Systems and methods for predicting vitreous half-life of therapeutic agent-polymer conjugates
A half-life, polymer technology, applied in chemical property prediction, drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulation, etc., can solve problems such as misinterpretation, potential defects of therapeutic agent-polymer conjugates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
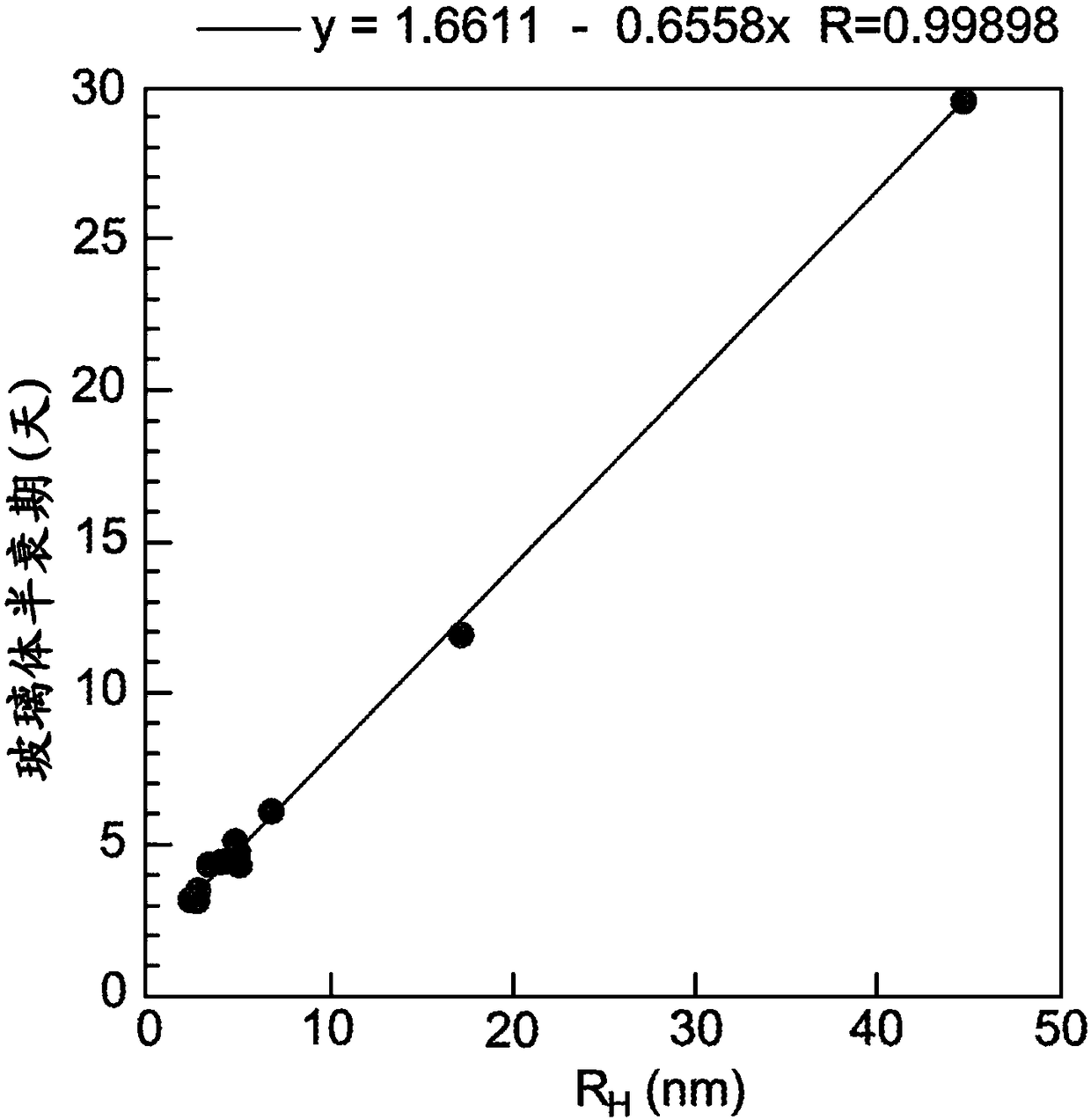
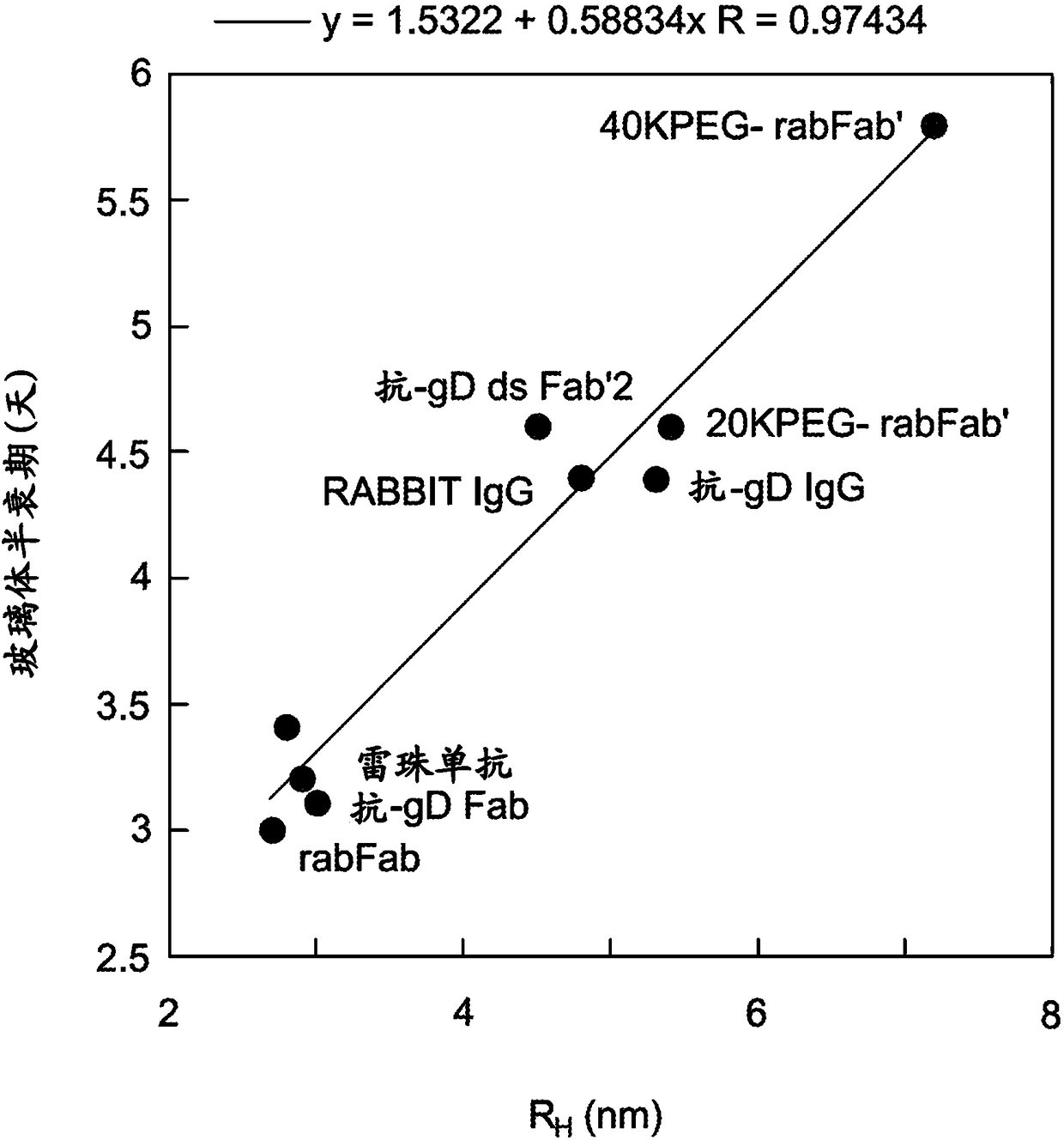
[0149] Example 1: Vitreous Pharmacokinetics of rabFab Surrogate Compounds
[0150] Development of delivery technologies for protein therapeutics requires testing in relevant animal models to demonstrate in vivo utility. Rabbit models were commonly used in early studies of ocular pharmacokinetics. Unfortunately, most human and humanized antibodies are immunogenic in rabbits, precluding the use of long-acting delivery technologies to estimate key pharmacokinetic parameters. To address this issue, a rabbit Fab ("rabFab"), a species-matched surrogate compound, was used to evaluate the delivery technology in a rabbit model. The rabFabs described herein are derived from rabbit monoclonal antibodies that bind human phospho-c-Met.
[0151] Methods of making rabbit antibodies, including rabbit monoclonal antibodies, are well known in the art. See, eg, US Patent Nos. 5,675,063 and / or 7,429,487. An exemplary rabbit monoclonal antibody that binds to human phospho-c-Met is commercial...
