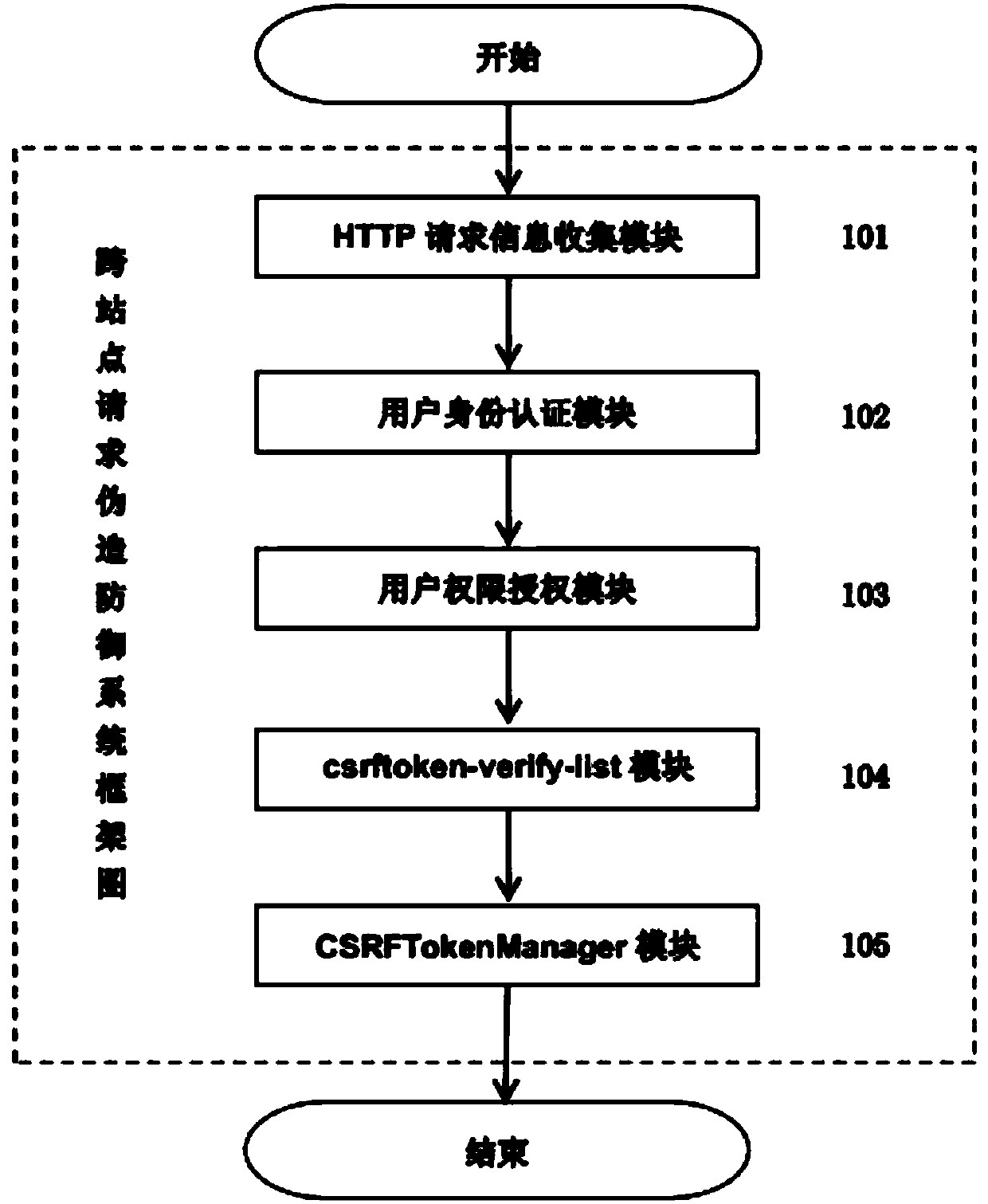
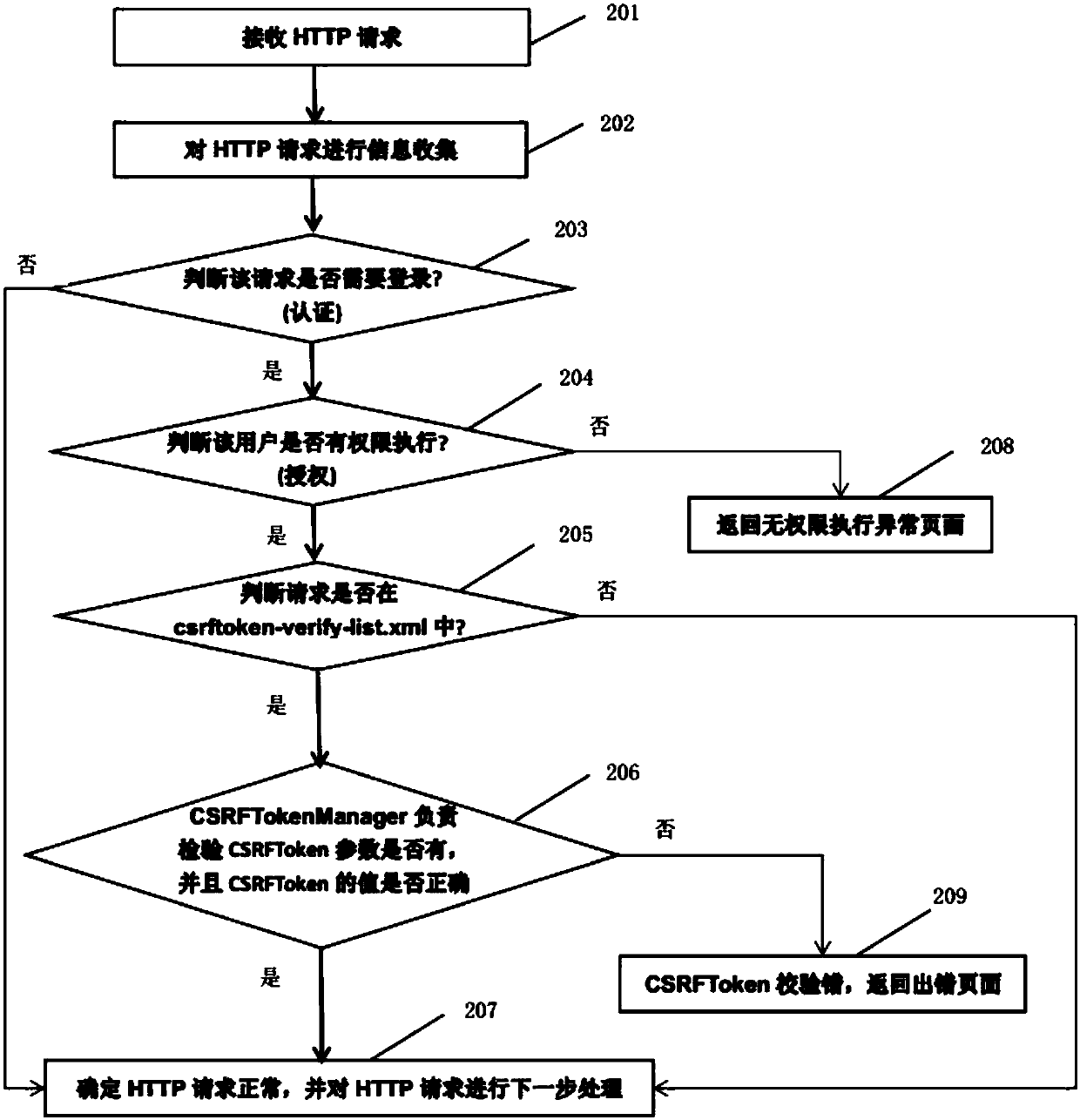
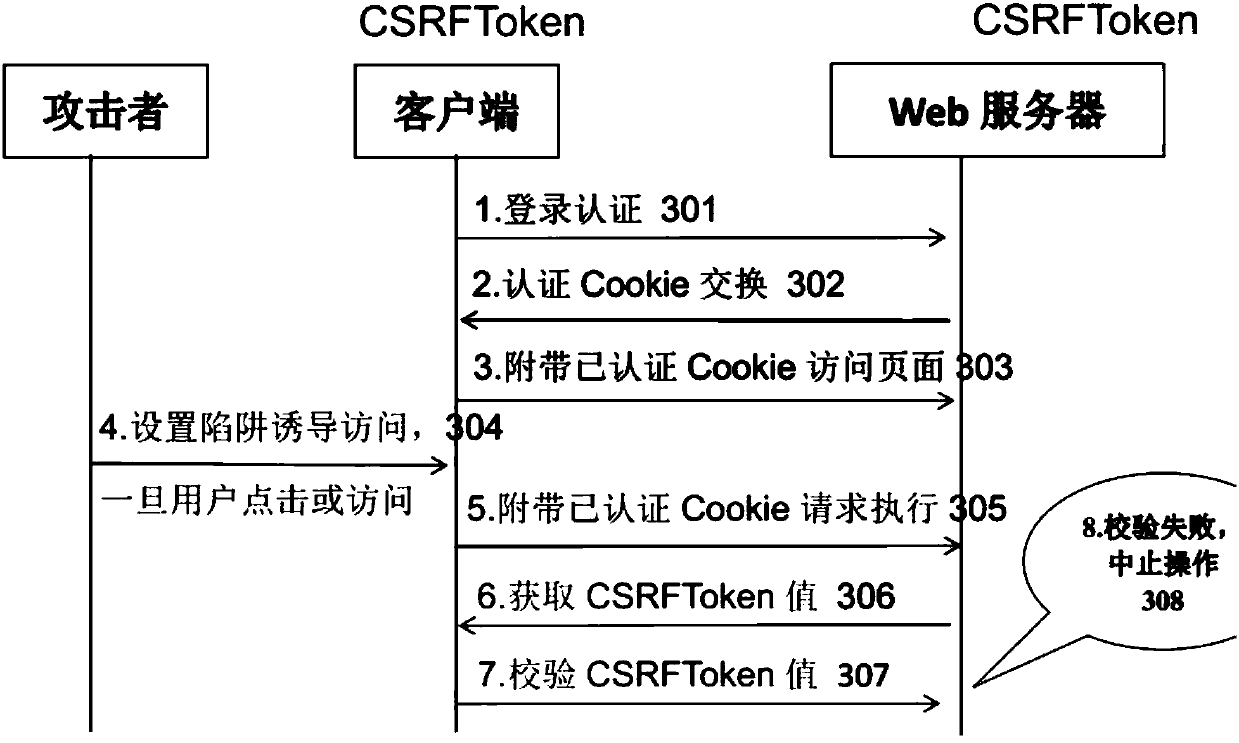
[0006] CSRF attacks are relatively hidden. Under normal circumstances, the user visits a webpage carefully constructed by the attacker, or clicks on an unknown
network link, and the attack takes effect. The attacker is like a hunter, first looking for easy-to-set traps Whether it is a cross-domain or same-domain website (looking for an occasion); then forges a request to set a trap (waiting for prey) in a relatively hidden occasion, and finally waits for the user to click a link or visit a certain webpage to cause the attack to take effect (successful capture); regardless of
the Internet Whether the user actively clicks on a malicious link or visits a webpage unintentionally, it is possible to enter the CSRF trap carefully designed by the attacker
[0007] CSRF attacks are highly concealed, destructive, and easily overlooked. How to effectively identify and locate CSRF attack points becomes very important. If these points that can be attacked can be quickly found,
software architects can prevent them from the design.
