Calculation method and device for explicit time iterative time domain electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field and time-domain technology, which is applied in the field of time-domain electromagnetic field simulation calculations, can solve problems such as algorithm instability, and achieve the effects of parallel computing, small amount of calculation, and wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] A prediction method in time-domain electromagnetic field numerical calculation, the time-domain electromagnetic field numerical calculation adopts explicit iteration on time, the iteration time step is limited by the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy condition, in the previous time step, only the position to be sought and the position to be sought Finding the electromagnetic field value at the adjacent position of the position will have an impact on the position to be sought at the current time step, and it is characterized in that:
[0080] The electromagnetic field value of the position to be requested in the current time step is predicted by the electromagnetic field value of the position to be requested in the previous time step and the adjacent positions of the position to be requested.
[0081] The numerical calculation of the electromagnetic field in the time domain includes but is not limited to numerical calculation methods such as FDTD and DGTD, which are not specificall...
Embodiment 2
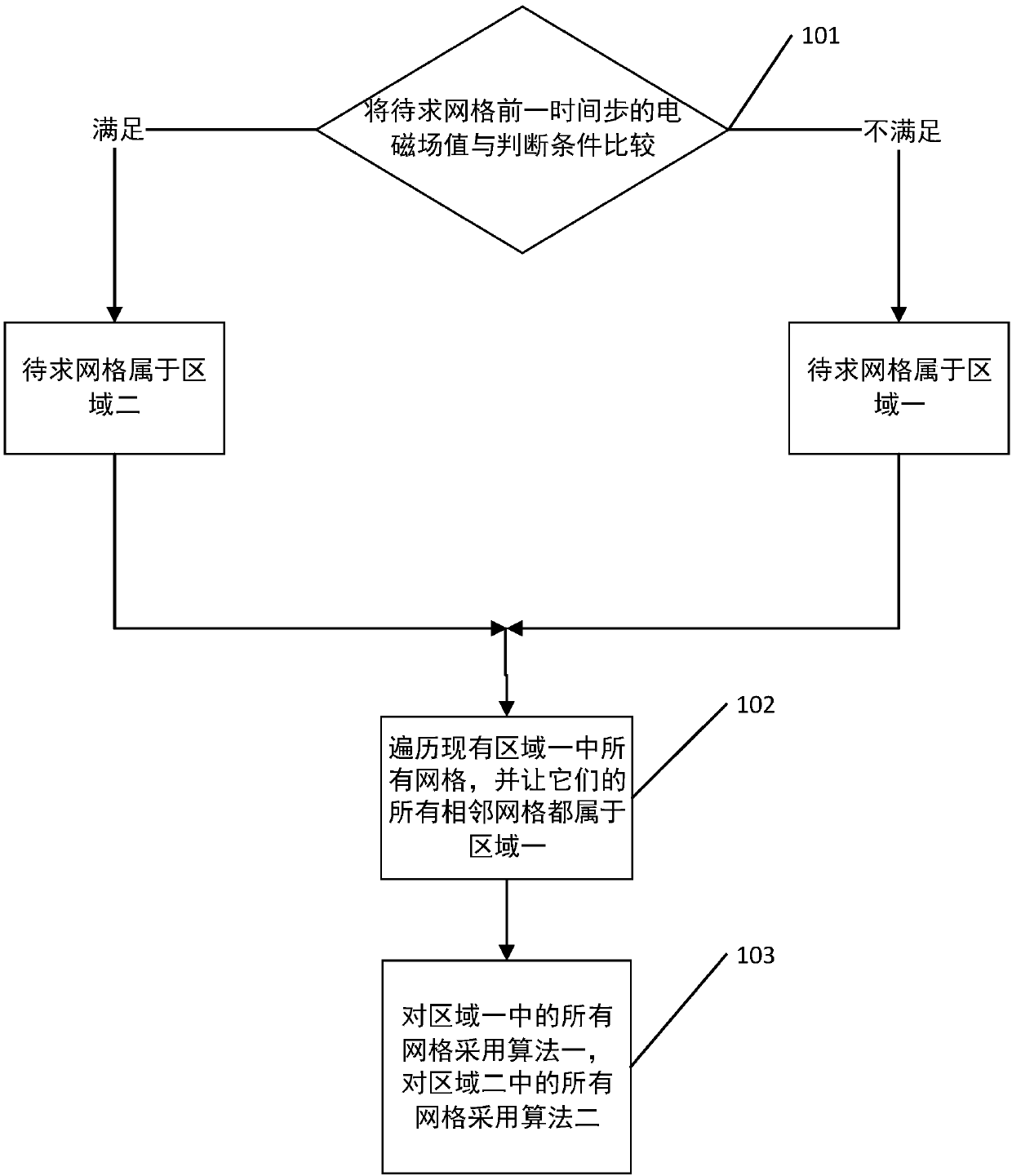
[0089] see figure 1 , this embodiment provides an explicit iterative time-domain limited electromagnetic field calculation method limited by the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy stability condition, including:
[0090] 101 Comparing the electromagnetic field value of each position to be requested in the previous time step with the judgment condition, if the judgment condition is satisfied, the position belongs to area 2, otherwise it belongs to area 1;
[0091] 102 traverse all the positions in the existing area 1, and let all their adjacent positions also belong to the area 1;
[0092] 103 adopt Algorithm 1 for all positions in Area 1, and use Algorithm 2 for all positions in Area 2;
[0093] said location is a grid cell or a grid edge or a grid node;
[0094] The first algorithm is a universal algorithm that can be used for any electromagnetic field value at the location to be sought, and the second algorithm is an approximate algorithm that can be used when the electromagnetic fie...
