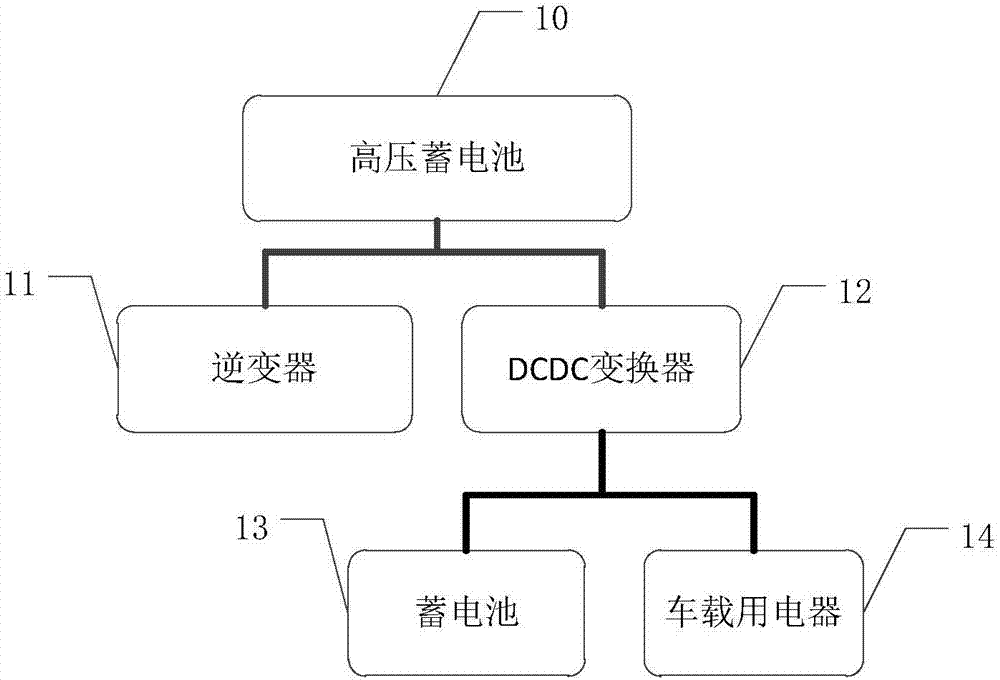
DCDC converter and control method therefor
A control method and converter technology, applied in the electronic field, can solve the problems of DCDC converter 12, such as reduced working efficiency, increased loss, and inability to realize zero-current shutdown of rectifier diodes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
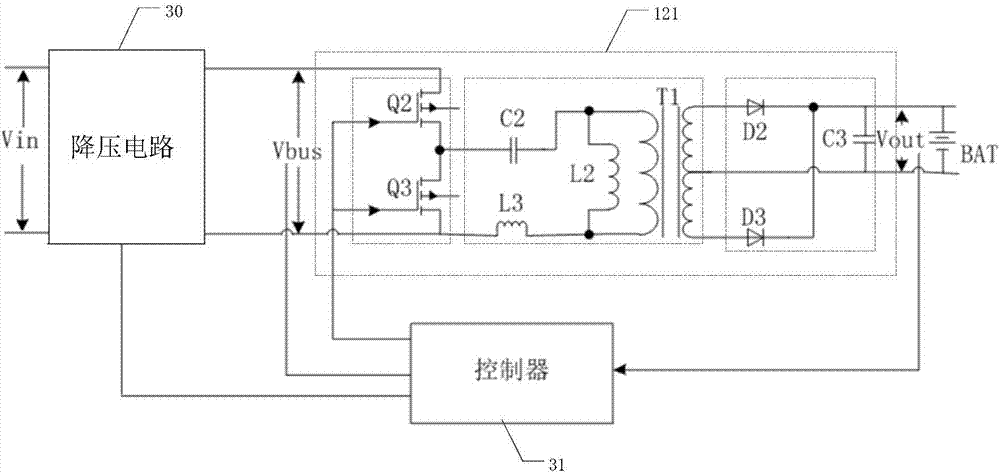
[0042] image 3 A structural diagram of a DCDC converter provided by an embodiment of the present invention. like image 3 As shown, it includes a step-down circuit 30 and a resonant unit 121 connected in series in sequence, and a controller 31 for controlling the step-down circuit 30 and the resonant unit 121 respectively. The step-down circuit 30 is used to step down the input voltage to input to the resonant The input terminal of the unit 121, the controller 31 is used to obtain the output terminal voltage of the resonance unit 121, and control the output voltage of the step-down circuit 30 and the switching frequency of the resonance unit 121 according to the target value of the output terminal voltage until the output terminal voltage reaches the target value , and control the switching frequency of the resonant unit 121 to be less than or equal to the resonant frequency after the output voltage reaches the target value, wherein the output terminal of the resonant unit 1...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Figure 4 A structural diagram of another DCDC converter provided by an embodiment of the present invention. On the basis of the above embodiments, as a preferred implementation manner, the step-down circuit 30 is specifically a Buck circuit, and the controller 31 controls the first switching tube in the Buck circuit.
[0055] like Figure 4 As shown, the Buck circuit includes a first switch tube Q11, a freewheeling diode D11, an inductor L11 and a capacitor C11, and the specific structure is as follows Figure 4 Shown, no more details.
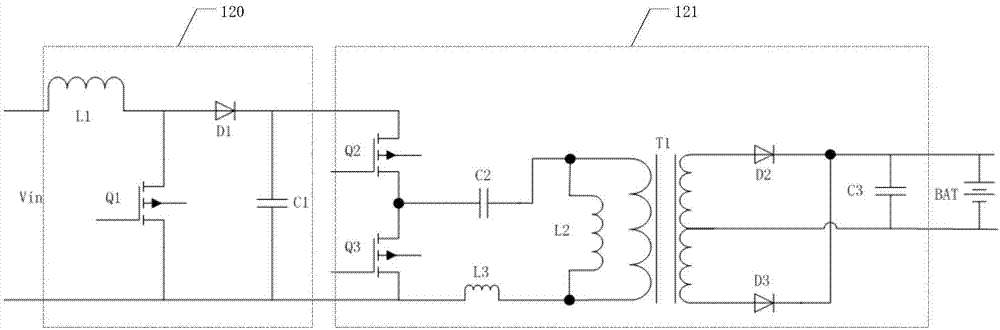
[0056] In the prior art, the front end of the resonant unit 121 adopts a Boost circuit, which is a boost circuit, and the minimum output is limited to 750V due to input requirements. Moreover, for the application limitations of existing components, the output voltage of the Boost circuit is generally set at about 800V, which cannot be too high, otherwise it will be difficult to select components. Therefore, the voltage reduction ra...
Embodiment 3
[0062] On the basis of the above embodiments, the number of resonance units 121 is at least two. Figure 6 An application scenario diagram of a DCDC converter provided by an embodiment of the present invention. Figure 6 , take two as an example. The output end of each resonant unit 121 is respectively connected to the corresponding load (the first load F1 and the second load F2, both of which are fans), wherein the resonant unit 121 corresponding to the first load F1 includes Q4, Q5, C4, L5, L4, T2, D4, D5 and C5, and the resonance unit 121 corresponding to the second load F2 includes Q2, Q3, C2, L3, L2, T1, D2, D3 and C3.
[0063] The controller 31 is used to separately collect the output terminal voltages (Vout1 and Vout2) in each resonant unit 121, and control the output voltage of the step-down circuit 30 and the switching frequency of each resonant unit 121 according to the target value of each output terminal voltage until each resonant unit 121 The voltages at the ou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com