Process for production and extraction of dihydrolipoic acid
A technology of dihydrolipoic acid and microbial culture, applied in the direction of fat oil/fat production, fat production, bacteria used in food preparation, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to separate and stabilize DHLA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
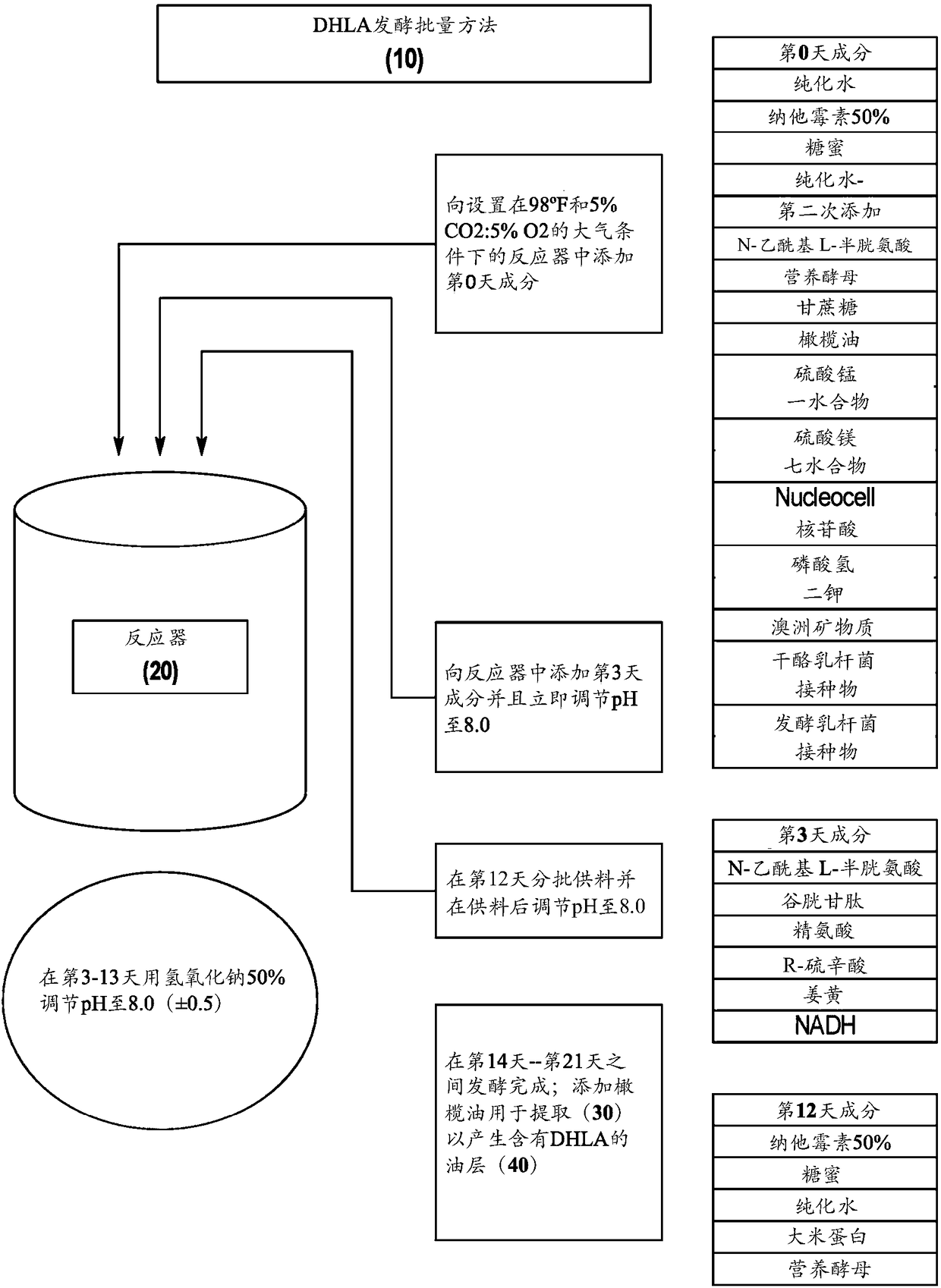
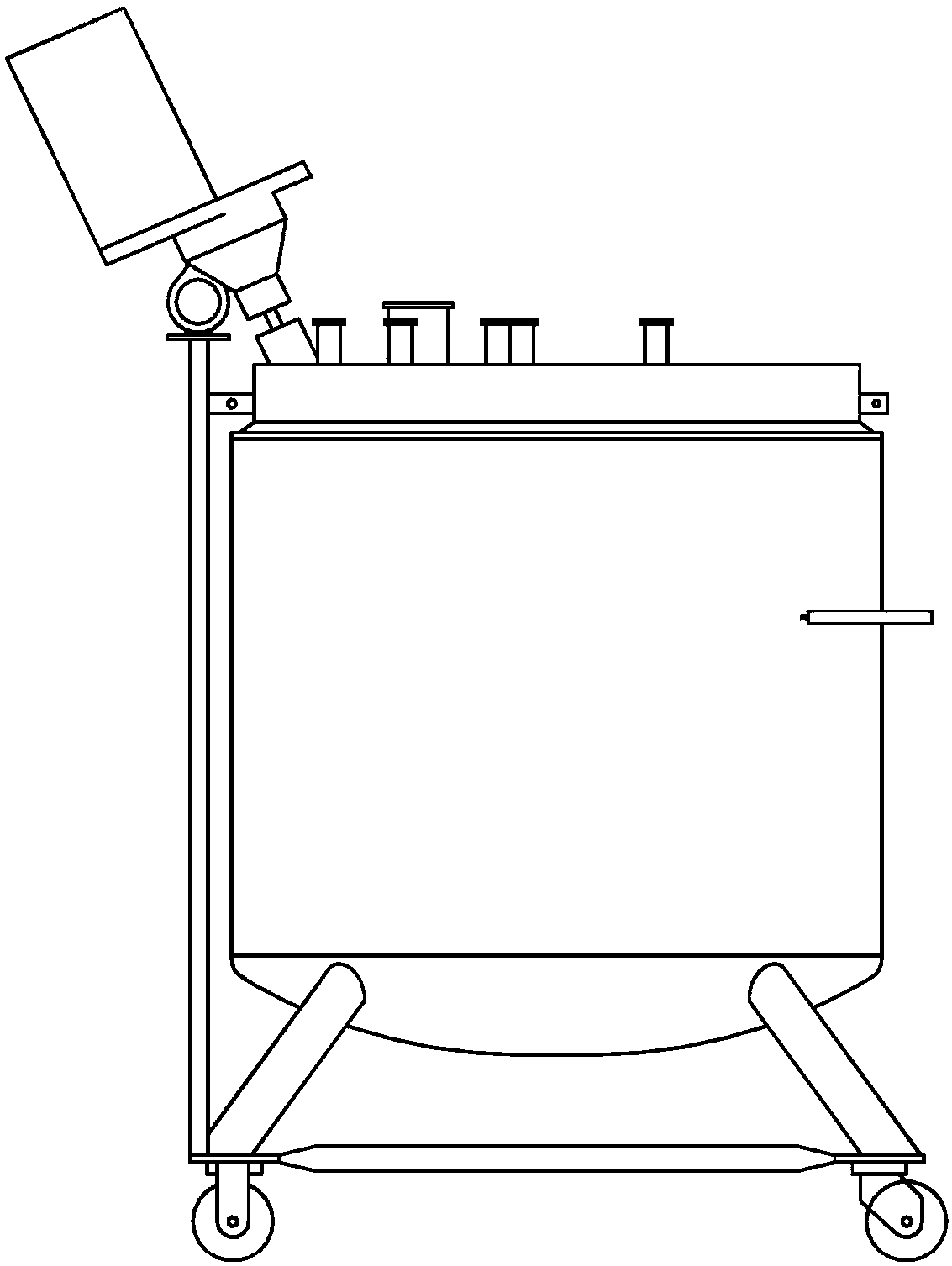
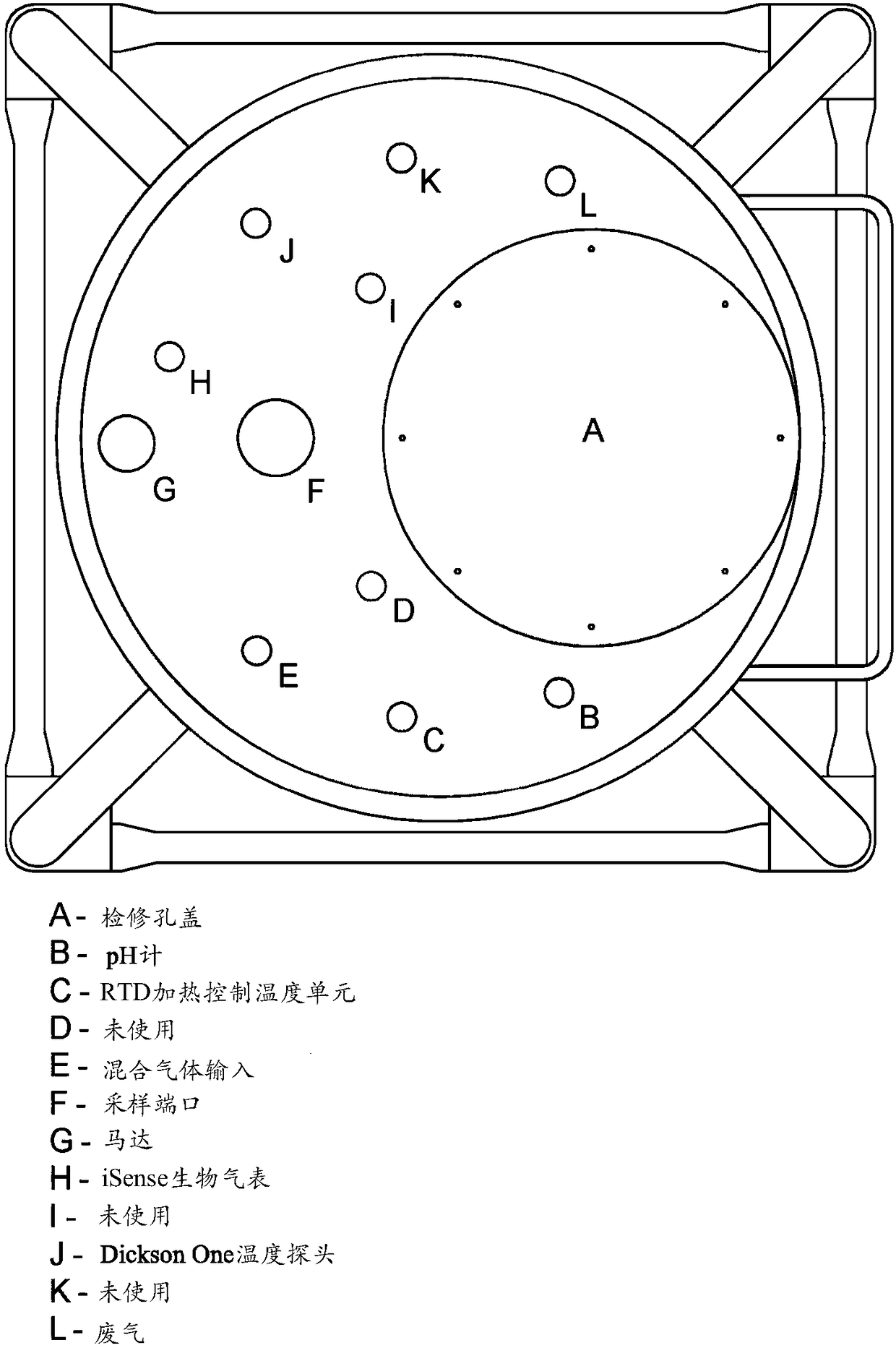
[0083] DHLA batch fermentation method (batch mode)
[0084] (1) A 48-hour inoculum culture was prepared from stock cultures of Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus fermentum as follows.
[0085] (1a) Lactobacillus casei inoculum preparation:
[0086] Forty-eight hours prior to the mixing start date, the L. casei inoculum was prepared. Ten (10) grams of stock (0022) freeze-dried 10 billion CFU / g Lactobacillus casei (from Nebraska Cultures, Inc.) was added to Edge Biologicals in Memphis, TN. Co., Ltd. Catalog No. B-0965 (Edge Biologicals, Inc. Catalog No. B-0965 Memphis, TN) provided 500mL MRS fermentation broth. The inoculum was incubated at 37°C in an atmosphere of 90% N2:5% CO2:5% O2. After 48 hours of incubation, 500 mL of the inoculum was washed twice with phosphate buffered saline using a centrifuge. The washed pellet was then reconstituted with a total of 100 mL of phosphate buffer and combined into one vessel to inoculate the DHLA fermentation batch.
[0087] (1b) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com