Ultra-thin OLED screen body and manufacturing process thereof
A production process and ultra-thin technology, applied in the field of ultra-thin OLED screens and their production processes, can solve problems such as poor reliability of the screen, glue overflow, and difficulty in cutting the screen, so as to improve product yield and improve product quality. Efficient, easy-to-achieve effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
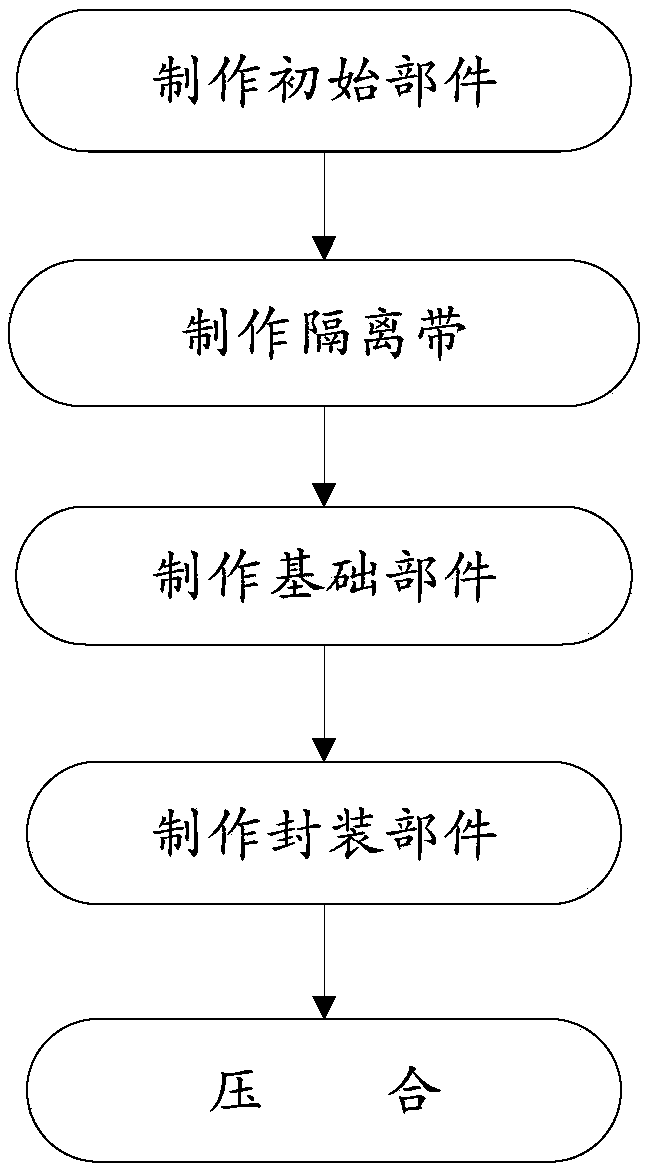
[0034] Please refer to figure 1 A disclosed manufacturing process of an ultra-thin OLED screen comprises the following steps:
[0035] Making the initial component: forming the first electrode on the substrate;
[0036] Making isolation strips: forming two parallel isolation strips on the substrate and the two isolation strips are distributed along the circumference of the substrate;
[0037] Making the basic components: forming a light-emitting layer on the first electrode, and forming a second electrode on the light-emitting layer;
[0038] Making packaging components: making a dispensing pattern along the circumference of the packaging cover plate and the dispensing pattern corresponds to the isolation belt pattern;
[0039] Pressing: Pressing the base part and the package part, so that the dispensing pattern on the package cover can be between the two isolation strips.
[0040] In the above manufacturing process steps, making initial components is a basic step.
[0041...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in the step of making the initial component, it also includes forming a metal auxiliary electrode on the first electrode through a photolithography process, and forming an insulating layer such as Figure 5As shown, the isolation zone and the insulating layer are prepared on the same layer.
[0052] In any preferred embodiment, the isolation zone and the insulating layer have the same material and are prepared on the same layer by a photolithography process.
[0053] In this embodiment, the metal auxiliary electrode is formed on the first electrode, and is patterned by a photolithography process, and then spin-coats PI photoresist on the entire surface of the substrate, and exposes and develops according to a predetermined pattern to obtain an insulating layer Graphics and Barrier Graphics.
