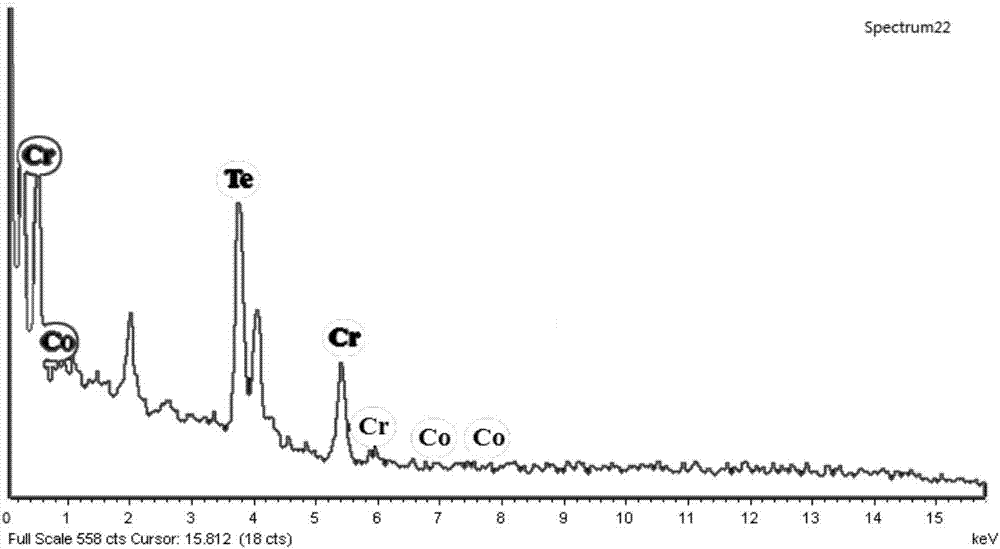
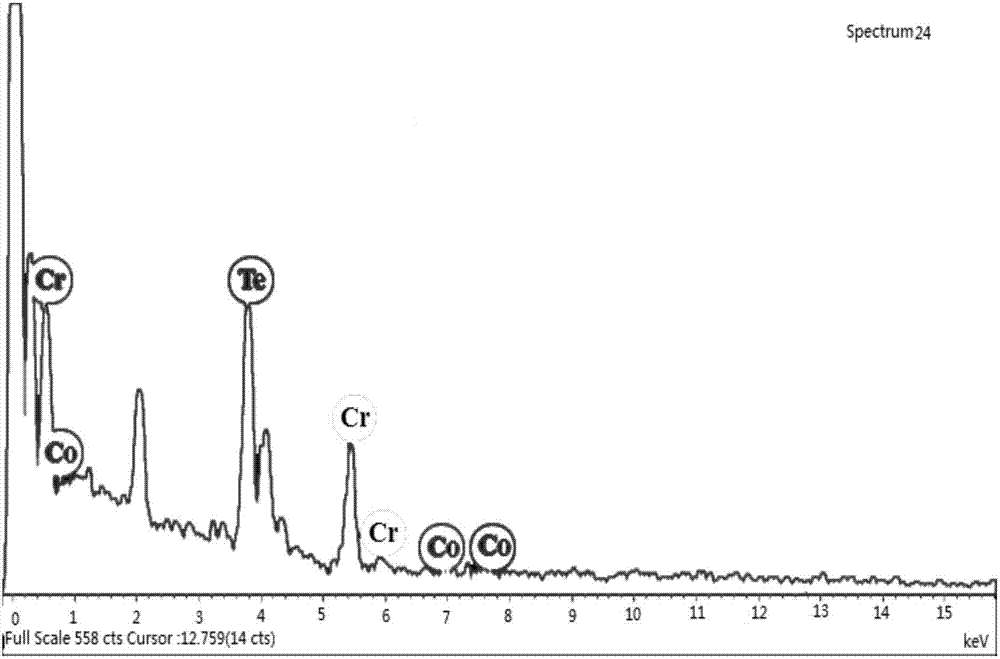
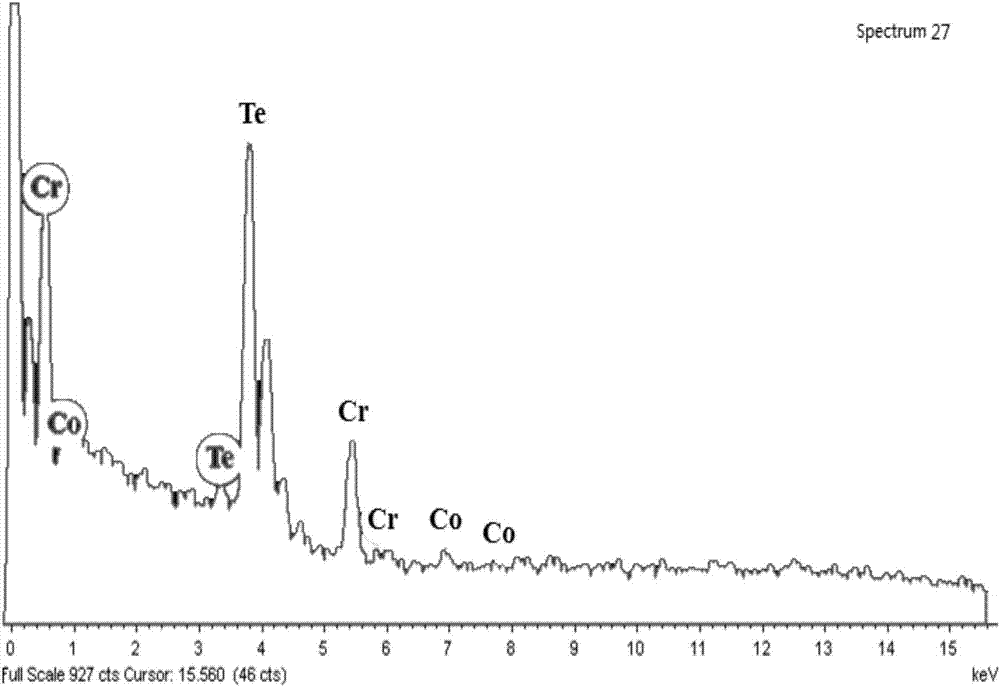
Cr-based chalcogenide hard magnetic nanomaterial
A technology of chalcogen compounds and nanomaterials, applied in the direction of magnetic properties of inorganic materials, can solve the problem of low coercive force and achieve high coercive force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment provides a Cr-based chalcogen compound hard magnetic nanomaterial, which is obtained through the following preparation steps:
[0029] (1) 1.9mmol of Cr(CO) 6 , 0.1mmol of Co(acac) 2 and 30mL oleylamine were added to a four-necked flask equipped with a temperature regulator and a magnetic stirrer to obtain a solution containing Cr and Co. 2 Warm up to 120°C under protection and keep warm for 30min;
[0030] (2) Dissolving 3.0 mmol of Te elemental powder in 5 mL of trioctyl phosphine (TOP) to obtain a suspension solution containing Te;
[0031] (3) Inject the suspension solution containing Te into the solution containing Cr and Co, raise the temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min under the protection of nitrogen, and keep the reaction for 1h to obtain Cr 1.9 co 0.1 Te 3 Hard Magnetic Nanomaterials.
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a hard magnetic nanomaterial with a Cr-based chalcogen compound, which is obtained through the following preparation steps:
[0034] (1) 1.8mmol of Cr(CO) 6 , 0.2mmol of Co(acac) 2 Add oleylamine and 30mL into a four-necked flask equipped with a temperature regulator and a magnetic stirrer, stir for 20min to obtain a liquid containing Cr and Co, raise the temperature to 110°C under the protection of argon, and keep it warm for 20min;
