Bladder volume measurement and calculation method under abdominal two-dimensional ultrasound
A technology of volume measurement and calculation method, which is applied in the field of bladder volume calculation, can solve the problems of high hardware equipment requirements, complex decomposition, high inspection cost, etc., and achieve the effects of ensuring practicability and accuracy, saving operation time, and simple measurement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Such as Figure 1~7 Shown, a kind of bladder volume measurement and calculation method under transabdominal two-dimensional ultrasound, it comprises the following steps:
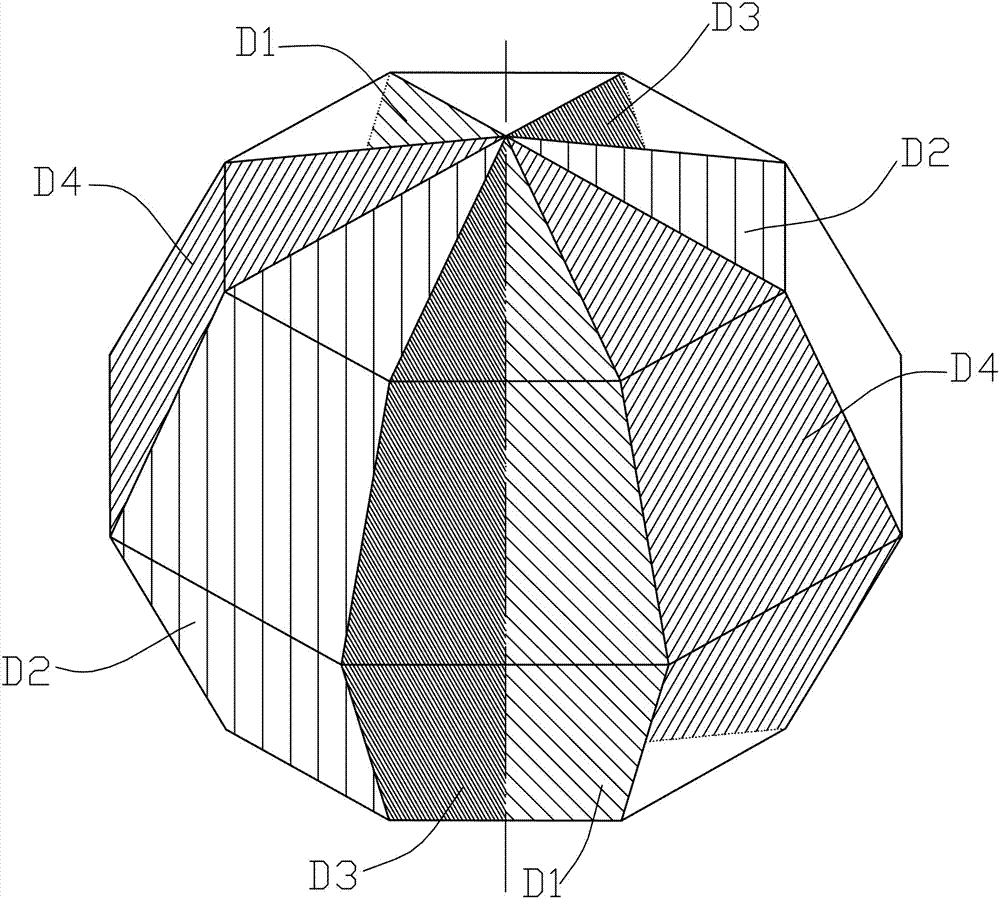
[0049] Step1: Scan the bladder through the abdomen, obtain a two-dimensional image of the bladder by ultrasound, fix the display depth of the acoustic window, try to distinguish the boundary of the bladder as clearly as possible, pressurize the probe appropriately, and stabilize the force to display the bladder as much as possible without affecting the general shape of the bladder The largest section of the median sagittal plane, that is, the median sagittal plane D1;
[0050] Step2: Rotate the probe counterclockwise by 90°, repeat the steps in Step1, and obtain the largest cross-section of the bladder, that is, cross-section D2;
[0051] Step3: Rotate the probe 45° clockwise on the basis of D1, and repeat the steps in Step1 to obtain the largest section of the left oblique section of the bladder, th...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Work process and working principle of the present invention are:
[0074] The present invention is mainly realized by being divided into two parts, one is measurement and the other is calculation.
