A Low-Voltage Driven Inverse Zoom Microlens
A micro-lens and low-voltage technology, applied in the field of micro-lens, can solve the problems of reducing device compactness, limited focal length adjustment range, electrode cracking, etc., and achieves high-efficiency manufacturing and uniformity, simple structure, and good integration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
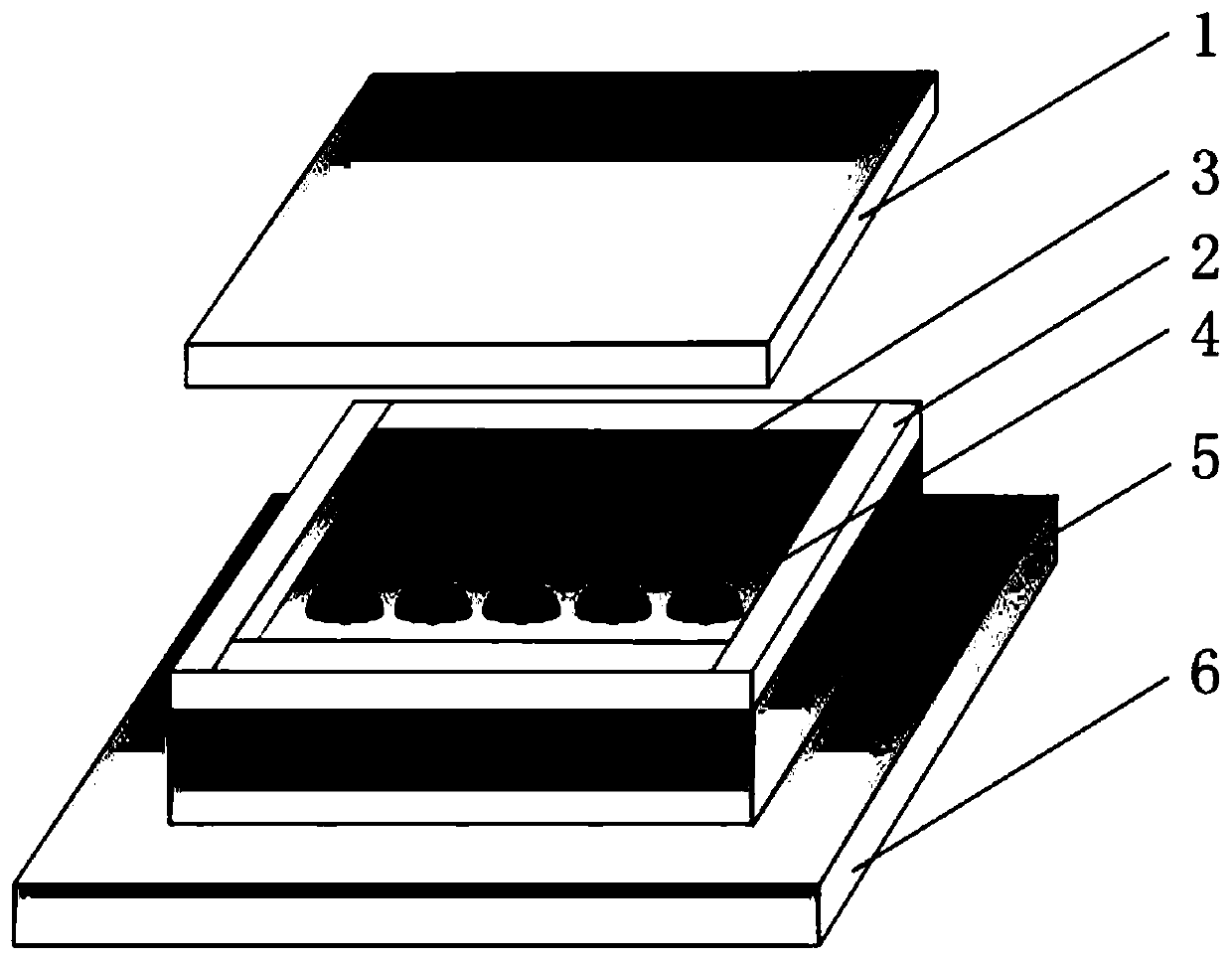
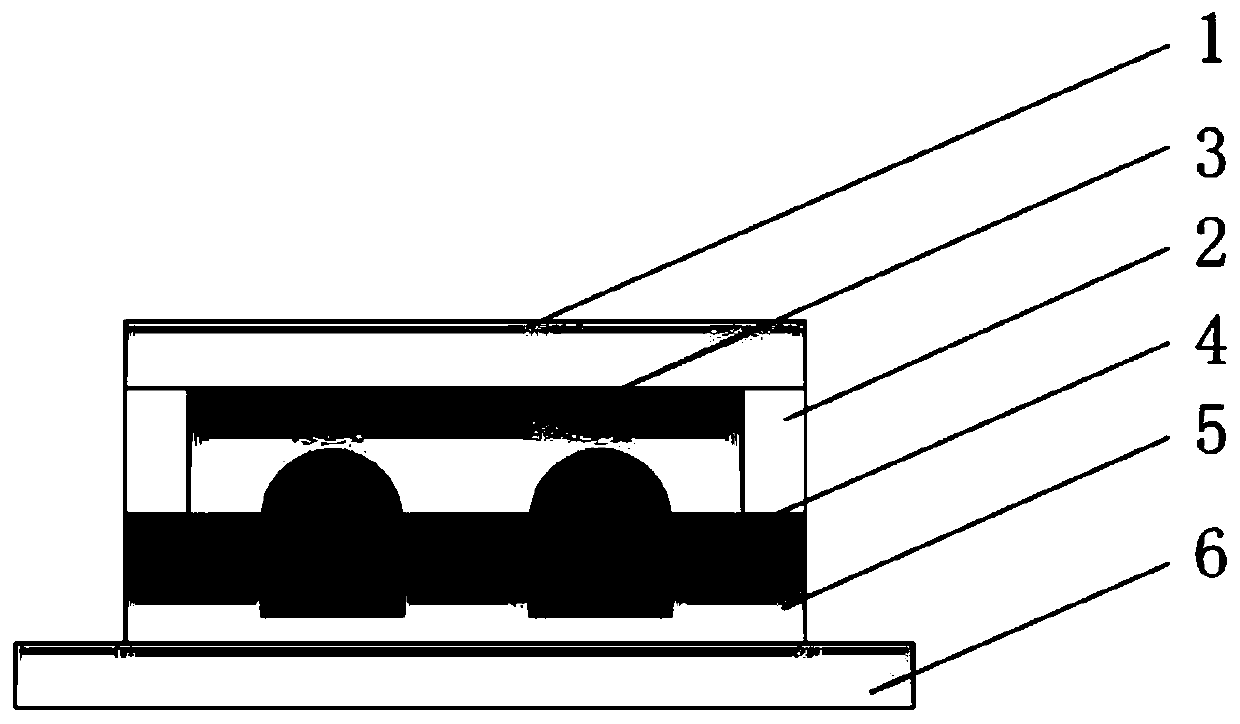
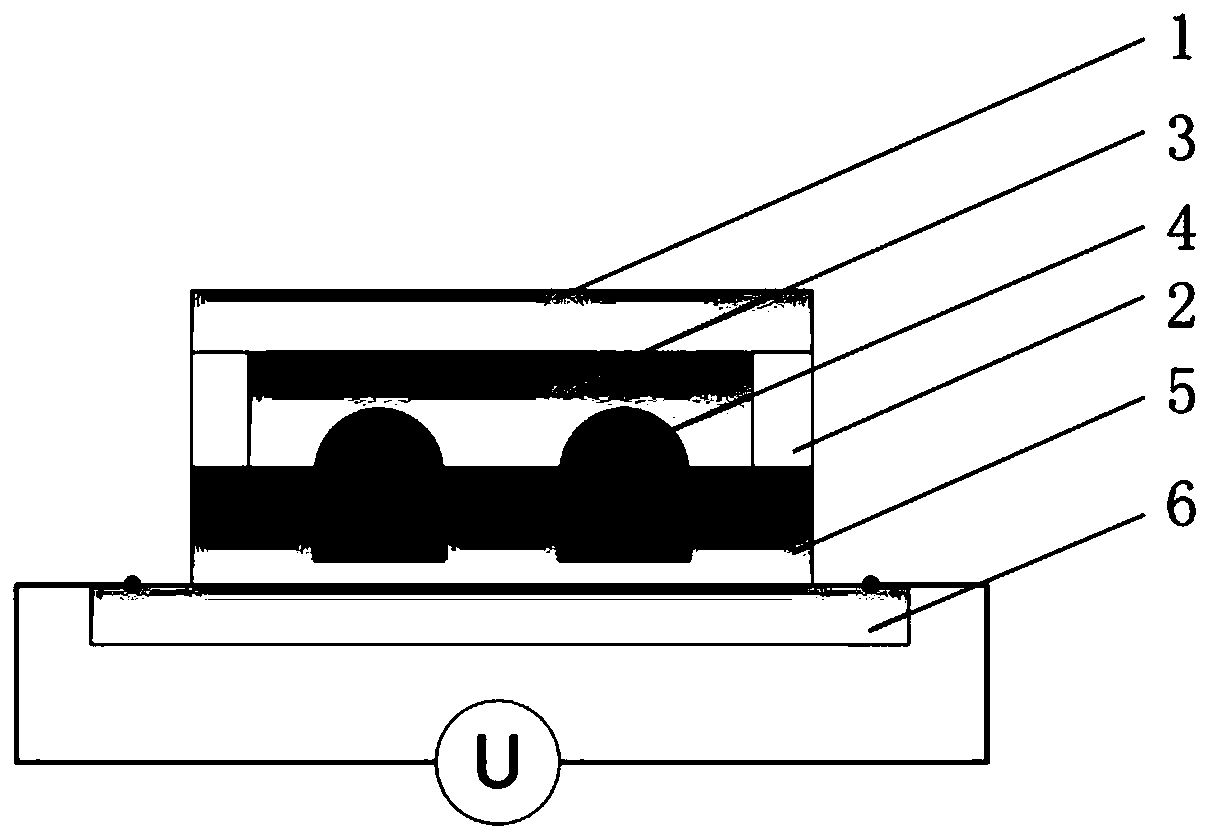
[0025] refer to Picture 1-1 and Figure 1-2 , a low-voltage-driven reverse zoom microlens, including a bottom layer 6, the bottom layer 6 is a transparent conductive layer, as an electrode; The porous structure 5 is used as the middle layer; the first transparent solid plate 2 is connected around the porous structure 5, and the first transparent liquid 3 is housed on the top of the porous structure 5 and the first transparent solid plate 2, the first transparent solid plate 2 and the transparent The upper part of the liquid 3 is encapsulated by the second transparent solid plate 1, and the first transparent solid plate 2, the first transparent liquid 3, and the second transparent solid plate 1 constitute the top layer, which is an encapsulation protection layer.
[0026] The porous structure 5 is a periodic transparent micropore array.
[0027] The material of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com