Embodiment 2
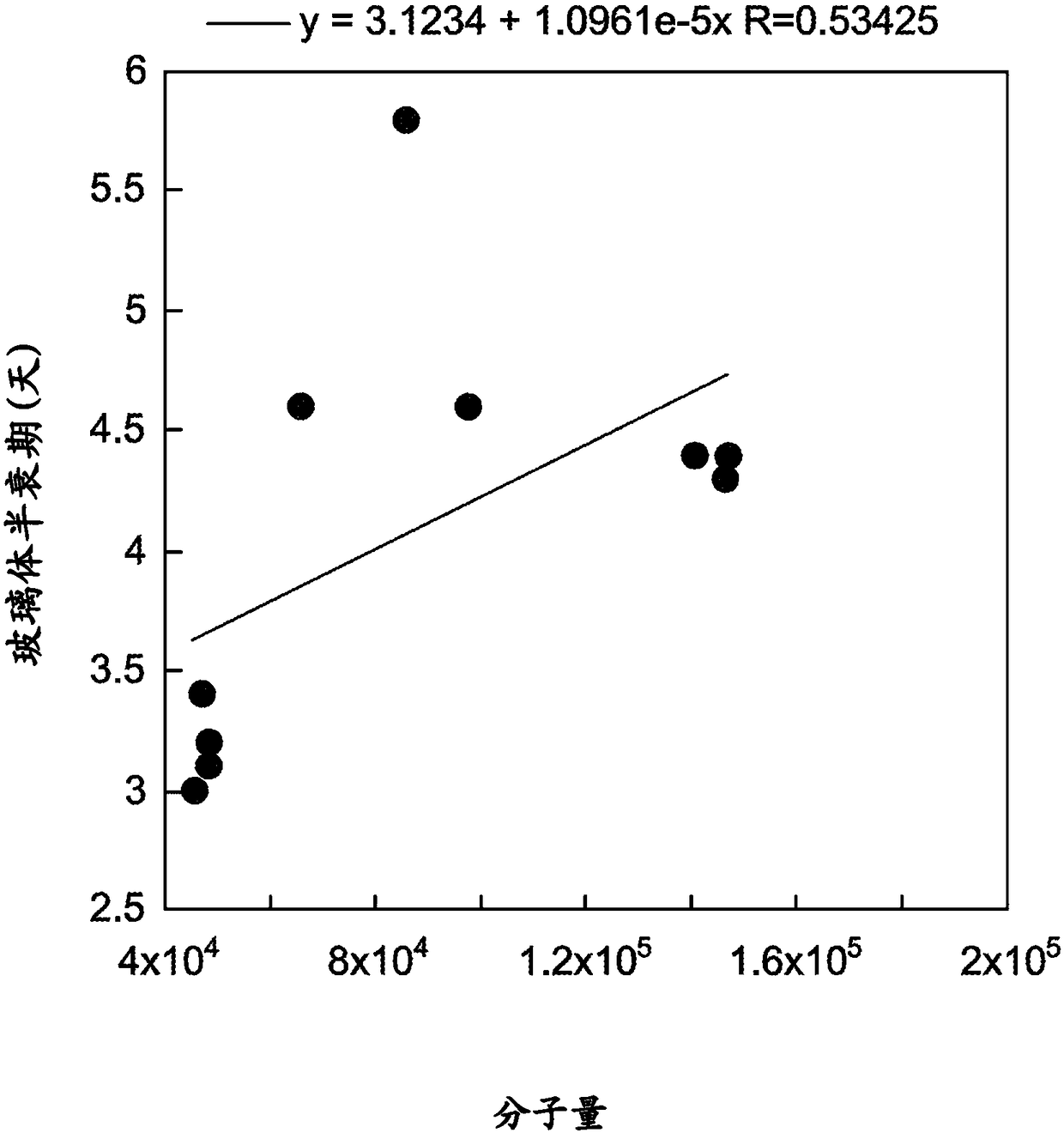
[0166] Example 2: Vitreous Pharmacokinetics of Surrogate-Polymer Conjugates
[0167] To further evaluate the efficacy of rabFab as a surrogate testing technology to improve vitreous pharmacokinetics, a PEGylated version of the rabFab molecule was generated as follows and PK tested using the method described in Example 1. To maintain the binding activity of the rabFab molecule, PEG-maleimide was used for site-specific conjugation to modify the free Cys (Cys-227) in the Fab' form of the rabbit antibody. Linear PEG chains of 20,000 Da and 40,000 Da molecular weight were conjugated to rabFabs to generate PEGylated (20 kD) anti-phospho cMet Fab conjugates and PEGylated (40 kD) anti-phospho cMet Fab conjugates.
[0168] Rabbit Fab' was dialyzed against PBS, pH 7.4, and then EDTA was added to a final concentration of 5 mM. To remove free thiol adducts, fresh DTT was added at a molar ratio of 1:1.2 (Fab':DTT) and samples were left overnight at room temperature. Adduct removal was ...
Embodiment 3
[0178] Example 3: Effect of FcRn Binding on Vitreous Half-Life
[0179] To test the effect of FcRn binding on the kinetics of vitreous clearance, the rabbit model and methods described in Example 1 were used to assess the vitreous half-life of two mutant forms of IgG.
[0180] The effect of binding to the recovered FcRn receptor on the vitreous half-life of IgG was tested with antibody mutations known to abolish FcRn binding. For circulating IgG antibodies, FcRn promotes half-life by protecting IgG from catabolism through non-specific pinocytosis (Roopenian & Akilesh (2007) Nat. Rev. Imm. 7:715). Substitutions H310A and H435Q in the Fc region of the antibody were associated with greatly reduced FcRn binding and rapid systemic clearance (Kenanova et al. (2005) Cancer Res. 65:622). These substitutions were introduced into the Fc portion of the humanized 5B6 (anti-gD) antibody using oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis as described in Example 4 below. Wild-type and H310A:H435...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com