Process for coupled production of sweet whey and lactic acid from acid whey
A technology for joint production, sweet whey, applied in fatty acid production, peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as cost, loss of milk components, and difficulty in spray drying
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
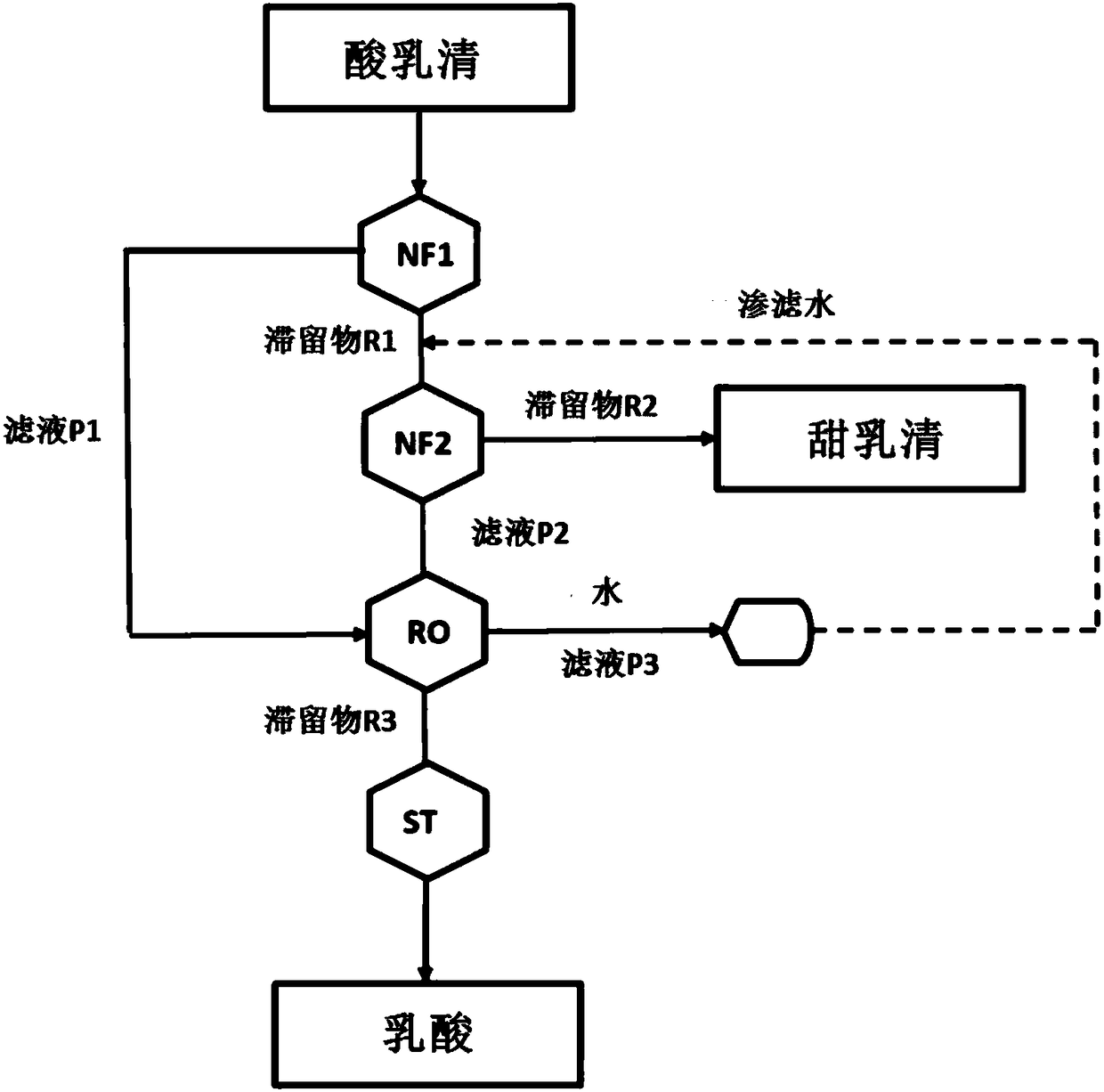
[0034] 100 kg of acid whey with a lactic acid content of 0.45% by weight and a pH value of 4.9 was fed to a nanofiltration step at a flow rate of 5 kg / min with a cut-off of 800 at a temperature of 20° C. and a pressure of 12 bar and a volume concentration factor of 4 Dalton's open membrane for filtration. 75 kg of first filtrate P1 were obtained, which contained 0.365% by weight of lactic acid, and 25 kg of retentate R1, which still contained 0.7% by weight of lactic acid. Thus, 80% of the original amount of lactic acid was detected in the filtrate. 75 kg of water were added to the first retentate and then sent to a further nanofiltration step, filtered through a closed membrane with a cut-off of 200 Daltons at a temperature of 20°C and a pressure of 35 bar. A second filtrate P2 containing 0.18% by weight of lactic acid was obtained, while a second retentate R2 was reduced to 0.2% by weight of lactic acid, thus having the quality of sweet whey.
Embodiment 2
[0036]100 kg of acid whey with a lactic acid content of 0.45% by weight and a pH value of 4.9 was fed to a nanofiltration step at a flow rate of 5 kg / min with a cut-off of 800 at a temperature of 20° C., a volume concentration factor of 4 and a pressure of 35 bar. Dalton's open membrane for filtration. A first filtrate P1 containing 0.23% by weight of lactic acid and a first retentate R1 containing 1.1% by weight of lactic acid were obtained. Therefore, only 50% of the original amount of lactic acid was detected in the filtrate in this example. 75 kg of water (P3) were added to the first retentate and then sent to a further nanofiltration step, filtered through a closed membrane with a cut-off of 200 Daltons at a temperature of 20° C. and a pressure of 35 bar. A second filtrate P2 is obtained, which contains 0.05% by weight of lactic acid, while a concentrate of 0.95% by weight of lactic acid is reduced in the second retentate R2, which roughly corresponds to about 0.27% by w...
Embodiment 3
[0038] 100 kg of acid whey with a lactic acid content of 0.45% by weight and a pH of 4.9 was fed to the nanofiltration step at a flow rate of 5 kg / min with a cut-off of 200 at a temperature of 20° C., a volume concentration factor of 4 and a pressure of 35 bar. Dalton's open membrane for filtration. 75 kg of the first filtrate P1 were obtained, which contained 0.11% by weight of lactic acid, and 25 kg of the first retentate R1, which still contained 1.47% by weight of lactic acid. Thus, 25% of the original amount of lactic acid was detected in the filtrate. 75 kg of water (P3) were added to the first retentate and subjected to nanofiltration through a closed membrane with a cut-off of 200 Daltons at a temperature of 20°C and a pressure of 35 bar. The second filtrate P2 was obtained, which contained 0.09% by weight of lactic acid, while the second retentate R2 concentrate contained 1.2% by weight of lactic acid, corresponding to the original concentration of 0.3% by weight of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com