Methods for assessing the phytotoxicity of antibiotics
A technology of phytotoxicity and antibiotics, applied in the direction of testing plants/trees, testing pharmaceutical preparations, instruments, etc., to achieve the effects of easy seed attachment, simple operation, and easy preservation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
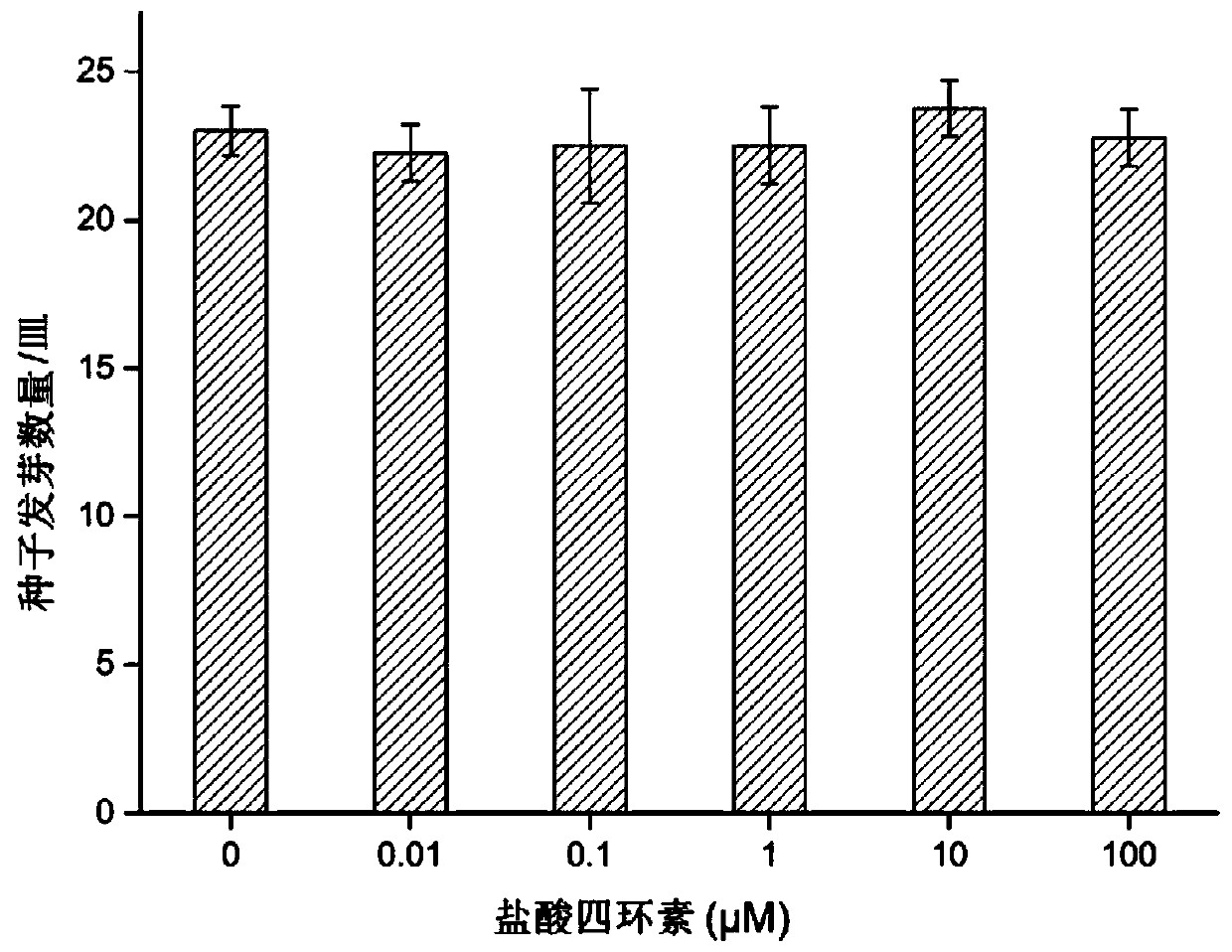
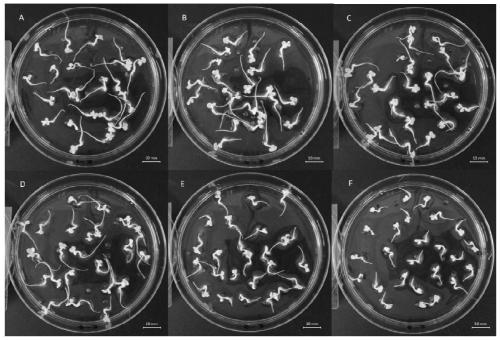
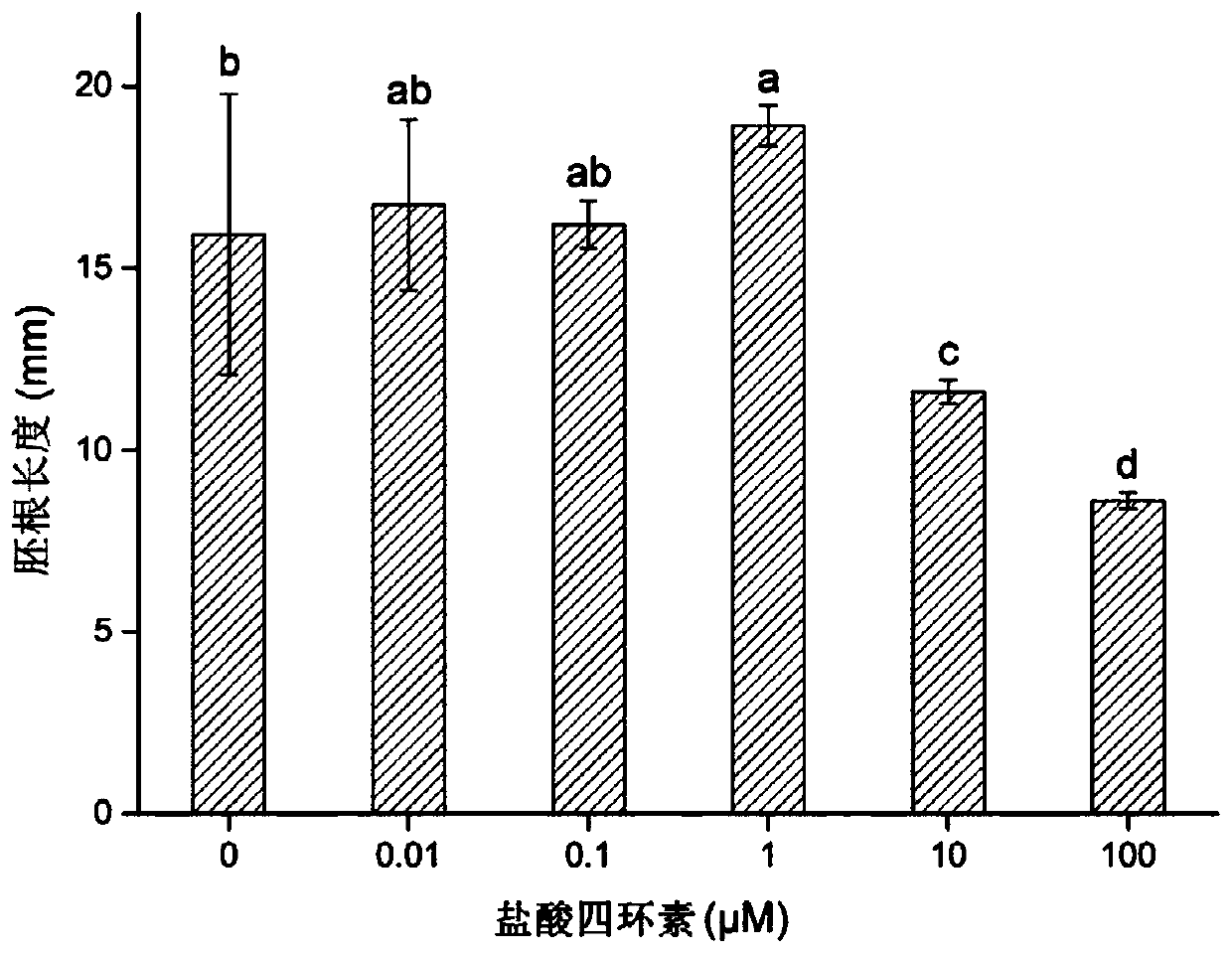
[0042] A method for evaluating antibiotic phytotoxicity, wherein the antibiotic is tetracycline hydrochloride, and the vegetable seeds are Chinese cabbage seeds of Brassicaceae Brassica, comprising the following steps:
[0043] (1) Prepare a semi-solid medium containing tetracycline hydrochloride:
[0044] (1.1) prepare salt solution, wherein the concentration of NaCl is 50mM, NH 4 The Cl concentration was 0.4 mM and the pH was adjusted to 4.7 with 0.01 M HCl.
[0045] (1.2) Agar is mixed with the salt solution obtained in step (1.1), and heated to dissolve the agar to obtain a salt solution containing agar, wherein the mass-volume ratio of the agar is 1.6% (w / v).
[0046] (1.3) Take the agar-containing salt solution obtained in step (1.2), and when the temperature drops to 50° C., divide it into 6 equal parts, and mix them with equal volumes of 0 μM, 0.02 μM, 0.2 μM, 2 μM, 20 μM and The 200 μM tetracycline hydrochloride solution was mixed evenly to obtain mixed solutions wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com