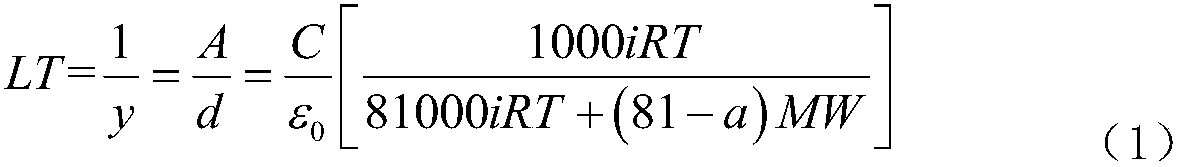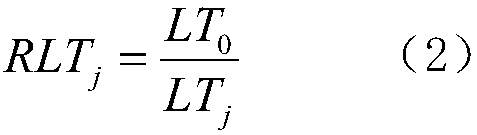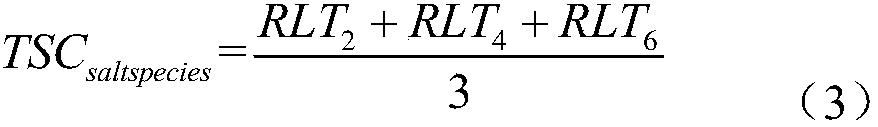Method for fast and quantificationally detecting plant salt resistant capability
A quantitative detection, plant technology, applied in the direction of testing plants/trees, measuring devices, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of long time, complex measurement process, no preventive effect, etc., to achieve the effect of less plant damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Take building a tree as an example. The healthy leaves with relatively consistent growth were picked on the campus of Jiangsu University for determination, and the salt resistance ability of the mulberry tree was quickly and quantitatively detected.
[0031] Step 1, select the fresh branch of the plant to be tested with leaves, and wrap the base of the branch with wet cotton to slow down the water emission;
[0032] Step 2, quickly return to the laboratory, after cleaning the dust on the surface of the leaves, pick the leaves with relatively consistent growth on the fresh branches, put them in a basin filled with water and soak for 1 hour;
[0033] Step 3, prepare reference salt solution (the NaCl of 0.1Mol / L) and other salt solutions to be tested (comprising the NaCl of 0.1Mol / L) 2 SO 4 and mixed salt solution); the NaCl of 0.1Mol / L, the Na of 0.1Mol / L 2 SO 4 Mixing is a mixed salt solution;
[0034] Step 4: After the leaves are soaked for 1 hour, ta...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Taking mulberry as an example, calculate its salt tolerance, and all steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0050] The plant physiological capacitance C of each leaf of the mulberry tree was measured with a capacitance sensor at different times, and then the corresponding leaf tissue water potential W was measured with a water potential meter, as shown in Table 1; the leaf tension of the mulberry tree at different times after the saturated leaves were soaked in salt water 2; the relative salt tolerance of mulberry to be tested in salt solution is shown in table 10.
[0051] Table 1 Physiological capacitance and tissue water potential of mulberry leaves and mulberry leaves soaked in NaCl saline solution at different times
[0052]
[0053] Table 2 Leaf tension of mulberry and mulberry leaves soaked in NaCl salt solution at different times
[0054] time
mulberry tree
mulberry
0
46.483
43.817
2
178.905
71.648
4
290.64
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com