Time-varying constraint electroencephalogram or magnetoencephalogram source tracing method based on functional magnetic resonance imaging
A fMRI and EEG technology, applied in medical science, diagnosis, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as location mismatch, inaccurate traceability results, and inability to measure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] In order to make the above-mentioned features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, the following specific embodiments are described in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0044] It should be pointed out that what is disclosed in the present invention is only a representative preferred embodiment. Apparently, the present invention is not limited to the described specific structure, function, device and method, and may also have other implementation modes, or a combination of other implementation modes. The number of elements described in the present invention may also be set in plural unless specifically limited to a singular number. In addition, in order to avoid confusion between other examples and the present invention, some technical features and details well known in the art have not been described.
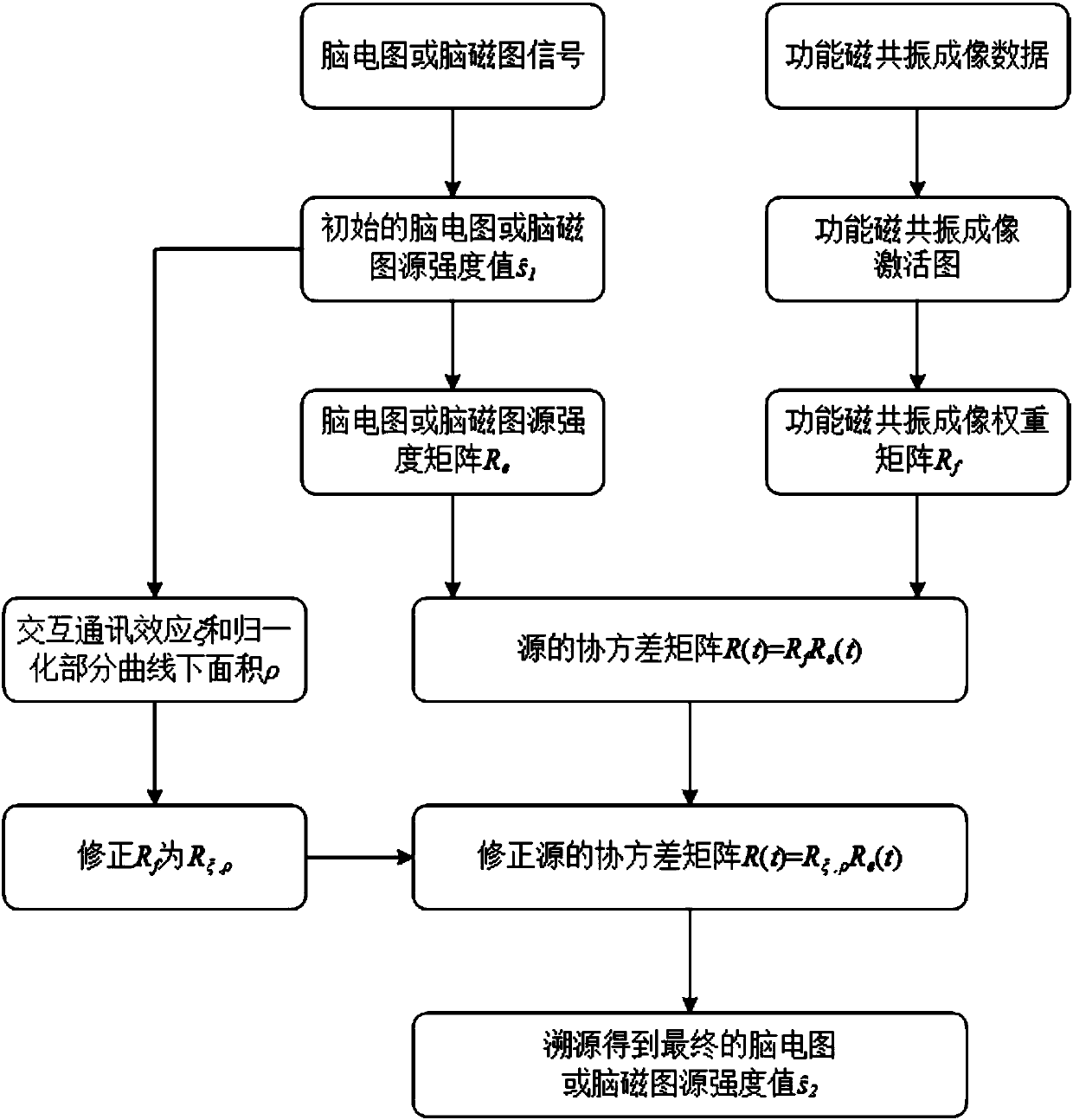
[0045] This embodiment proposes a method for traceability of EEG or MEG with dynamic constraints based on functional magne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com