Device and method for measuring the angle between the normal line of the light-transmitting surface of an electro-optic crystal and the optical axis of the crystal
A technology of electro-optic crystal and crystal optical axis, which is applied in the direction of geometric characteristics/aberration measurement and optical performance test, which can solve the problems of crystal scratches, difficult analysis of conoscopic interferograms, and difficult construction of measurement devices, etc., to achieve data repeatability Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
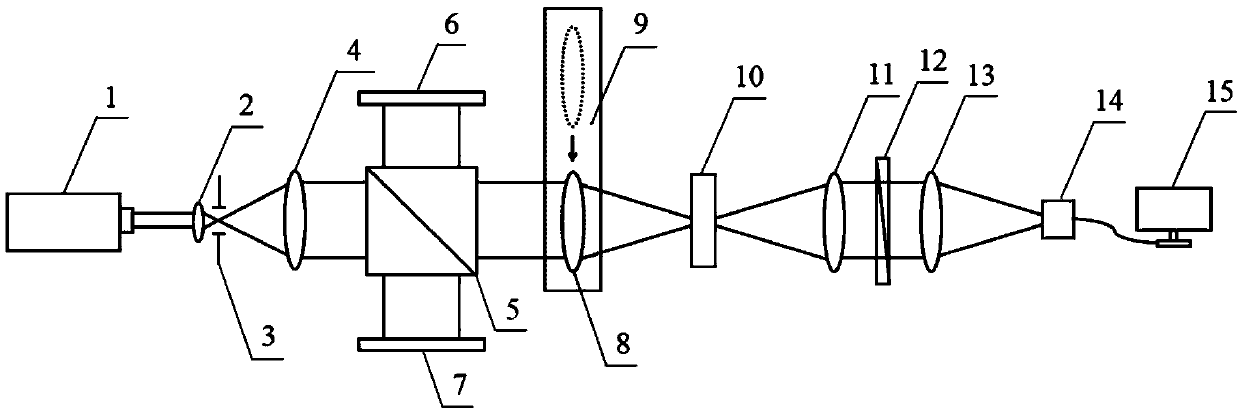
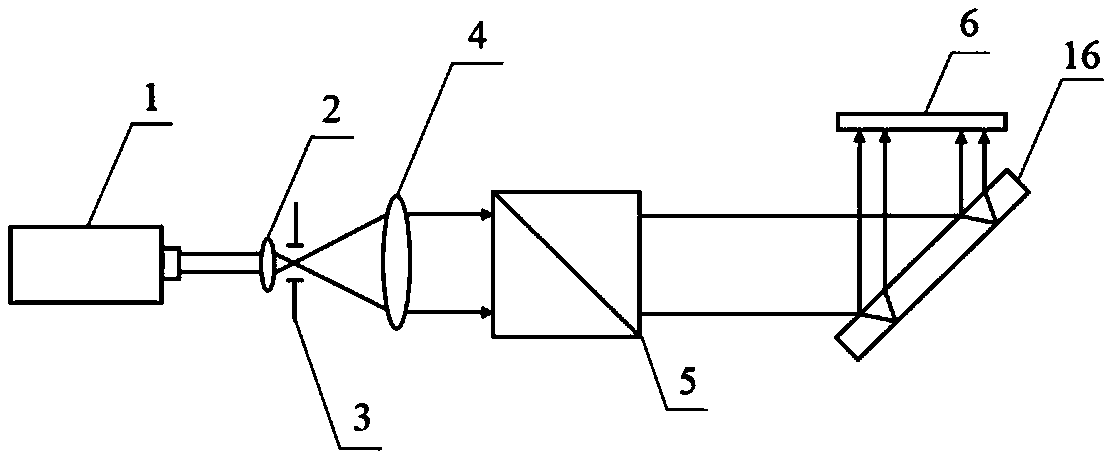
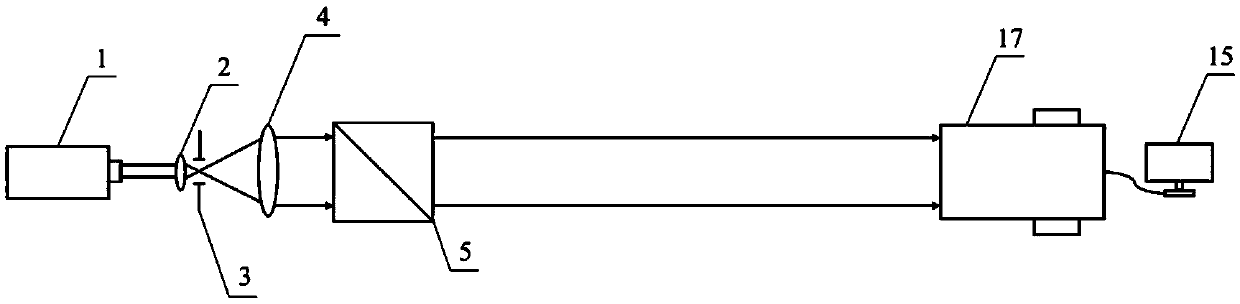
[0034] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the angle measuring device between the normal line of the light-passing surface of the electro-optic crystal and the optical axis of the crystal of the present invention. It can be seen from the figure that the measuring device for the angle between the normal line of the light-passing surface of the electro-optic crystal of the present invention and the optical axis of the crystal includes: laser 1, the first First lens 2, pinhole diaphragm 3, second lens 4, beam splitter 5, receiving screen 6, plane mirror 7, third lens 8, one-dimensional precision electric translation stage 9, electro-optic crystal to be tested 10, fourth lens 11, linear polarizing plate 12, the fifth lens 13, image detector 14 and computer 15; Described laser device is linearly polarized light laser 1, and the laser direction that sends out along described linearly polarized light laser 1 is described successively A lens 2, an aperture stop 3, a second lens 4 an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com