Dynamic cooperative relay transmission method based on power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology
A non-orthogonal multiple access and access technology, applied in the field of dynamic cooperative relay transmission, can solve the problems of low reliability of edge users and waste of time slot resources of base stations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
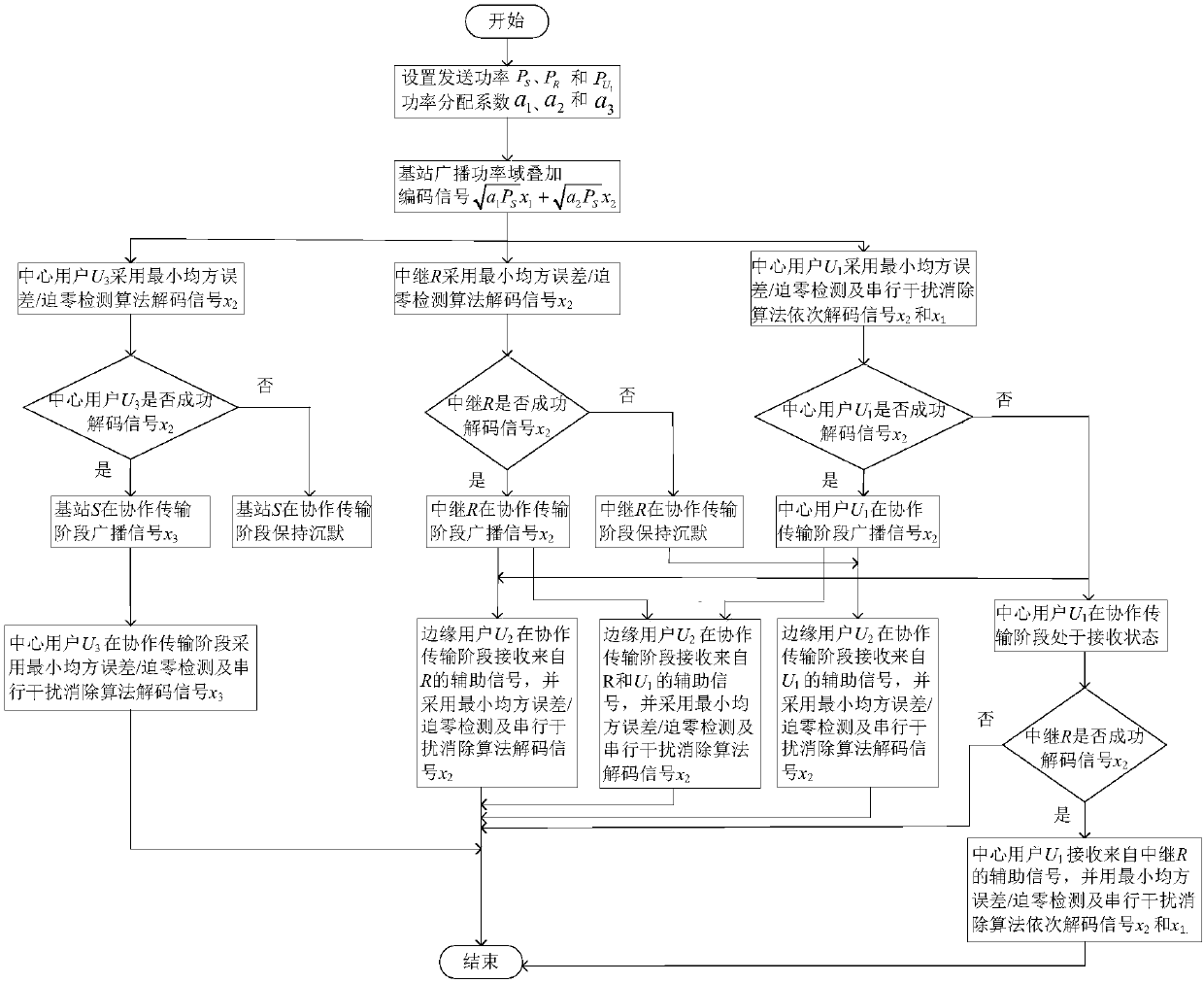
[0068] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the specific process of the dynamic cooperative relay transmission method based on power domain non-orthogonal multiple access technology in this embodiment is as follows:
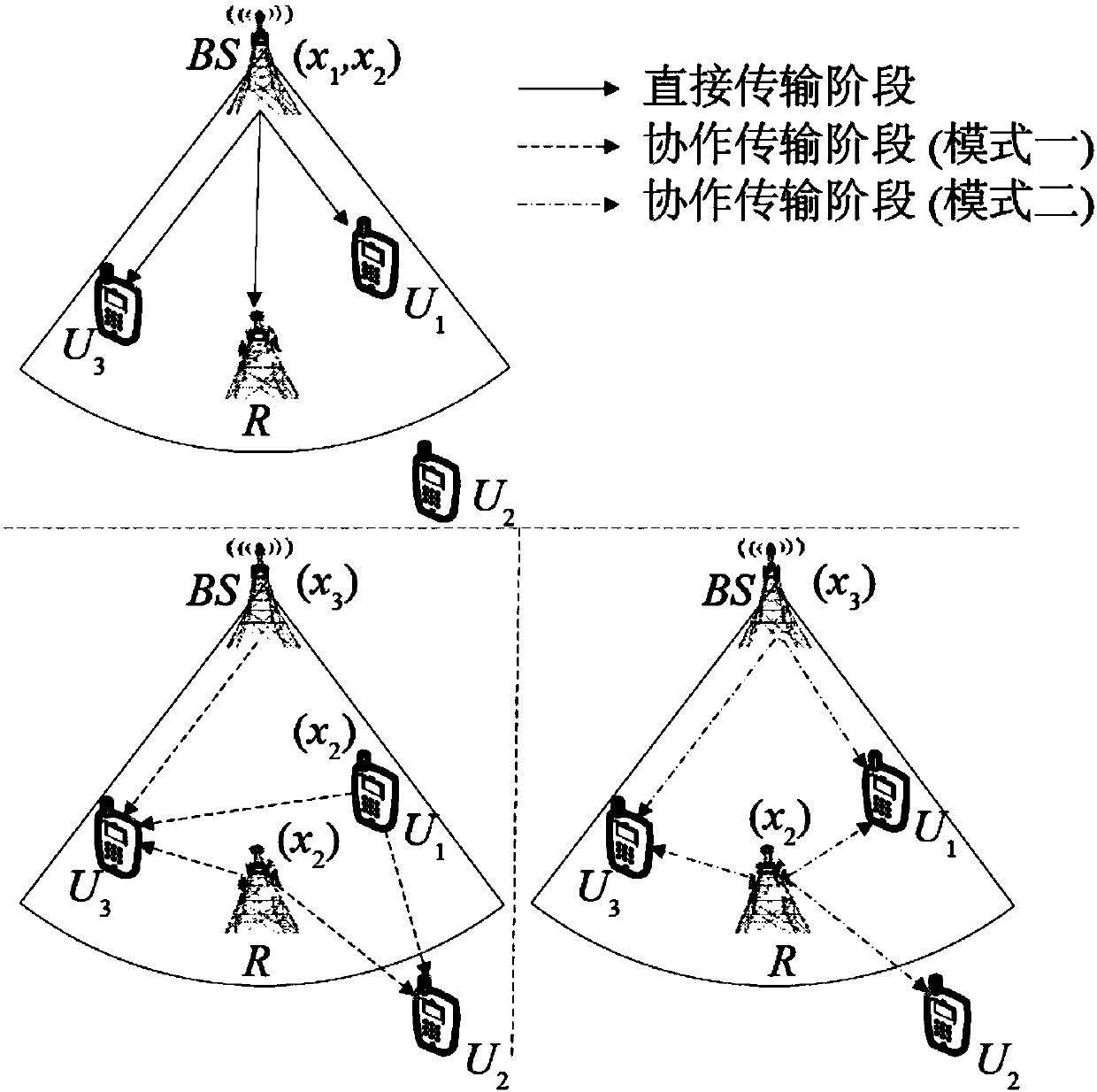
[0069] Step 1. Set up a cell containing N mobile users. The number of central users who communicate directly with the base station S is M, and the number of edge users who cannot directly communicate with the base station S is L. L≥M / 2, N=L+M , sort the channel quality of the central users, and select two central users with the best channel quality, an edge user with the best channel quality, and a decoding and forwarding relay closest to the edge user for pairing. Therefore, M / 2 user pairs can be obtained, and frequency division multiple access is used to distinguish between different user pairs;
