Communications receiver equalizer
A technology of equalizer and inductor, which is applied in the shaping network of transmitter/receiver, digital transmission system, baseband system components, etc. It can solve the problems of clock and data recovery circuit failure, poor signal quality, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
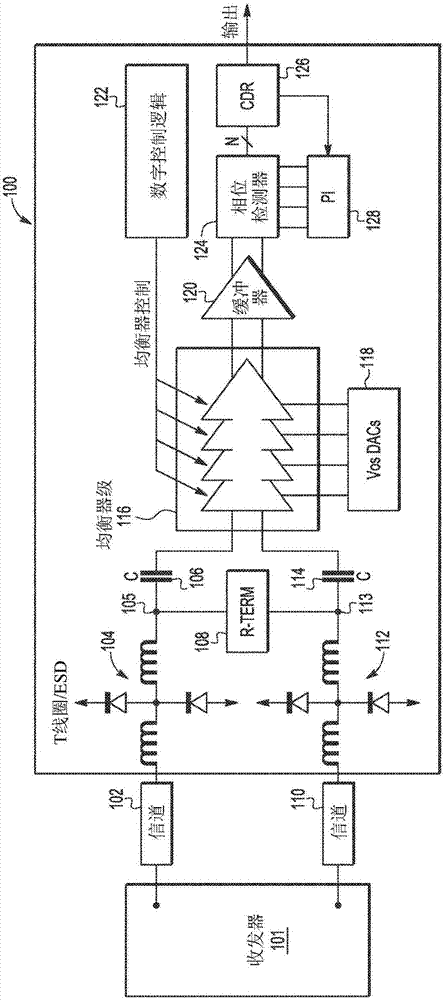
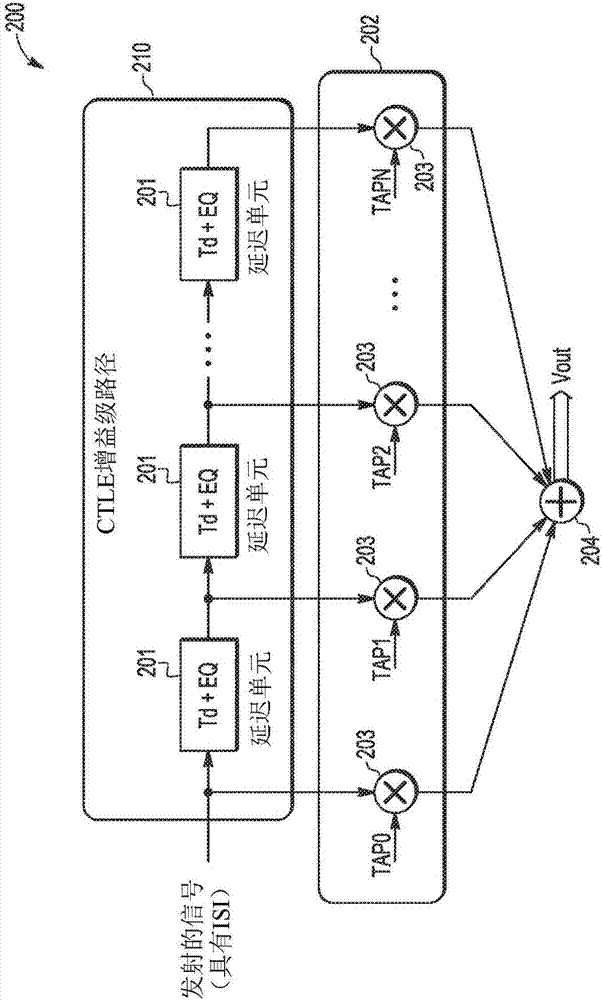
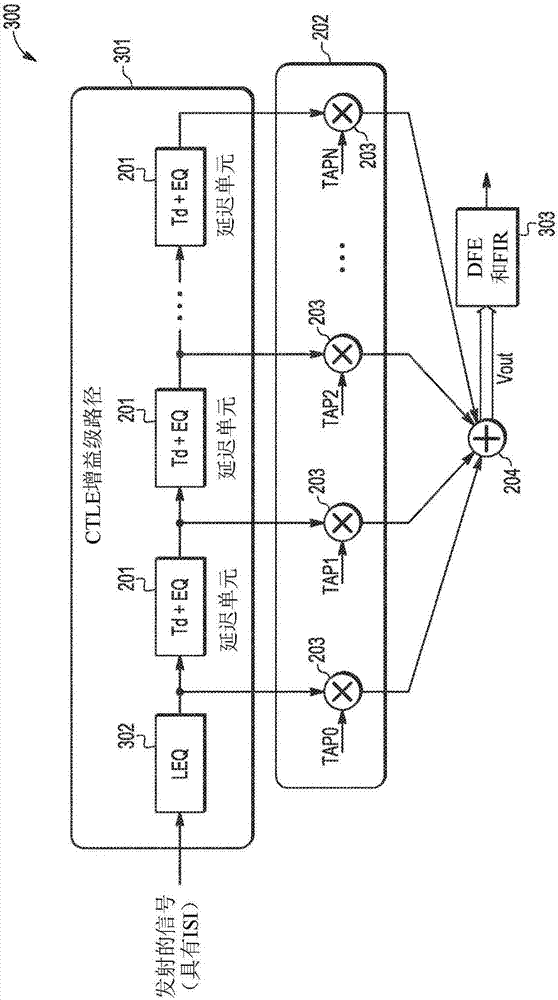
[0017] Due to the foregoing, transmit and / or receive equalization may be provided to compensate for losses associated with analog signals to be transmitted over a communication channel. In communication systems, equalization is the process of correcting channel-induced distortions caused by inherent losses within the communication channel (ie, the aforementioned inherent ISI characteristics of the communication channel). Equalizers are filters that can be adjusted to compensate for channel distortion. Since the communication channel essentially acts as a low pass filter, the function of the equalizer is to equalize the levels between the various frequencies of the transmitted signal. In some aspects, such equalizers act as high-pass filters. The basic problem is that the eye diagram of the received signal (i.e., the oscilloscope display of the received signal that can provide an indication of the effects of channel noise and / or ISI) is somewhat closed, which can introduce ina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com