Cellular Analysis Of Body Fluids
A technology of cells and body fluids, applied in the fields of individual particle analysis, material analysis, material excitation analysis, etc., which can solve difficult and less common problems in analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0108] Analyzing Low Cell Count Samples
[0109] A prototype analyzer with a 1:35 (blood:reagent) dilution ratio, 2.3 microliter / second injection rate, and 32 second sample measurement (data collection) resulted in over 20 events collecting a sample of 10 cells / microliter.
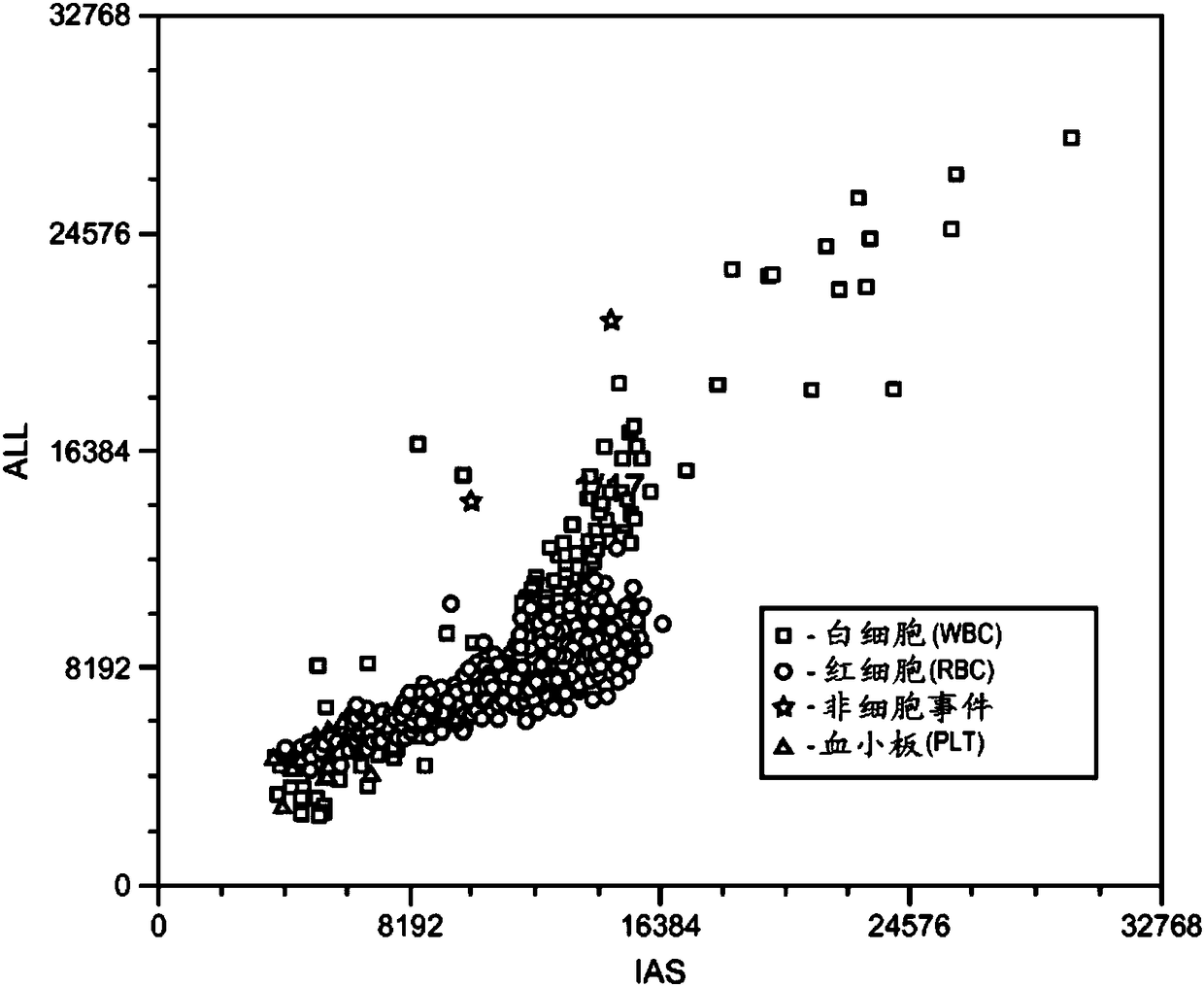
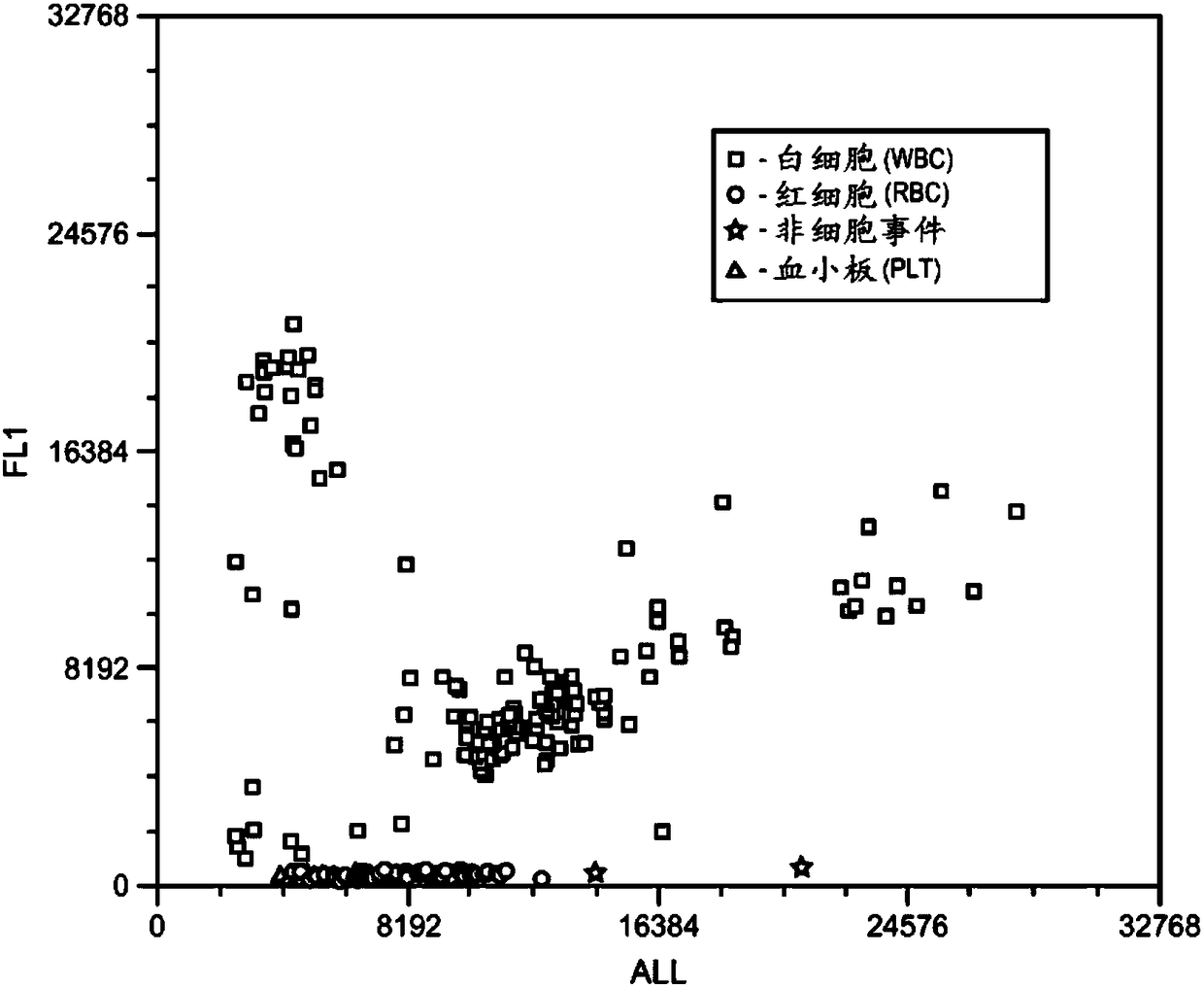
[0110] Figure 2A and 2B A scatterplot showing cellular analysis of a bodily fluid sample. Cells were spotted after analysis: WBC = 89 / μL (ref = 81 / μL); RBC = 2012 / μL (ref = 1733 / μL). Figure 3A and 3B Scatterplot showing cellular analysis of another body fluid sample. Cells were spotted after analysis: WBC = 0.95 / μL (ref = 0.33 / μL); RBC = 142 / μL (ref = 122 / μL).
Embodiment 2
[0112] Analysis of Very Low Cell Count Samples
[0113] The limit of detection was further validated in studies using diluted buffy coat samples. Serial dilutions were used to prepare six levels of diluted buffy coat samples. The FL1 versus IAS scatterplots for six horizontally diluted buffy coat samples are