Embodiment 3
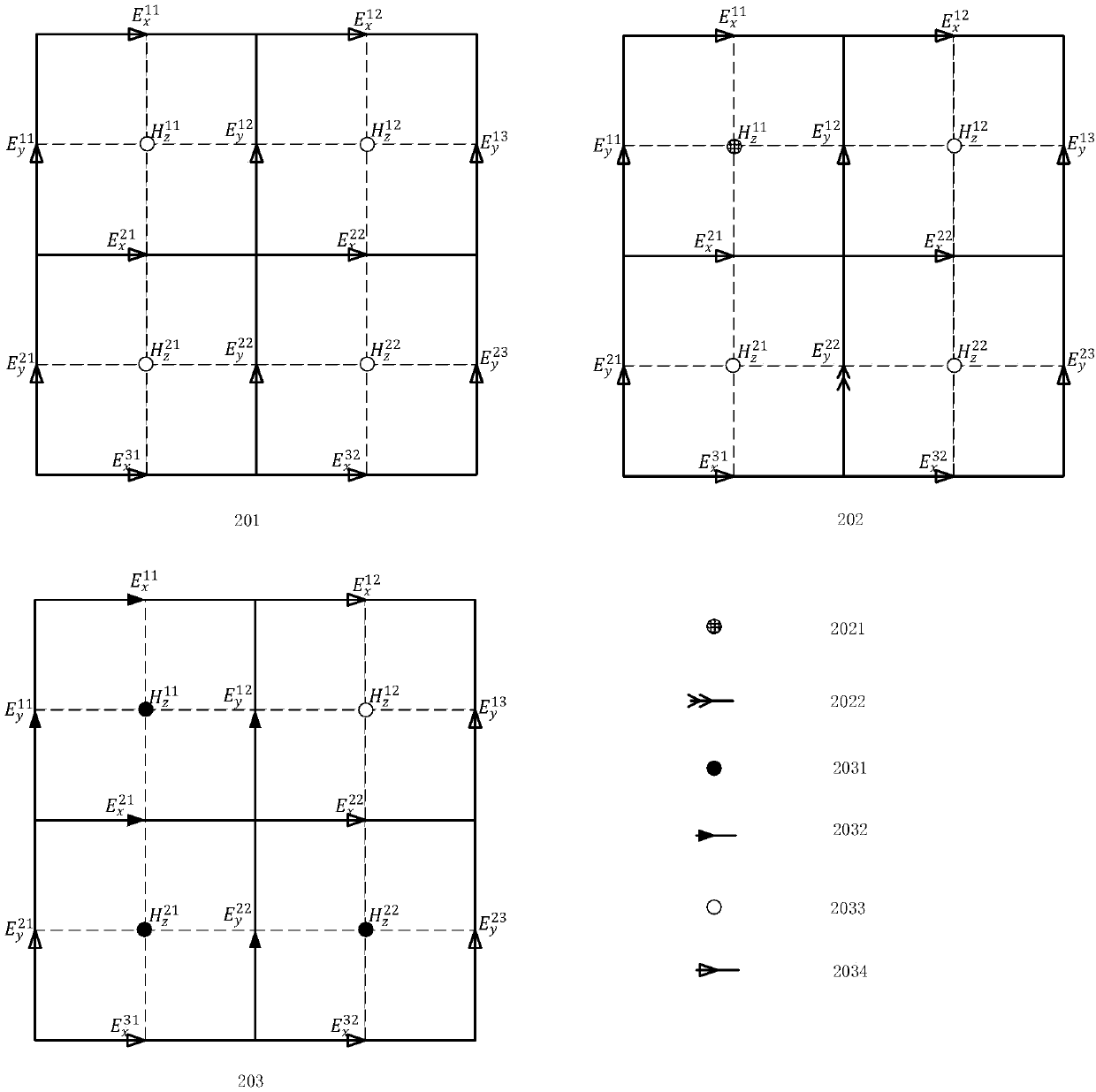
[0107] Referring to FIG. 201 , it is a rectangular two-dimensional calculation area and grid division. This embodiment uses this structure as a specific embodiment, and this structure is not intended to limit the present disclosure. This embodiment provides an explicit iterative time-domain limited electromagnetic field calculation method limited by the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy stability condition, the process is as follows figure 1 ,include:
[0108] 101 Comparing the electromagnetic field value of each position to be requested in the previous time step with the judgment condition, if the judgment condition is satisfied, the position belongs to area 2, otherwise it belongs to area 1;
[0109] 102 traverse all the positions in the existing area 1, and let all their adjacent positions also belong to the area 1;
[0110] 103 adopt Algorithm 1 for all positions in Area 1, and use Algorithm 2 for all positions in Area 2;
[0111] The locations are mesh edges or mesh nodes.
[01...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com