Method for measuring residual stress on surface of milling part based on strain change and inverse inference method
A technology of residual stress and milling, which is applied to force/torque/work measuring instruments, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inconsistent stress values and inconsistent rigidity of parts, and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] The technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
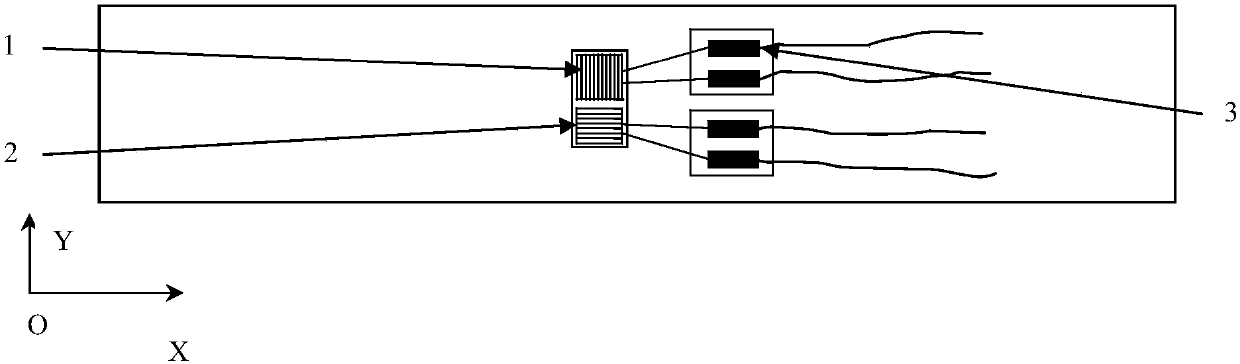
[0056] Firstly, a two-way strain gauge is pasted on the back of the machined surface of the part to measure the change of the strain in the X and Y directions on the back when the residual stress layer is corroded and peeled off.
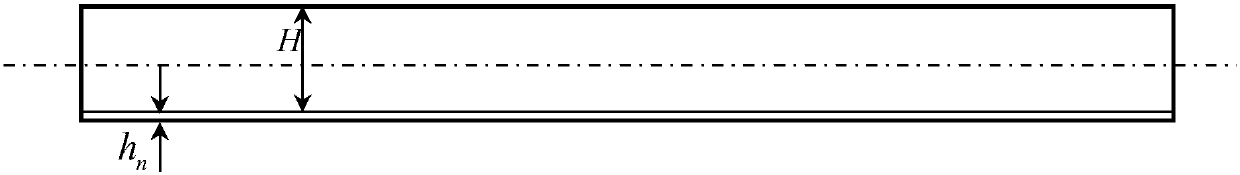
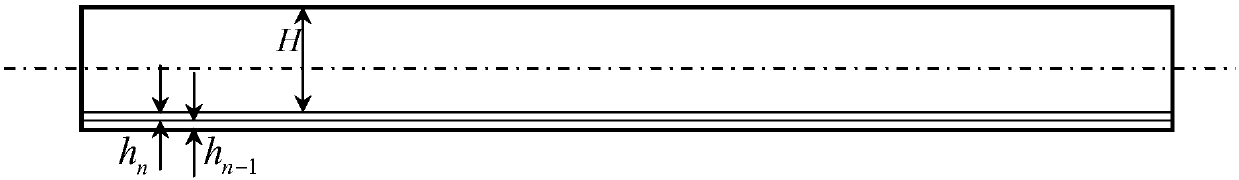
[0057]The calculation of the bending moment caused by the residual stress is mainly based on the magnitude of the stress in the stress layer and the distance between the stress layer and the neutral layer. The neutral layer is always located in the geometric middle of the part, which is removed for each corrosion After a layer of material, the position of the neutral layer of the part will change accordingly. Therefore, after each layer of material is removed, the stress of the remaining part changes due to its distance from the neutral layer, so the bending moment caused by it will also change. Corresponding chan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com