Method for calculating first-order natural cyclic frequency of bending vibration of stepped beam
A bending vibration and calculation method technology, applied in the direction of complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as complex formulas, failure to find out, and heavy calculation workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
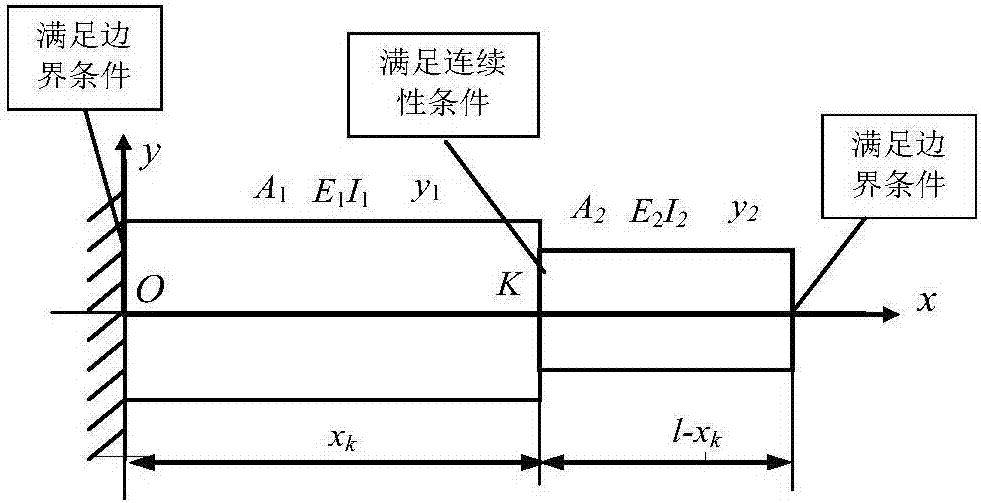
[0089] Example 1: Take figure 1 The shown cantilever stepped beam is taken as an example, and the natural circular frequency equation of its bending vibration is given. This equation is suitable for cantilever stepped beams with different section properties, different section sizes and segment lengths.
[0090] Such as figure 1 As shown, let the total length of the stepped beam be L, and the left beam L 1 The mass per unit volume is ρ 1 , Cross-sectional area A 1 , The shaft moment of inertia is I 1 , The elastic modulus of the material is E 1 ; Right beam L 2 The mass per unit volume is ρ 2 , The cross-sectional area is A 2 , The shaft moment of inertia is I 2 , The elastic modulus of the material is E 2 , That is, the bending stiffness of the two beams is E 1 I 1 , E 2 I 2 .
[0091] Let y(x,t) be the lateral vibration displacement of the cross section of the stepped beam from the coordinate origin x at time t, according to the lateral forced vibration equation of Bernoulli-Euler...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com