[0075] The measurement method is mainly based on the theory created by the inventor.
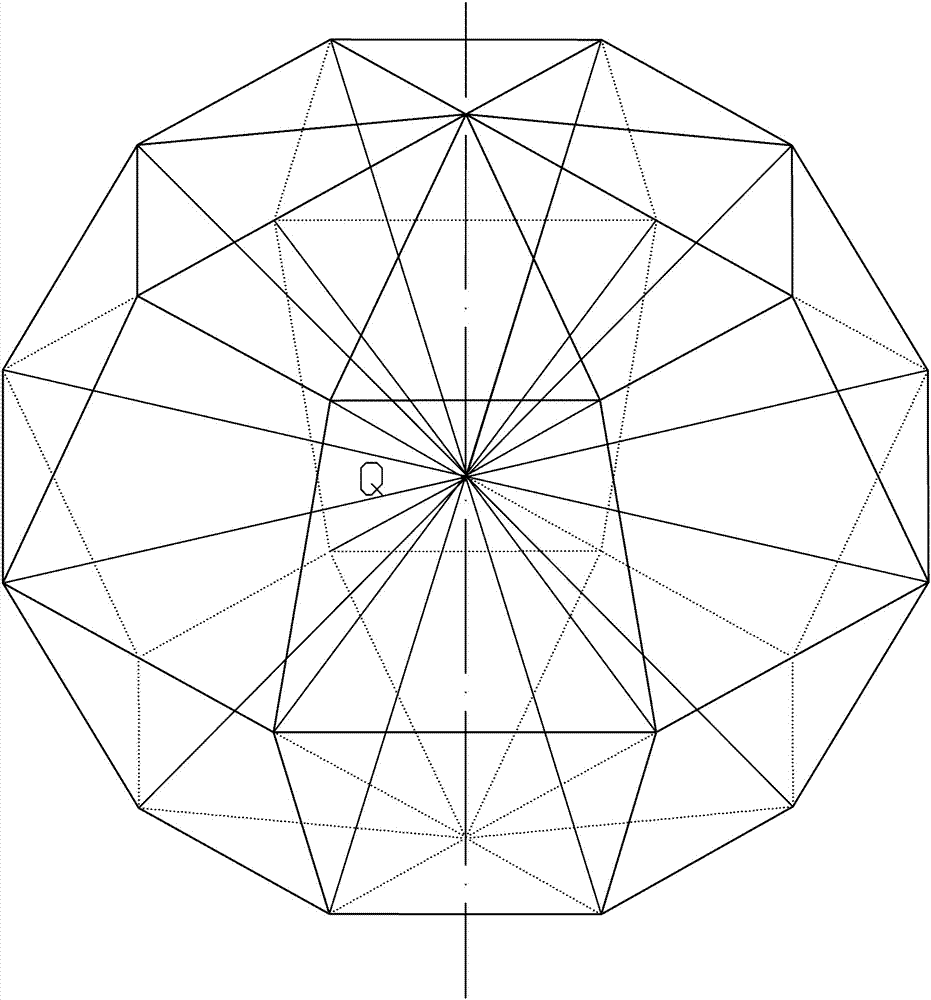
[0076] The theory is: assuming that object A and object B have the same volume (VA=VB), A is a perfect sphere, and B is an irregular shape, then the number of points of the smallest unit in object A and object B is the same, and these smallest units The straight-line distances formed by the points are equal. If any point in the cavity of object B is taken as the center point Q, and any point on the surface of B can be connected to the center point Q by a straight line, then the average value of the sum of the lengths of all radial lines passing through the center point in the irregular object must be equal to the diameter of A .
[0077] From this, it is deduced that for an irregular sh...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Such as Figure 8-9 , Figure 8 (a), (b), (c) and (d) are two-dimensional images of four sections of the bladder obtained by ultrasound during the specific implementation of the present invention.