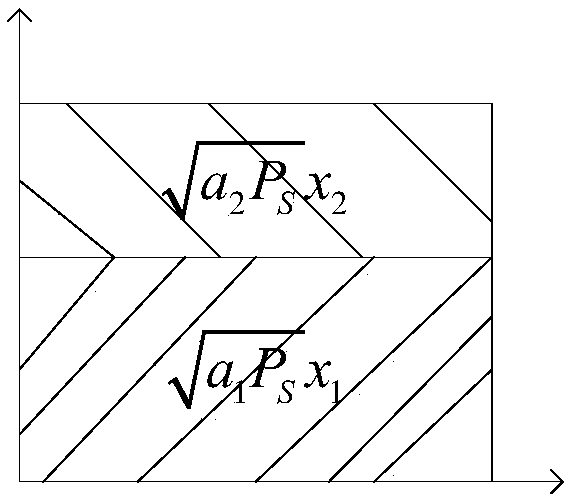
[0070] The information transmission process includes two phases: the direct transmission phase and the cooperative transm...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0115] Specific embodiment 2: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is: in the step 4, it is judged that the central user U 3 Whether the edge user U is successfully decoded 2 Information x 2 , yes, go to step 6; no, go to step 5;
[0116] The specific process is:
[0117] Set the bit error rate threshold (manually set), greater than or equal to the bit error rate threshold, the decoding fails; less than the bit error rate threshold, the decoding is successful;
[0118] BER threshold is 10 -3 -10 -5 .
[0119] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0120] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in the step nine, it is judged whether the decoding and forwarding relay R has successfully decoded the information x 2 , yes, go to step 10; no, go to step 11; the specific process is:
[0121] Set the bit error rate threshold (manually set), greater than or equal to the bit error rate threshold, the decoding fails; less than the bit error rate threshold, the decoding is successful;
[0122] BER threshold is 10 -3 -10 -5 .
[0123] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com