[0054] In this embodiment, the metal auxiliary electrode is selected from but not limited to Mo / Al / Mo, Cr / Al / Cr, and the insulating layer ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The difference from Embodiment 2 is that in the step of making the initial component, it also includes forming a metal auxiliary electrode on the first electrode through a photolithography process, forming an insulating layer on the metal auxiliary electrode through a photolithography process, and forming an isolation layer on the insulating layer. Zhuru Image 6 As shown, the isolation zone is prepared in the same layer as the isolation column.
[0060] The isolation column is prepared on the insulating layer and has an inverted trapezoidal structure, and the material of the isolation column is selected from but not limited to PI photoresist.
[0061] In this embodiment, the isolation strip and the isolation column are prepared on the same layer, and both are inverted trapezoidal structures, and both have the same shape, which greatly saves the process.
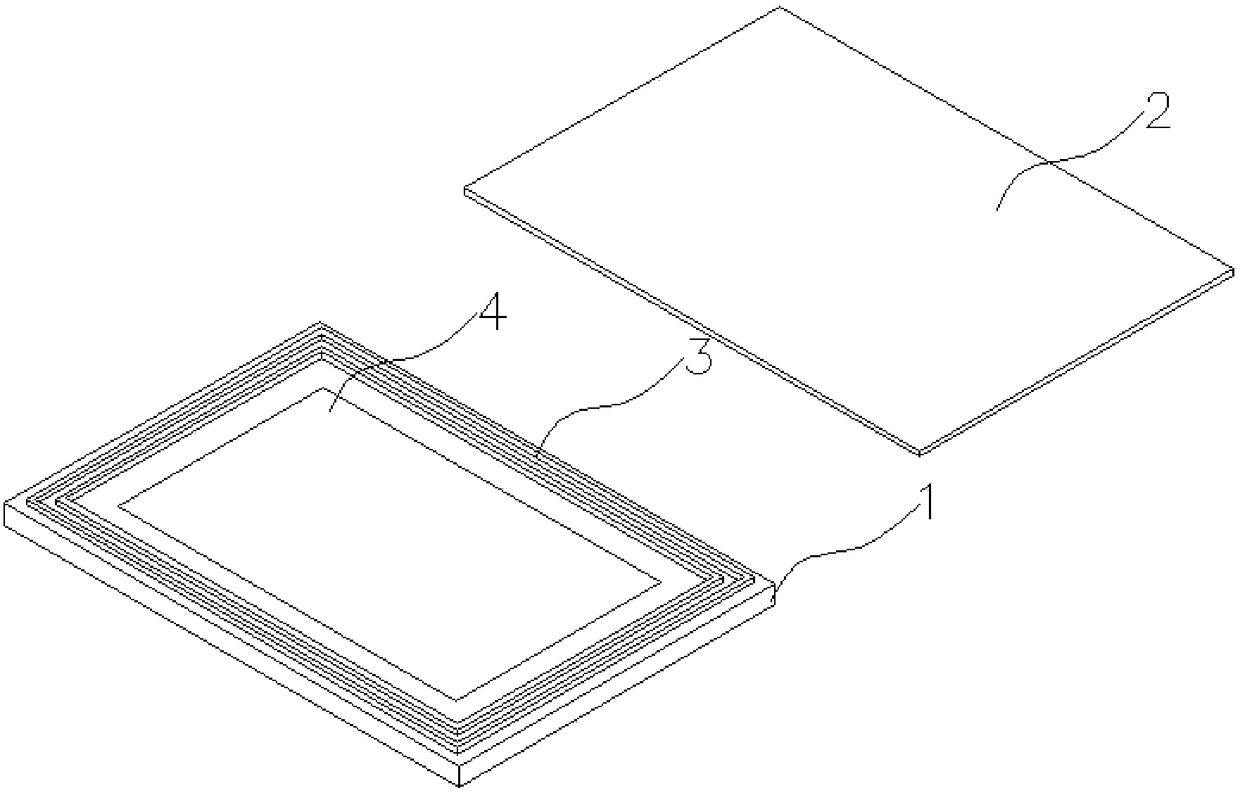
[0062] The structure of an ultra-thin OLED panel obtained according to Embodiment 1, 2 or 3 is as follows.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com