shown in Figures 4A-4F . Figure 5 Demonstration of correlation of WBC (measured vs calculated). A good correlation was obtained: (A) for all six levels, Y=1.0239X-4.9 (R 2 =0.9984), and (B) for the three levels with the lowest cell concentration, Y=1.0787X-1.5(R 2 = 0.9598).
Embodiment 3
[0115] Cell Analysis of Body Fluid Samples at 1:35 Dilution Ratio
[0116] A comprehensive body fluid study was performed to evaluate the methods presented herein. A total of 91 body fluid samples, including CSF fluid, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, and ascitic fluid, were measured on the prototype analyzer at a 1:35 (blood:reagent) dilution ratio, 2.3 μl / sec infusion rate, and 32-second sample measurement (data collection ) for measurement and analysis. Reference values for WBC and RBC were obtained by manual chamber counting.
[0117] An excellent correlation of WBC was obtained between the method described above and the reference method ( Figure 6 ): (A)Y=1.1305X-9.8411, R 2 = 0.997 (full range, up to approximately 40,000 / μL); (B) Y = 1.017X+7.1395, R 2 =0.9765(2 =0.9663(2 =0.8459 ( Figure 7 ): (A)Y=0.8996X+403.62, R 2 = 0.9595 (full range, up to approximately 200,000 / μL); (B) Y = 1.0833X-11.427, R 2 =0.9513(2 =0.8284(2 =0.6917 (<50 / μL). For RBC analysis, samp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com