Variable-stiffness double-arm automatic tensioner
A technology of variable stiffness and tensioner, applied in the field of transmission system, can solve the problems that the belt tension cannot ensure the design value, the tensioner is difficult to ensure the working position, and the installation of the single-arm tensioner is difficult, so as to avoid noise, large noise, etc. Installation space, the effect of prolonging the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
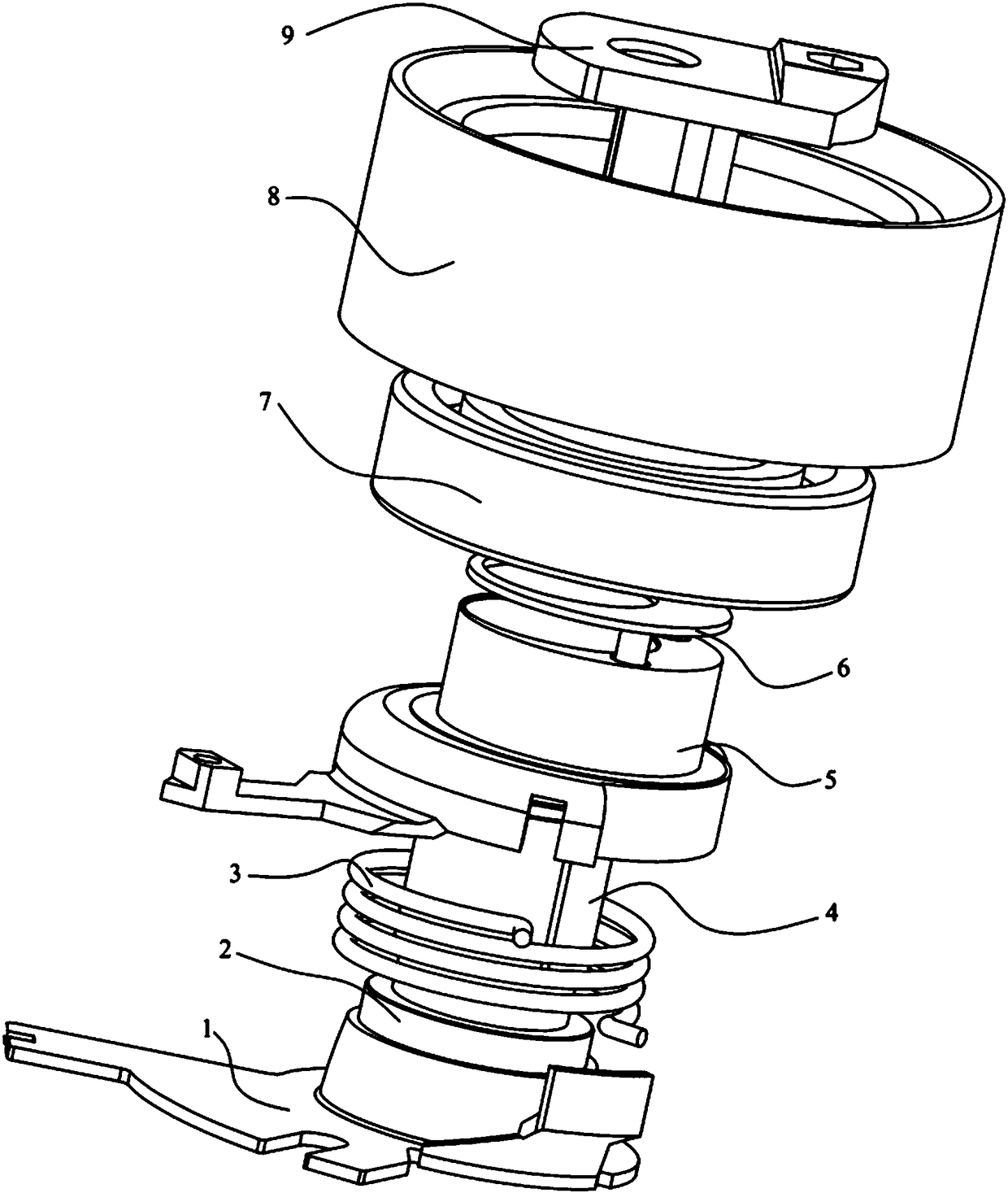
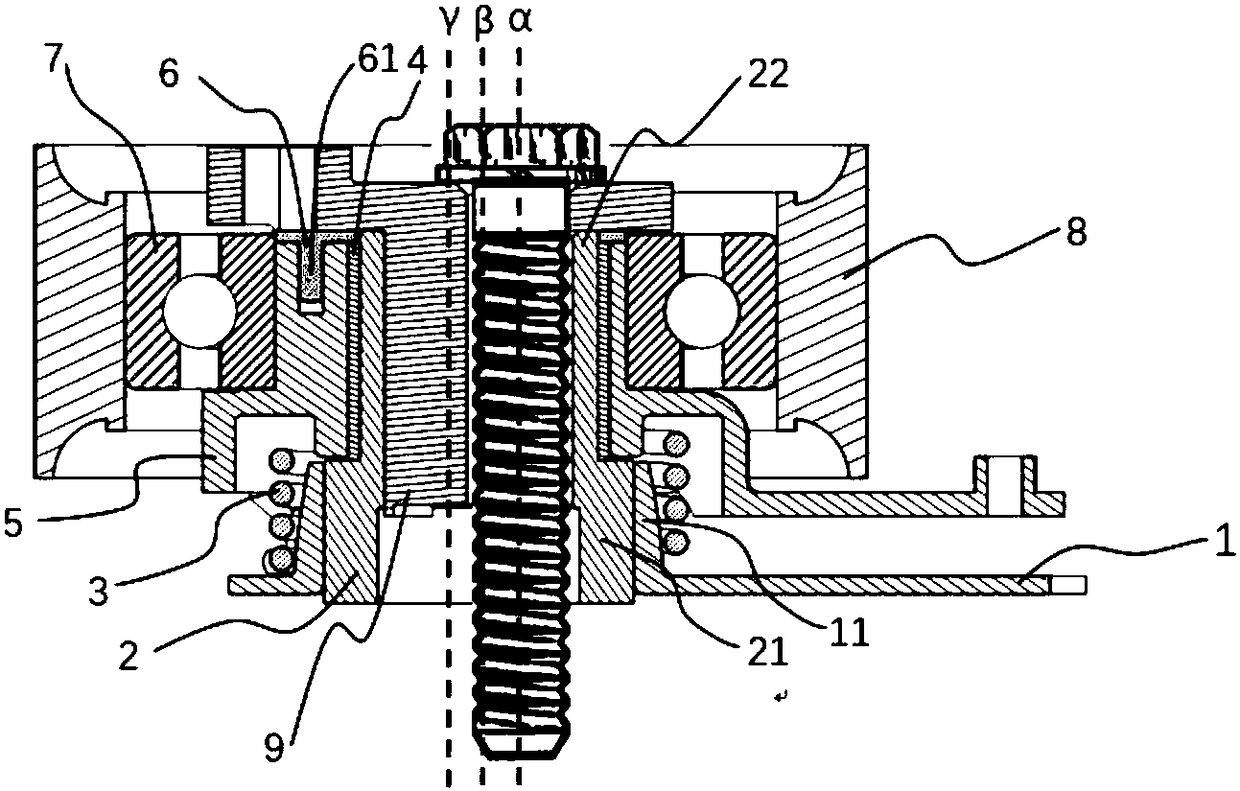
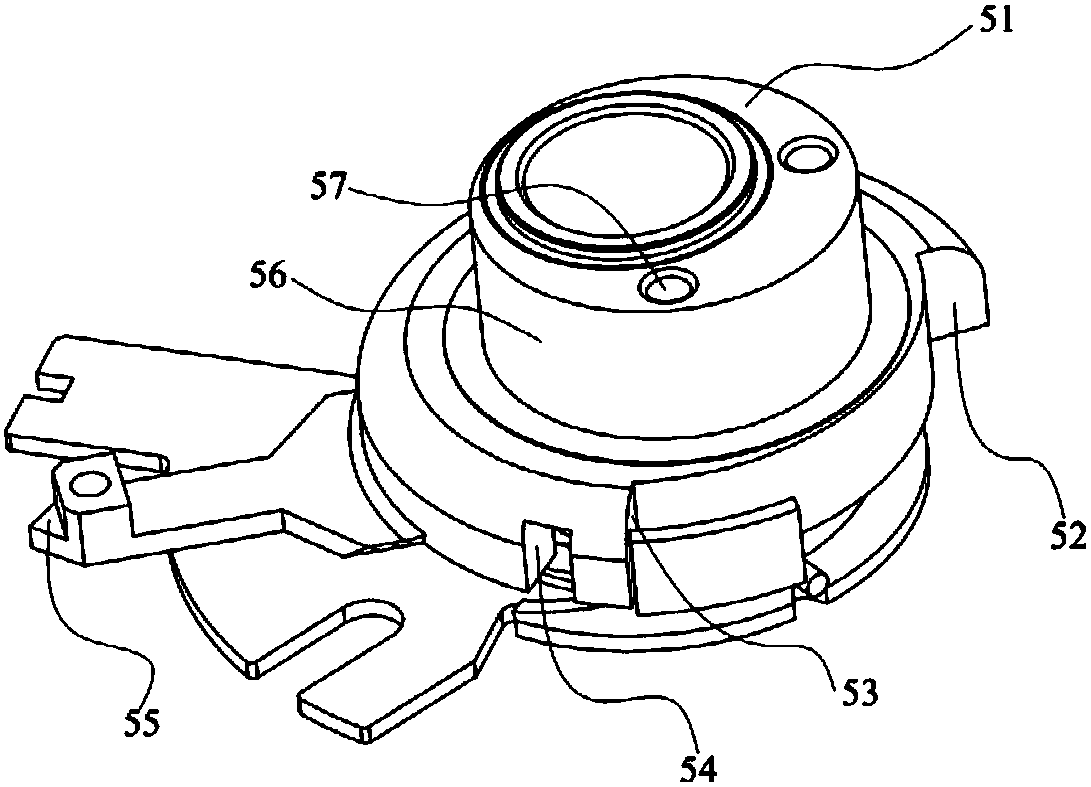
[0035] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4A double-arm automatic tensioner with variable stiffness is shown, including an adjusting arm 9, a working arm 5, a pivot shaft 2, a bushing 4, a bottom plate 1, a torsion spring 3, a rolling bearing 7 and a pulley 8, and the adjusting arm 9 is passed through A bolt is mounted on the engine body, the pivot shaft 2 is pivotally mounted on the adjusting arm 9, the working arm 5 is pivotally mounted on one end of the pivot shaft 2 through a bushing 4, and the pivot shaft The other end of 2 is