 Hela-CD63-3*Flag cells were planted in a 100mm culture dish and cultured for 1 day using the aforementioned cell culture medium;
[0076] 2) Wash the cells with serum-free a-MEM, 5 times, 5ml each time;
[0077] 3) Culture with 10ml 10% a-MEM without exosome FBS for 3 days, collect the supernatant, centrifuge at 1000g for 5min, then centrifuge at 12000g at 4 degrees for 30min to remove broken cell debris and apoptotic bodies;
[0078] 4) After centrifugation, mix the supernatant with PBS at a ratio of 1:1;
[0079] 5) Add flag antibody-coated beads (magnetic beads) to the medium solution containing exosomes, incubate at 2°C for 20 minutes, and the magnetic beads bind to exosomes with corresp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com