Software development engineers can also carry out targeted protection, and
software test engineers can also perform targeted CSRF attack
verification tests, thereby eliminating potential CSRF threats and providing a relatively safe Internet environment for network users. Unfortunately, currently There is no specific and accurate tool for scanning CSRF attack vulnerabilities on the market. At the same time, since CSRF attacks are mostly artificially designed traps, the identification and positioning of CSRF are very weak through the current tools for scanning or penetration attacks based on
pattern matching. , taking static scanning tools such as Coverity and JTest as examples, these tools can easily scan out XSS attacks, but they are basically powerless against CSRF attacks, while security dynamic penetration tools such as AppScan, ZAP, etc., can easily penetrate
SQL Injection or XSS attacks, but only a small amount of CSRF attacks can be scanned, and the scanned results need to be manually analyzed to see if the scanned results are correct, and a large number of CSRF vulnerabilities cannot be accurately identified. So far, there is no one on the market. The tool can accurately identify and locate CSRF attacks
[0008] Due to the great
impact of CSRF attacks, the research on the defense of CSRF attacks mainly includes the following aspects; early developers believe that the reason why CSRF attacks can be successful is that the attacker simulates an
executable URL, and the parameters in this URL They are all displayed in the
address bar of the browser, which is very convenient for attackers to
forge the same URL to attack, but developers soon found that this protection only slightly increases the threshold for attackers, in fact, as long as there is a little
HTML web programming foundation It is very easy for people to change Get to Post to send out, so this kind of protection can not really protect against CSRF attacks, but only increases the threshold of attacks; in addition, HTTP Referer header protection is proposed, and early developers think that CSRF can happen , mainly due to cross-domain forged URL requests, which lead to successful CSRF attacks, so programmers think that checking the HTTP Referer header will be a very effective way to avoid CSRF attacks. As long as the linked domain is inconsistent with the original domain of the website, it will not be allowed Its access, so that it can prevent CSRF attacks. This method can indeed have a certain protective effect, but the current browser Referer header can be tampered with, and the Referer header in the pop-up window is often empty, which leads to the Referer header. There are flaws in the solution. At the same time, the Referer header can only prevent cross-domain attacks, and it can’t do anything to CSRF attacks in the same domain. Another solution is to install a plug-in in the browser. This plug-in is used to limit which sites can jump and which The site cannot be redirected. Many security engineers and programmers think this is a good method. You don’t need to change the code of each application. As long as the browser adds a plug-in to do this, all problems can be solved, but this The problem is that not all users know that this plug-in needs to be installed in the browser to access
the Internet. In addition, even if the plug-in is installed, ordinary users do not know how to set it up, because browser plug-in protection can only prevent cross-domain CSRF attacks. Attacks in the same domain cannot be protected. At the same time, the
client plug-in is easily disabled by other programs. Once the plug-in is disabled, this protection is useless; it is also proposed that each key operation requires user confirmation, or secondary
authentication (possibly Graphical
verification code, SMS
verification code,
payment password, etc.), for example, you may need to log in again when you need to check out. At present, Amazon adopts this method. For example, you need to enter the
payment password when you finally check out. Currently, Alipay adopts this method, such as when paying online banking. , the system will send a
text message to the user to confirm the
payment behavior, such as key operations, requiring the user to enter a graphic verification code or select a suitable graphic (12306
ticket purchase), etc. If the user does not confirm further, the corresponding operation cannot be performed. This can prevent users from performing some key operations in the case of ignorance. These designs can indeed remind users and prevent some Unnecessary losses, but at the same time bring inconvenience to user operations; there is also a proposal to use CSRFToken for protection, because CSRFToken is always changing, and the attacker cannot predict it, so it can ensure that each key link cannot be constructed by the attacker. CSRF attacks can be protected. This solution is currently the most widely used by major
software companies in CSRF protection. It is considered to be the safest solution without changing user behavior or increasing the burden of frequent
user authentication. However, based on CSRFToken protection needs to first consider how to generate CSRFToken. At the same time, it is necessary to consider when CSRFToken is generated and when to verify CSRFToken. The existing technology basically brings and verifies CSRFToken in every step, which requires an additional
database for effective support. , used to save and verify CSRFToken, which will greatly increase additional overhead and increase the input cost of the enterprise
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More