connected with the base 1, and the base 1 is fixed on the engine body through a bolt, and the torsion spring 3 is torsionally set between the bottom plate 1 and the working arm 5, while the torsion spring 3. The torsion arms at both ends are respectively fixedly connected with the bottom plate 1 and the working arm 5; the pulley 8 is mounted on the working arm 5 through a rolling bearing 7, and the pivot center and the geometric center of the adjusting arm...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the cylindrical boss 11 is an equidiametric cylindrical shape with a cross-sectional diameter consistent up and down, and the torsion spring 3 is a coil spring with variable middle diameter and equal pitch. It shows that the middle diameter of the torsion spring 3 starts to decrease gradually along the direction away from the base 1, and is conical, correspondingly, as Figure 10 As shown, the spring stiffness Ke in the second embodiment is compared with the torsional spring stiffness K of the prior art 0 , when the torsion spring 3 is loaded to a certain angle, that is, the working arm 5 is twisted to a certain angle θ 0 , the spring stiffness Kt becomes larger, and the stiffness changes will vary with the speed of the change of the spring pitch diameter.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the difference between the third embodiment and the second embodiment is that the shown torsion spring 3 adopts a coil spring with variable middle diameter and variable pitch, and the middle diameter of the shown torsion spring 3 gradually becomes smaller along the direction away from the base 1, and the pitch The distance also changes synchronously. Correspondingly, as Figure 12 As shown, the spring stiffness K in this embodiment f Compared with the prior art torsion spring stiffness K 0 , when the torsion spring 3 is loaded to a certain angle, that is, the working arm 5 is twisted to a certain angle θ 0 , spring stiffness K f becomes larger; and the second embodiment is Figure 9 Compared with the structure in the middle, the spring structure with variable pitch diameter will have a different stiffness change from that of the spring with only variable pitch diameter.
[0049] The above-mentioned embodiments can realize that when the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com