Light Emitting Diodes for Parallel Illumination
A technology of light-emitting diodes and parallel light, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low radiation emission, unobtainable, small divergence angle, etc., to reduce light radiation, optimize lighting design, and reduce light output area Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
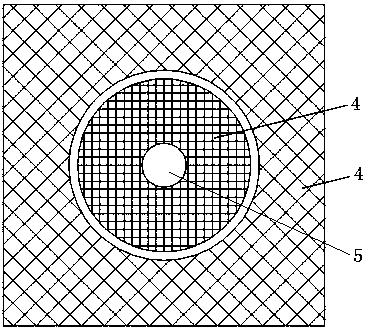
[0052] When both electrodes of the light emitting diode chip are located on the upper surface of the light emitting diode chip, such as Figure 5 As shown, the cover layer 4 is formed by two electrodes, and the two electrodes are designed to jointly cover the upper surface of the light-emitting diode chip 1 and only form a circular light exit hole 5 in the center. The diameter of the circular light exit hole 5 is preferably 0.1-0.5 mm. The area of the two electrodes on the upper surface of the light-emitting diode chip 1 is much larger than the area of the two electrodes of ordinary light-emitting diodes. Since the area of the light-emitting area decreases, the total radiant flux decreases, but the radiation emission in the area of the central circular light exit hole 5 increases. It is beneficial to reduce the divergence angle of parallel light. The corresponding light-emitting diode packaging structure is as follows: Figure 11 As shown, it includes a light emittin...
Embodiment 2
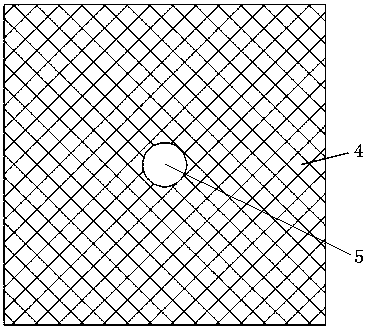
[0054] When the two electrodes of the light-emitting diode chip are respectively located on the upper surface and the lower surface of the light-emitting diode chip, such as Figure 6 As shown, the cover layer 4 is formed by electrodes located on the upper surface of the LED chip 1, and the area of the electrodes located on the upper surface of the LED chip 1 is increased so that the electrodes located on the upper surface of the LED chip 1 cover the upper surface of the LED chip 1 And only a circular light exit hole 5 is formed in the center, and the diameter of the circular light exit hole 5 is preferably 0.1-0.5 mm. Since the area of the luminous area is reduced, the total radiant flux is reduced, but the radiation output degree in the area of the central circular light exit hole 5 is increased, which is beneficial to reduce the divergence angle of the parallel light. The corresponding light-emitting diode packaging structure is as follows: Figure 11 As shown, it in...
Embodiment 3
[0056] When the light-emitting diode adopts a flip-chip package structure and both electrodes are located on the lower surface of the light-emitting diode chip in contact with the heat sink, the substrate of the light-emitting diode chip 1 is located on the top of the light-emitting diode chip 1, such as Figure 7 As shown, the substrate 7 on the top of the LED chip 1 is thinned, so that the thickness of the remaining substrate 7 is 0-80 microns, or as Figure 8 As shown, the substrate 7 of the light-emitting diode chip 1 is completely peeled off, and the light-emitting area of the four sides of the light-emitting diode chip 1 is reduced by thinning or peeling off the substrate, reducing the light radiation on the side, and, as Figure 9 As shown, the upper surface of the light-emitting diode chip 1 after thinning or peeling off the substrate is covered with a cover layer 4 that suppresses light radiation, and the cover layer 4 is a metal film plated on the upper surface of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com