Method for deducting whole spectrum background of gamma energy spectrum by using successive approximation SNIP calculation
A technique of gradually approximating and subtracting the background, which is applied in calculation, X-ray energy spectrum distribution measurement, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problem of excessive dependence, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and high operating efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
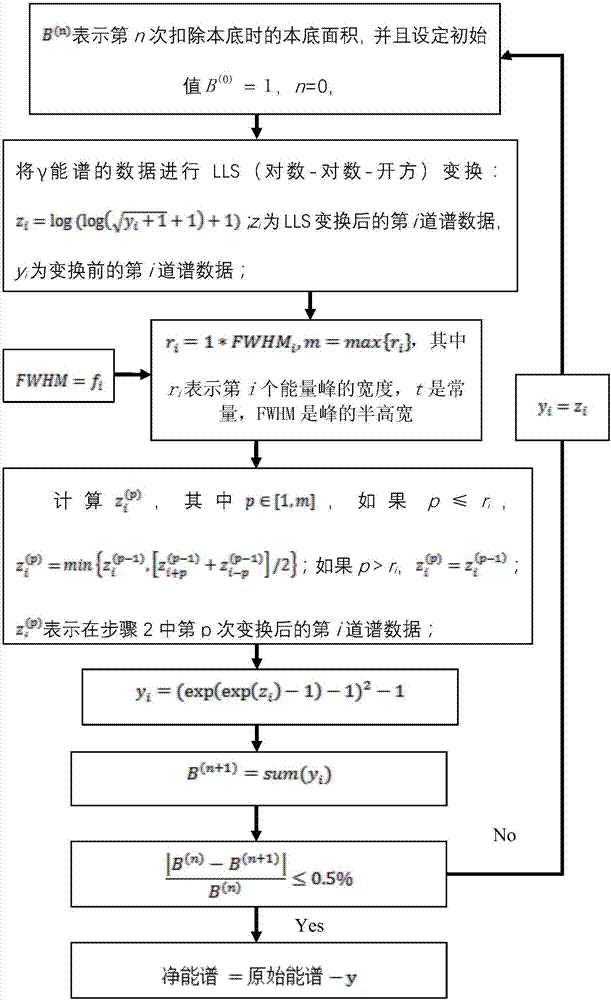
[0035] Embodiment 1, using the method of the present invention to calculate and deduct the full-spectrum background of the gamma-energy spectrum by using stepwise approximation to SNIP to subtract the full-spectrum background of the gamma-energy spectrum, proceed according to the following steps:
[0036] 1.B (n) Indicates the background area when the background is deducted for the nth time, and sets the initial value B (0) =1, n=0, then calculate B according to the following steps (n) ;
[0037] 2. Perform LLS (logarithm-logarithm-square root) transformation on the data of the gamma energy spectrum: z i is the i-th channel spectral data after LLS transformation, y i is the i-th channel spectral data before transformation;
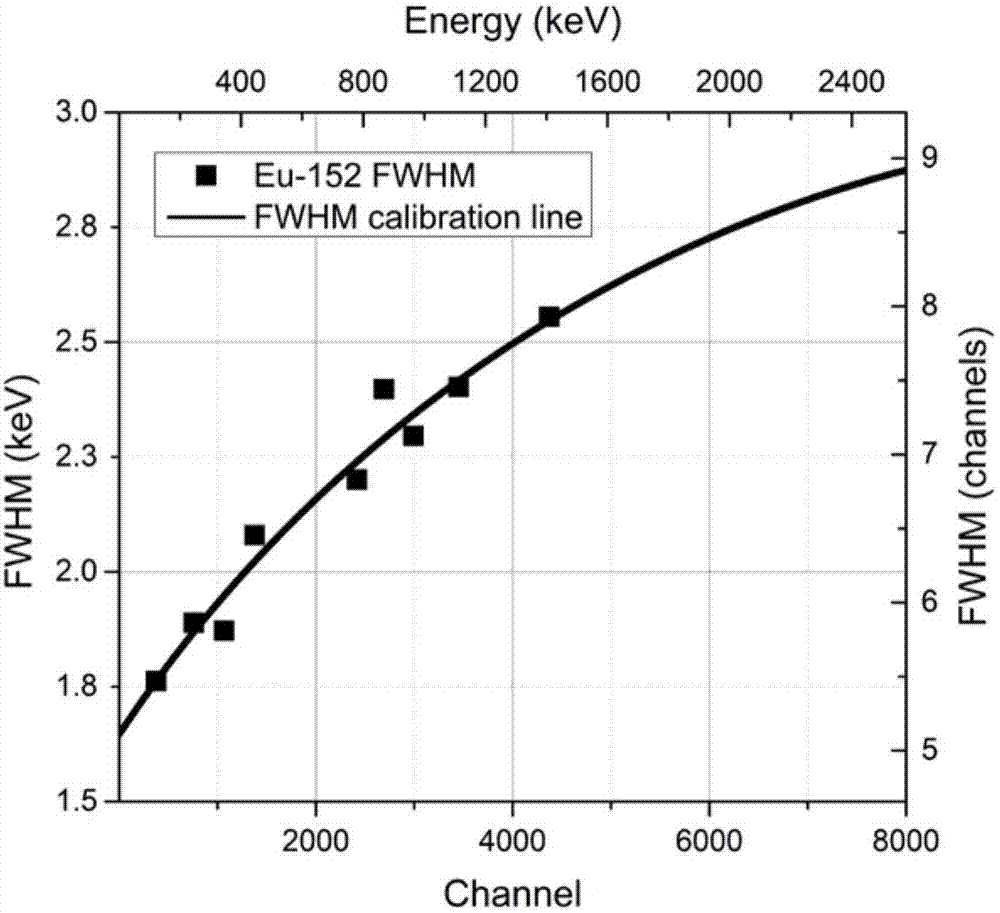
