Item semantic annotation method based on use event of heterogeneous item
A technology using events and items, applied in computer parts, semantic tool creation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems of lack of manual annotation in cyber-physical space, inability to achieve annotation performance, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the examples. The description of the following examples is provided only to aid the understanding of the present invention. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, without departing from the principle of the present invention, some improvements and modifications can be made to the present invention, and these improvements and modifications also fall within the protection scope of the claims of the present invention.
[0037] The item semantic labeling method based on heterogeneous item usage events includes the following steps:
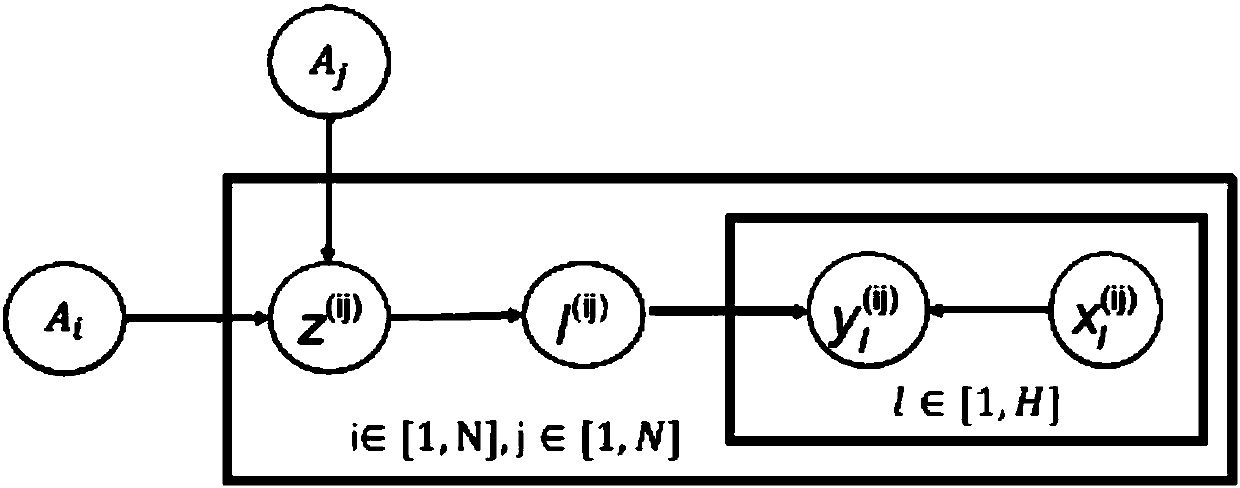
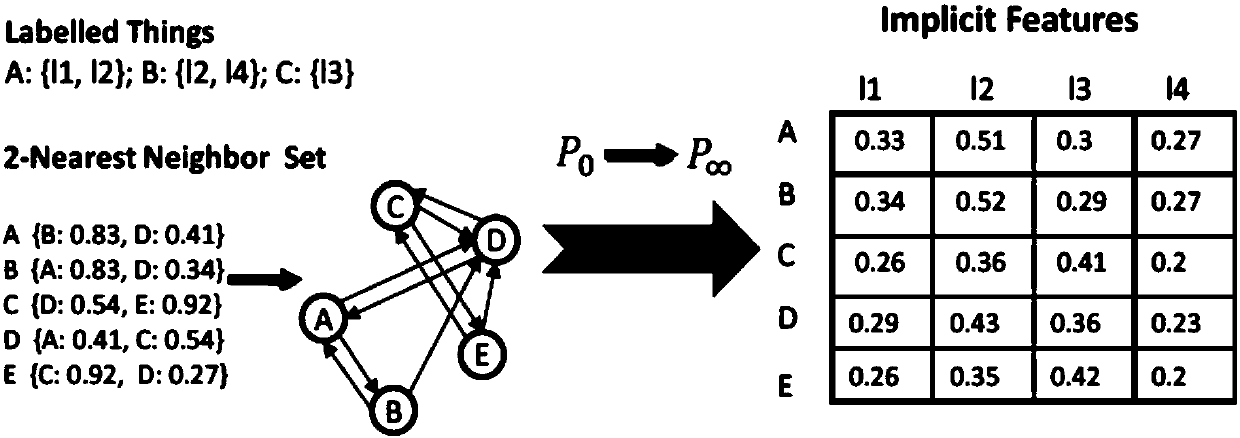
[0038] 1. Training item potential relationship strength mining model
[0039] definition for the item o i and o j Between usage events, I (ij) for the item o i with o j The strength of the underlying relationship between, is the evaluation index of attribute similarity between items, Represents some auxiliary variables introduced to increas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com