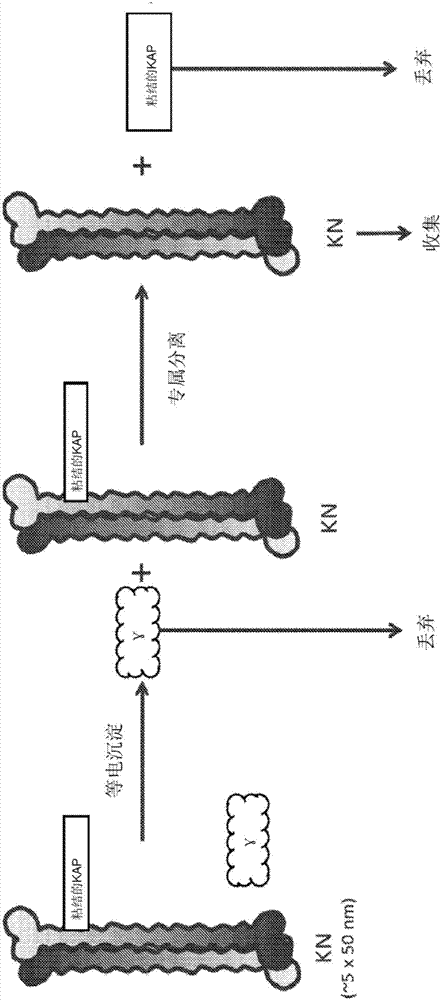
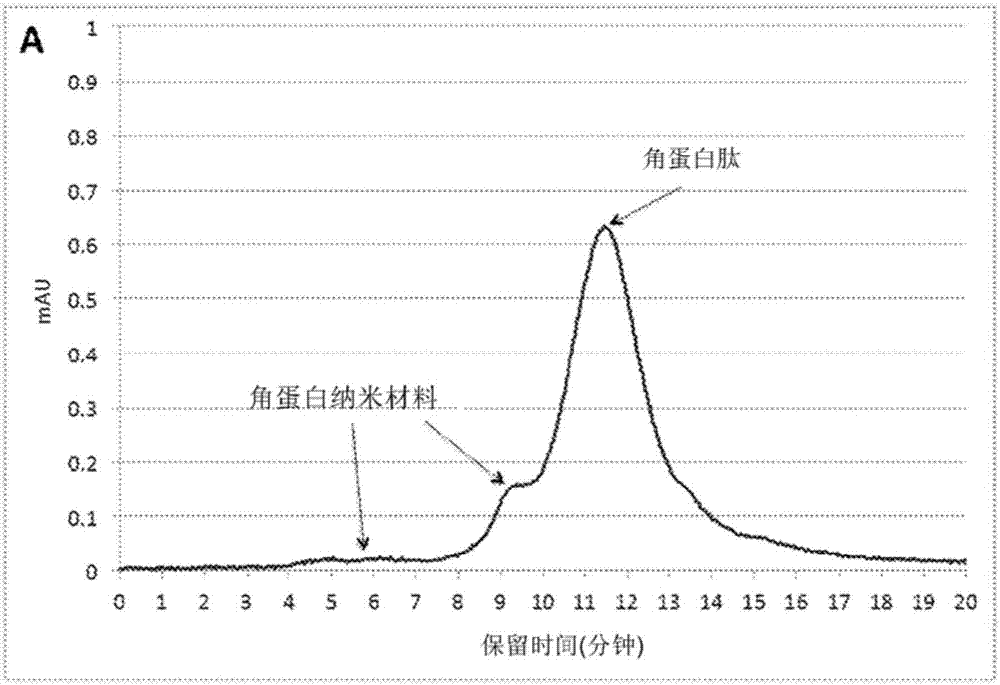
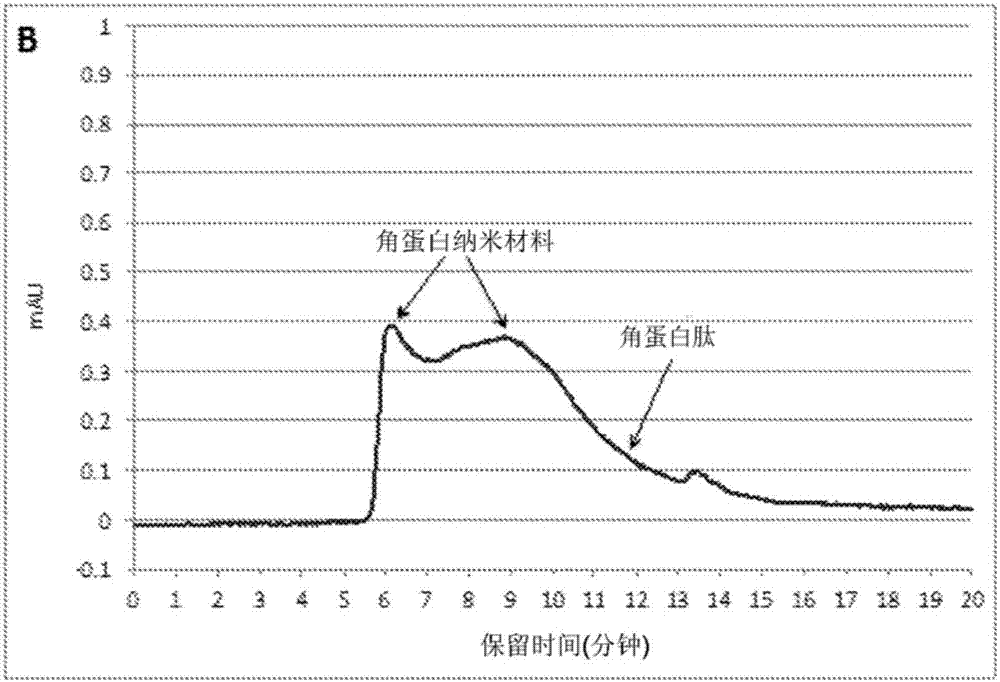
Keratin nanomaterials and methods of production
A technology of nanomaterials and keratin, which is applied in the preparation and application of keratin nanomaterials, macromolecular keratin complexes, and keratin nanomaterials, and can solve the problem of low immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Embodiment 1: prepare oxidized keratin nanomaterial
[0096] Samples of Chinese hair were obtained from commercial suppliers and used directly without treatment. 100 g of hair fibers were placed into 2 liters of 2% w / v peracetic acid and shaken at 150 rpm for 8 hours at 37°C. The oxidized hair was recovered through a sieve and extracted with 4 liters of 100 mM Tris base by shaking at 150 rpm for 15 hours at 37°C. The hair was recovered through a sieve, the extract solution was retained, and the hair fiber was further extracted using 4 liters of pure water by shaking at 150 rpm for 2 hours at 37°C. Recover the hair with a sieve and discard, reserving the extract solution. The two extract solutions are combined to form a solution of crude keratin extract which is purified of particulate matter by centrifugation through a solid separator operating at 40000 rpm, followed by filtration through a membrane with an average pore size of 20-25 microns . Keratin nanomaterial...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Embodiment 2: prepare oxidized keratin nanomaterial
