Adaptive Correction Method for MRI Diffusion Weighted Imaging
A diffusion-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted image technology, applied in application, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of complex hardware detection device or algorithm, limited degree of artifact suppression, ADC value error, etc., so as to suppress motion artifacts. shadows, improved image quality, excellent image quality effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
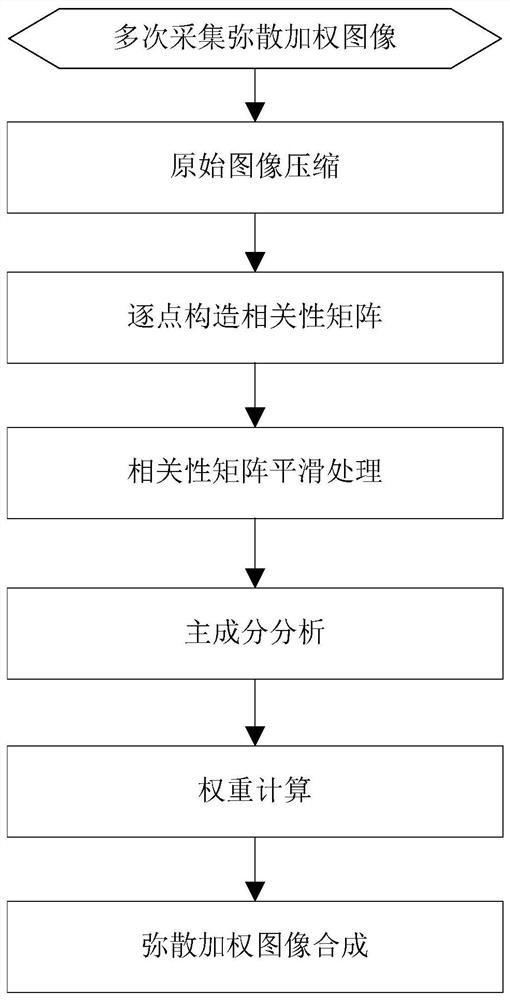
[0050] The MRI diffusion weighted imaging adaptive correction method disclosed in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0051] Step 1, with the same scanning parameters, repeat acquisition of diffusion weighted images N times, N is a natural number, N≥3;
[0052] Step 2, constructing a correlation matrix point by point based on the original image or the compressed image: specifically includes the following steps;
[0053] Step 2.1, for any pixel point (x, y) in the image collected for the nth time, take K surrounding adjacent points to form a neighborhood vector Xn;
[0054] Step 2.2, for the images collected repeatedly for N times, each pixel corresponds to N neighborhood vectors, and the correlation between the nth vector Xn and the mth vector Xm is calculated according to formula (1);
[0055]
[0056] In formula (1), x i is the i-th element in the vector Xn, y i is the i-th element in the vector Xm, is the mean value of the vector Xn, is the mean of the...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that before step 2, all collected original images are compressed using an interpolation algorithm. The advantages are that first, it can reduce the amount of calculation, and second, it can increase the signal-to-noise ratio of the input data of subsequent algorithms.
Embodiment 3
[0072] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 or 2 is: as figure 1 As shown, the correlation matrix is smoothed and filtered before step 3. Wherein, the smoothing filtering process includes the following steps;
[0073] Step a, from the correlation matrix R(x, y) corresponding to each pixel point (x, y), take the i-th correlation coefficient to form a matrix Ri with the same size as the image matrix;
[0074] Step b, performing two-dimensional low-pass filtering on the matrix Ri;
[0075] Step c, replace the corresponding element in R(x,y) with the filtered result;
[0076] Step d, repeat a-c until all elements in R(x,y) are processed.