[0035] (2) Dissolving 3.3 mmol of Te elemental powder in 5 mL of trioctyl phosphine (TOP) to obtain a suspension solution containing Te;
[0036] (3) Inject the suspension solution containing Te into the solution containing Cr and Co, raise the temperature to 380°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min under the protection of argon, and keep the reaction for 2h to obtain Cr 1.8 co 0.2 Te 3 Hard Magnetic Nanomaterials.
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment provides a Cr-based chalcogen compound hard magnetic nanomaterial, which is obtained through the following preparation steps:
[0039] (1) 1.6mmol of Cr(CO) 6 , 0.4mmol of Co(acac) 2 and 30mL oleylamine were added into a four-necked flask equipped with a temperature regulator and a magnetic stirrer, and stirred for 30min to obtain a solution containing Cr and Co. 2 Under protection, the temperature was raised to 100°C and kept for 20 minutes;
[0040] (2) Dissolve 3.6 mmol of Te elemental powder in 5 mL of trioctyl phosphine (TOP), and sonicate for 20 min to obtain a suspension solution containing Te;
[0041] (3) Inject the suspension solution containing Te into the solution containing Cr and Co. Under the protection of nitrogen, the temperature is raised to 100°C and then the temperature is raised to 400°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min, and the temperature is kept for 3 hours to obtain Cr 1.6 co 0.4 Te 3 Hard Magnetic Nanomaterials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com