Copolymer and lubricating oil composition
A technology of lubricating oil composition and copolymer, applied in lubricating composition, petroleum industry, base material, etc., can solve the problems of limited use range, low viscosity, difficult application, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
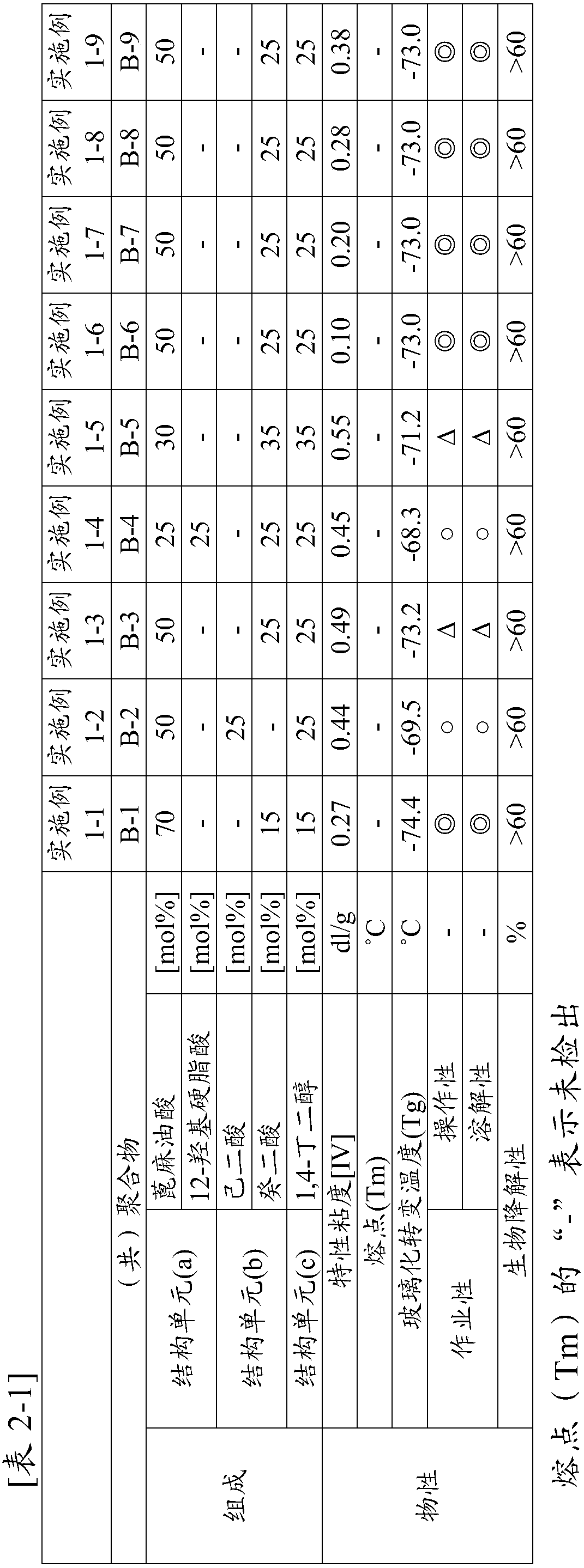
Embodiment 1-1
[0204] [Example 1-1] (manufacture of copolymer B-1)
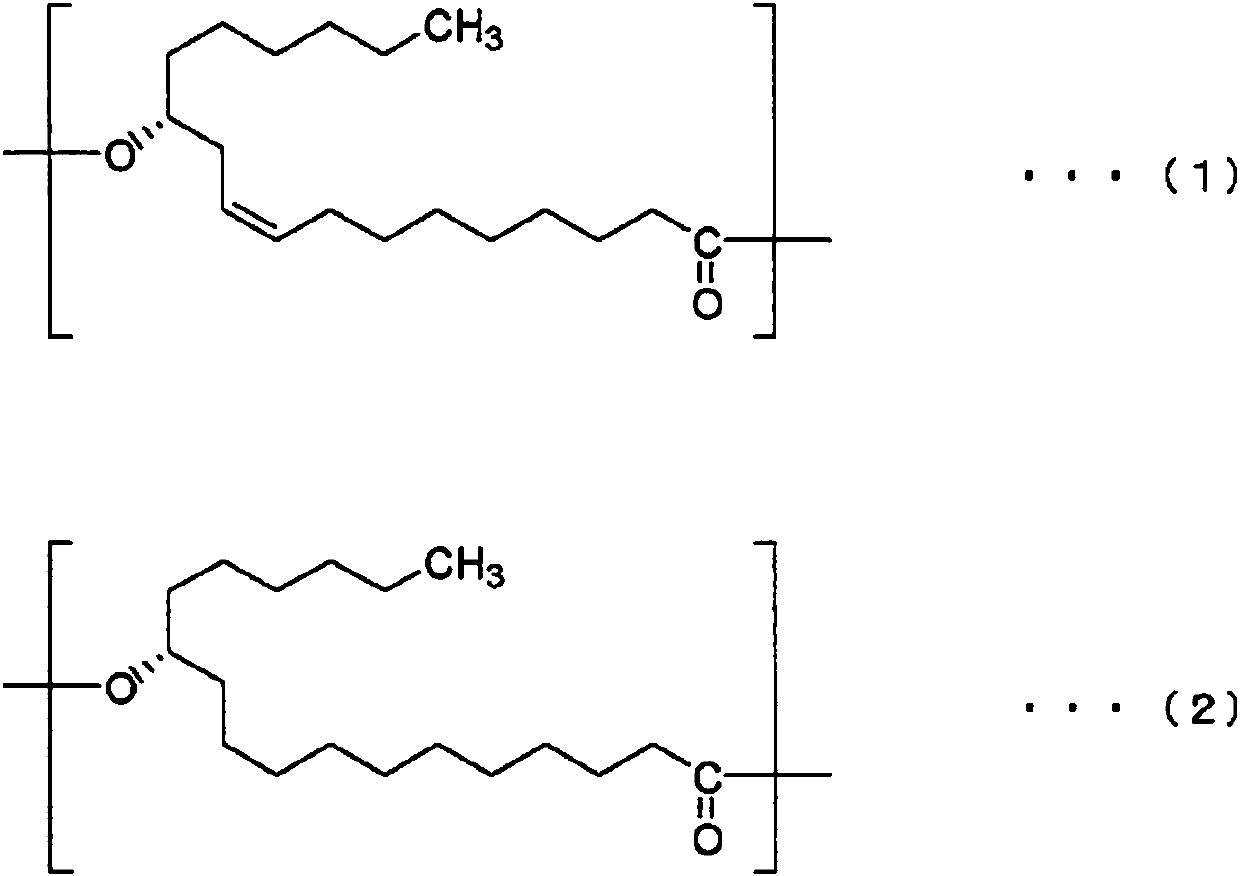
[0205] 40.0 parts by mass of ricinoleic acid, 5.8 parts by mass of sebacic acid, and 5.2 parts by mass of 1,4-butanediol were heated from normal temperature to 210° C. over 30 minutes. After reaching 210° C., 0.20 parts by mass of titanium tetrabutoxide and 0.03 parts by mass of a 20 wt % aqueous solution of ethylammonium hydroxide were added, and the mixture was kept at 210° C. for 5 hours to conduct an esterification reaction.
[0206] After completion of the esterification reaction, 1.36 parts by mass of titanium tetrabutoxide was added as a polymerization catalyst, and the pressure was reduced to 0.133 kPa (1 Torr) while raising the temperature to 230° C. over 60 minutes to perform a polycondensation reaction. This polycondensation reaction was performed while stirring the reaction mixture. Here, as the polycondensation reaction proceeds, the stirring torque required for stirring the reaction mixture gradually increase...
Embodiment 1-2
[0207] [Example 1-2] (manufacture of copolymer B-2)
[0208] 40.0 parts by mass of ricinoleic acid, 10.2 parts by mass of adipic acid, and 9.7 parts by mass of 1,4-butanediol were heated from normal temperature to 210° C. over 30 minutes. Thereafter, polyester was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1-1.
Embodiment 1-3
[0209] [Example 1-3] (manufacture of copolymer B-3)
[0210] 40.0 parts by mass of ricinoleic acid, 13.6 parts by mass of sebacic acid, and 9.7 parts by mass of 1,4-butanediol were heated from normal temperature to 210° C. over 30 minutes. Thereafter, polyester was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1-1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pour point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com