Journey path planning method, device and electronic device
A technology of stroke planning and path planning, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, road network navigators, instruments, etc., can solve the problems that the navigation map is not updated in time, cannot make detour navigation, etc., and achieve the effect of improving operation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
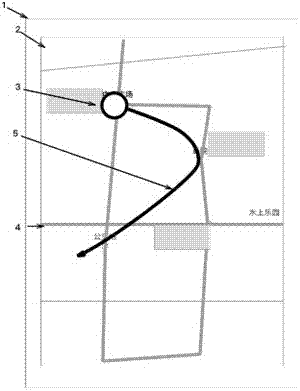
[0095] like figure 1 As shown, the electronic ground is displayed on the display screen 2 of the navigation device 1 Figure 4 , electronically Figure 4 There are a large number of discrete keypoints. These key points are information points secondary processed by the electronic map data provider or specific location points of the electronic map itself, such as crossroads, roads, or locations of shopping malls, hospitals, stations, etc. or POI (Point of Interest). The present invention uses the POI point as an example to illustrate the present invention, but is not limited to the POI point.
[0096] The user can slide the finger, touch pen or mouse to indicate the electronic location displayed on the display screen 2. Figure 4 Form a track representation on the screen, for example, the display screen 2 can be a touch screen, and the user touches the display screen 2 with a finger or a touch pen, and the electronic ground displayed on the display screen 2 Figure 4 Swipe u...
Embodiment 2
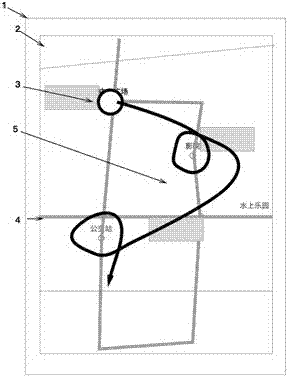
[0105] In one embodiment of the present invention, usually, the user forms a track representation in the electronic map with continuous gesture input. In order to distinguish the key points from the common track in the continuous input, a specific operations to identify the key points of the itinerary.
[0106] Optionally, the nearest information point within a certain range from the trajectory representation is automatically selected as the key point of the itinerary. Typically, when the user's gestures slide continuously indiscriminately, it is automatically judged whether there is an information point within a certain range of the gesture track, and if there is, the information point closest to the gesture track is automatically selected as the key point of the journey here. In this way, the user only needs to swipe the contact and ensure that the gesture trajectory is as close as possible to the desired POI point (in order to avoid misuse, it may also need to be as far awa...
Embodiment 3
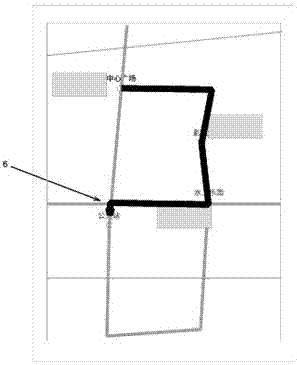
[0131] On the basis of Embodiments 1 and 2, the user can select meaningful POI points in a delineated manner. In order to specify POI points more clearly, some users are accustomed to delineating a certain POI point from multiple POI points as a meaningful POI point by drawing a circle.
[0132] When the user's finger slides on the display screen 2 of the navigation device 1 to form a trajectory, a closed circle can be formed around a certain POI point. like image 3 As shown in , the user forms a closed circle around two POIs, the theater and the bus station. When the navigation device 1 detects that a circle appears around the POI points of the trajectory, these two POI points are regarded as meaningful POI points, not as the trajectory.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com