Degradation method for polyethylene plastics
A polyethylene plastic and raw material technology, applied in the field of environmental protection, can solve pollution and other problems, and achieve the effect of easy contact degradation and secondary reuse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
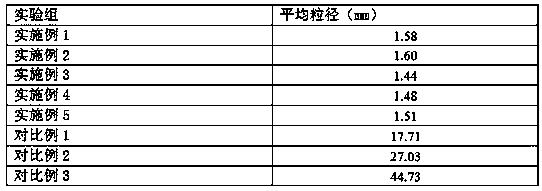
Embodiment 1
[0026] A method for degrading polyethylene plastics is characterized in that it comprises the following specific steps:
[0027] S1. Sieve the collected plastic raw materials, clean them, and perform mechanical destruction to reduce their volume;
[0028] S2. Put the pretreated raw materials into the soaking solution for soaking for 24 hours, and keep the soaking temperature at 37°C;
[0029] S3. Cleaning the soaked raw materials, adding them to the fermenter for fermentation and degradation;
[0030] S4. Collect the degraded mixed solution, waiting for secondary extraction and recycling.
[0031] The soaking solution in the step S2 includes the following components in parts by weight: calcium hydroxide 6, sodium hydroxide 9, ammonium chloride 6, ammonium bicarbonate 11, triethanolamine 5, and isopropanol 4.
[0032] Further, the concentration of the soaking solution is 0.12moL / L-0.46moL / L.
[0033] The soaking liquid in the present invention can be combined with the functi...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for degrading polyethylene plastics is characterized in that it comprises the following specific steps:
[0039] S1. Sieve the collected plastic raw materials, clean them, and perform mechanical destruction to reduce their volume;
[0040] S2. Put the pretreated raw materials into the soaking solution for soaking for 72 hours, and keep the soaking temperature at 60°C;
[0041] S3. Cleaning the soaked raw materials, adding them to the fermenter for fermentation and degradation;
[0042] S4. Collect the degraded mixed solution, waiting for secondary extraction and recycling.
[0043] The soaking solution in the step S2 includes the following components in parts by weight: calcium hydroxide 13, sodium hydroxide 15, ammonium chloride 18, ammonium bicarbonate 26, triethanolamine 19, and isopropanol 9.
[0044] Further, the concentration of the soaking solution is 0.46moL / L.
[0045] Further, the process of fermentation and degradation in the step S3 is: the total n...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A method for degrading polyethylene plastics is characterized in that it comprises the following specific steps:
[0050] S1. Sieve the collected plastic raw materials, clean them, and perform mechanical destruction to reduce their volume;
[0051] S2. Put the pretreated raw materials into the soaking solution for soaking for 48 hours, and keep the soaking temperature at 49°C;
[0052] S3. Cleaning the soaked raw materials, adding them to the fermenter for fermentation and degradation;
[0053] S4. Collect the degraded mixed solution, waiting for secondary extraction and recycling.
[0054] The soaking solution in the step S2 includes the following components in parts by weight: 10 calcium hydroxide, 12 sodium hydroxide, 12 ammonium chloride, 19 ammonium bicarbonate, 12 triethanolamine, and 7 isopropanol.
[0055] Further, the concentration of the soaking solution is 0.29moL / L.
[0056] Further, the fermentation degradation process in the step S3 is: the total number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com