[0038] 3. Construct a vector r whose size is equivalent to the length of the energy spectrum, let r i =t*FWHM i , where r i Indicates the width of the i-th energy peak, t is a constant, representing the relationship between the full peak width and...
Embodiment 2
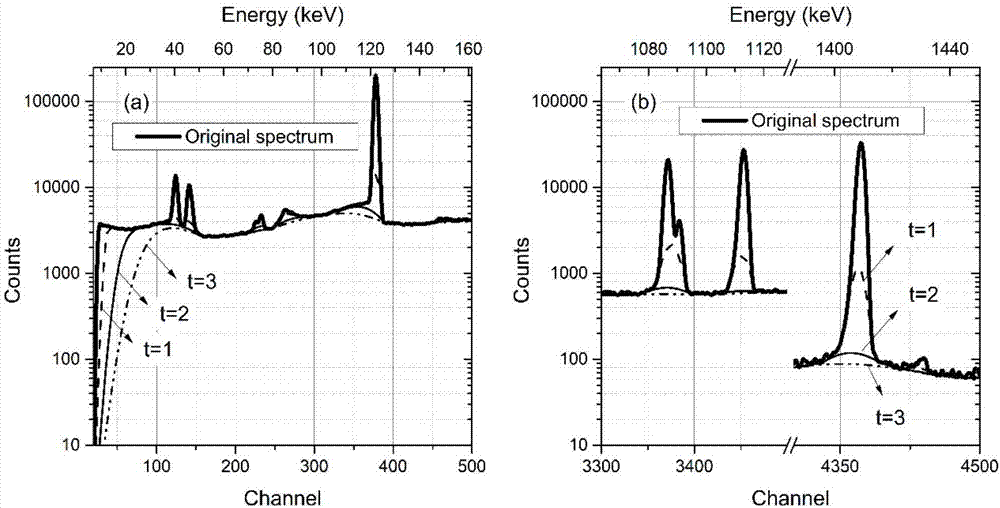
[0060] Example 2, use the Morhac algorithm to calculate the background to subtract the full-spectrum background of the gamma energy spectrum, use the symmetrical zero-area conversion method when finding the peak, and finally obtain the background subtraction results of the low-energy region and high-energy region as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0061] The result obtained after deducting the full-spectrum background of the gamma energy spectrum by utilizing the stepwise approximation SNIP calculation of the present invention to deduct the full-spectrum background of the gamma energy spectrum (such as Figure 4 shown) and the result obtained after subtracting the background of the full spectrum of the gamma energy spectrum by using the Morhac method to calculate the background (such as Figure 5 shown) for comparison.
[0062] like Figure 5 As shown, it can be seen that the background of the peak obtained by the Morhac algorithm in the low energy region is deformed, and the bac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com