[0090] The first step is to scan the bladder through the abdomen. The two-dimensional image of the bladder obtained by ultrasound, the display depth of the acoustic window is fixed, and the boundary of the bladder is clearly distinguished as much as possible. Try to show the mid-sagittal plane D1 of the bladder, that is, the long-axis section of the catheter or the long-axis section of the urethra, and the largest cross-section D2. The left oblique plane D3 and the right oblique plane D4 are obtained by rotating the probe clockwise and counterclockwise by about 45º respectively on the basis of the midsagittal plane. In principle, the above four cut planes are obtained by rotating the probe on the same axis.
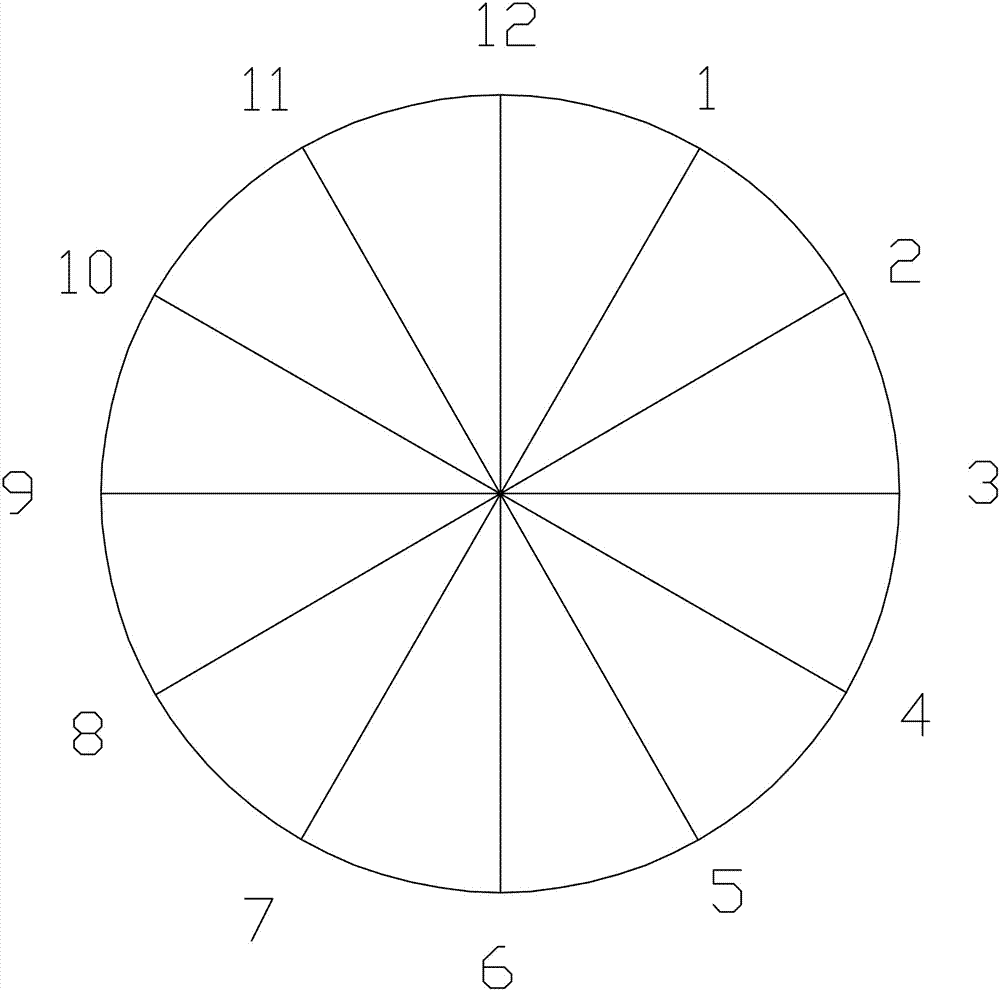
[0091] The second step is the positioning method of Q point (th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com