A Trajectory-Based Sliding Verification Code Human-Machine Recognition Method
A recognition method and human-machine coding technology, which is applied in the field of trajectory-based sliding verification code human-machine recognition, can solve the problems of lagging confrontation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A trajectory-based human-machine recognition method for sliding verification codes, comprising the following steps:
[0038] S1: collect user trajectory data;
[0039] Collect user trajectory data (x, y, t), including the horizontal coordinate x and vertical coordinate y at different time points t during the trajectory triggering process. Specifically, it is to obtain the trajectory record of the user during the sliding verification code trigger process, Provide data support for the construction of the multi-dimensional feature system of the sliding verification code code.
[0040] S2: Construct a multi-dimensional feature system based on trajectory data;
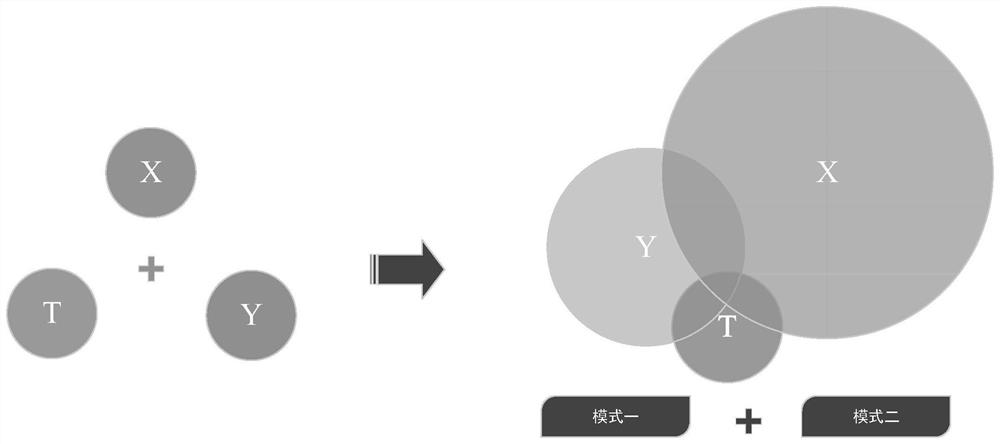
[0041] Based on the discovery of two modes, one is the end-retracement phenomenon of human trajectories; the other is the phenomenon of long-distance and short-distance human trajectories; multi-dimensional feature extraction is carried out, and then a multi-dimensional feature system is constructed to facilitate th...
Embodiment 2
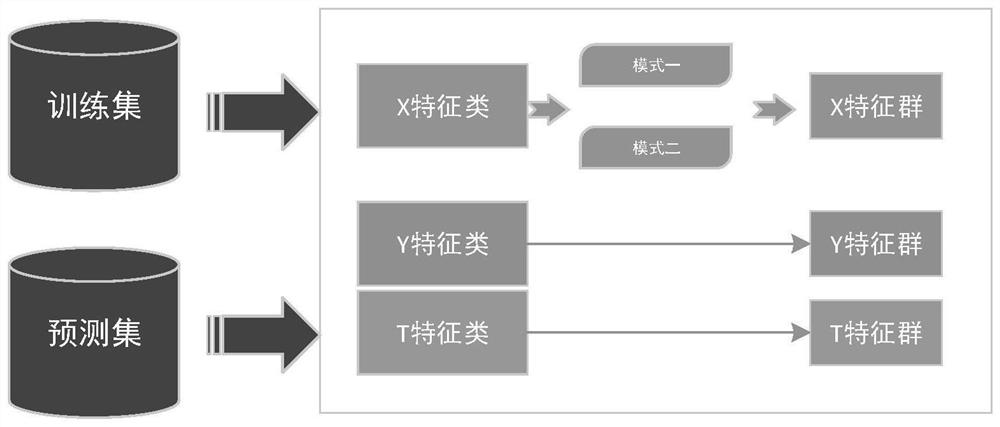
[0046] On the basis of Example 1, the multi-dimensional feature system includes X features, Y features, and T features.
[0047] The present invention mainly uses the horizontal feature x to describe the behavior habits of "people" when performing sliding verification, and uses the longitudinal feature y to describe the characteristics of "machines", and uses the time feature T as a supplement to describe the difference between "human" and "machine". Such as figure 2 shown.
[0048] Further, the specific steps of the X feature extraction are as follows:
[0049] S201: Extracting the X feature class, and normalizing the horizontal coordinate x of the trajectory;
[0050] S202: Combining the phenomenon of "far, fast, near slow" in human trajectory mode 2, the trajectory will be divided into the first half and the second half;
[0051] Specifically, "far, fast, near, slow" indicates that in the process of sliding the verification code, the speed is faster when the distance fr...
Embodiment 3
[0075] On the basis of embodiment 1, the specific steps of the design of the human-machine recognition model of the step S3 are as follows:
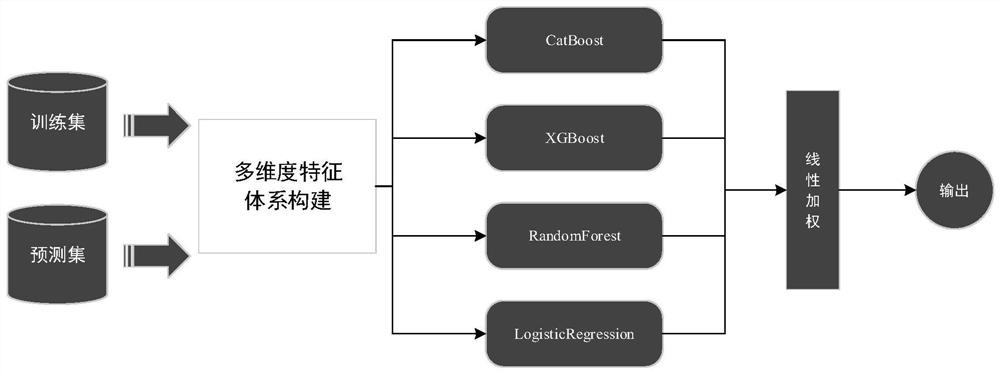
[0076] S301: Input the features in the multi-dimensional feature system into multiple training models for algorithm training;
[0077] S302: Perform linear weighting on the training output of the feature algorithm;
[0078] Further, the training model includes: CatBoost model, XGBoost model, RandomForest model, LogisticRegression model.
[0079] Such as image 3 As shown, specifically, the probability values of the training outputs of the CatBoost model, XGBoost model, RandomForest model, and LogisticRegression model are linearly weighted to obtain a human-machine recognition model linearly weighted by the four basic models.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com