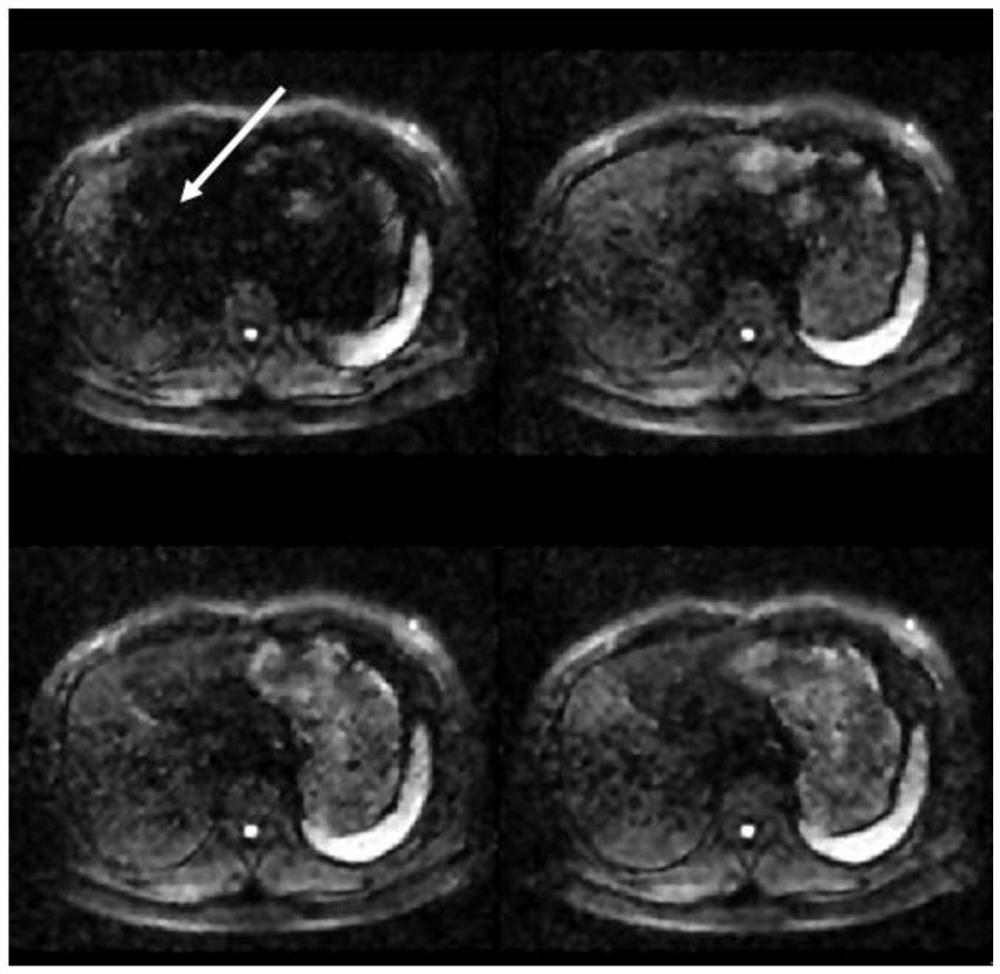
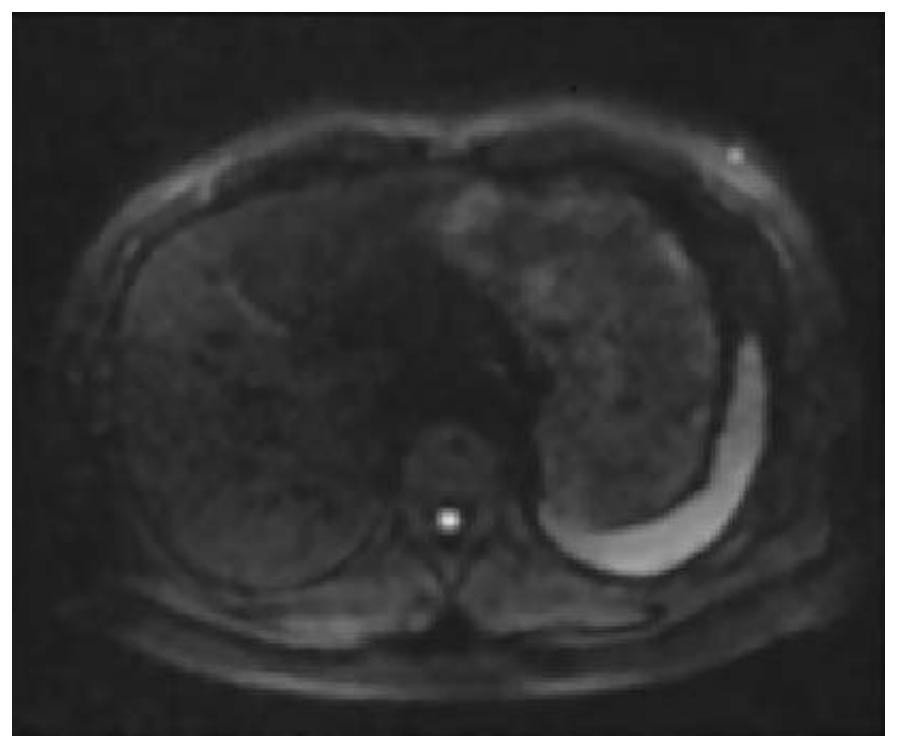
[0077] Such as figure 2 As shown, as indicated by the arrow, obvious motion artifacts can be seen in the first image, resulting in complete loss of part of the signal. Such as image 3 As shown, the diffusion-weighted image synthesized by direct averaging has a limited degree of artifact suppression and poor image qua...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com