[0100] Samples of Chinese hair were obtained from commercial suppliers and used directly without treatment. 200 g of hair fibers were placed into 4 liters of 2% w / v peracetic acid and shaken at 125 rpm for 8 hours at 37°C. The oxidized hair was recovered through a sieve and extracted using 8 liters of 100 mM Tris base by shaking at 125 rpm for 14 hours at 37°C. The hair was recovered through a sieve, the extract solution was retained, and the hair fiber was further extracted using 8 liters of pure water by shaking at 125 rpm for 2 hours at 37°C. Recover the hair with a sieve and discard, reserving the extract solution. The two extract solutions were combined to form a solution of crude keratin extract that was purified of particulate matter by centrifugation through a solid separator operating at 43,000 rpm, followed by centrifugation through a membrane with an average pore size of 20-25 microns. filter. Kerati...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Embodiment 3: preparation reduces keratin nanomaterial
[0104] Samples of Chinese hair were obtained from commercial suppliers and used directly without treatment. Keratin extraction was achieved by a multi-step reduction process as follows: 100 g of hair was placed in 2 liters of a 0.5 M thioglycolic acid (TGA) solution adjusted to a pH of 10.5 and heated at 150 rpm at 37° C. Shake for 15 hours. The hair is recovered with a sieve, and the extraction solution is retained. Then, the hair fibers were placed in 4 liters of a solution of 100 mM Tris and shaken at 150 rpm for 2 hours at 37°C. The resulting extraction solution was kept, and the hair was placed in 4 liters of pure water and shaken at 150 rpm for 2 hours at 37°C. The hair was recovered with a sieve, placed in 1 liter of a freshly prepared 0.5 M TGA solution adjusted to a pH of 10.5, and shaken at 150 rpm for 15 hours at 37°C. The hair is recovered with a sieve, and the extraction solution is retained. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com