Method for predicting thermal expansion coefficient of polymer-based composite material based on free-radical content prediction thermal cycle
A thermal expansion coefficient and composite material technology, applied in the thermal expansion coefficient of materials, analysis materials, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of high measurement difficulty and long measurement time, and achieve the effect of saving measurement time and simplifying the measurement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
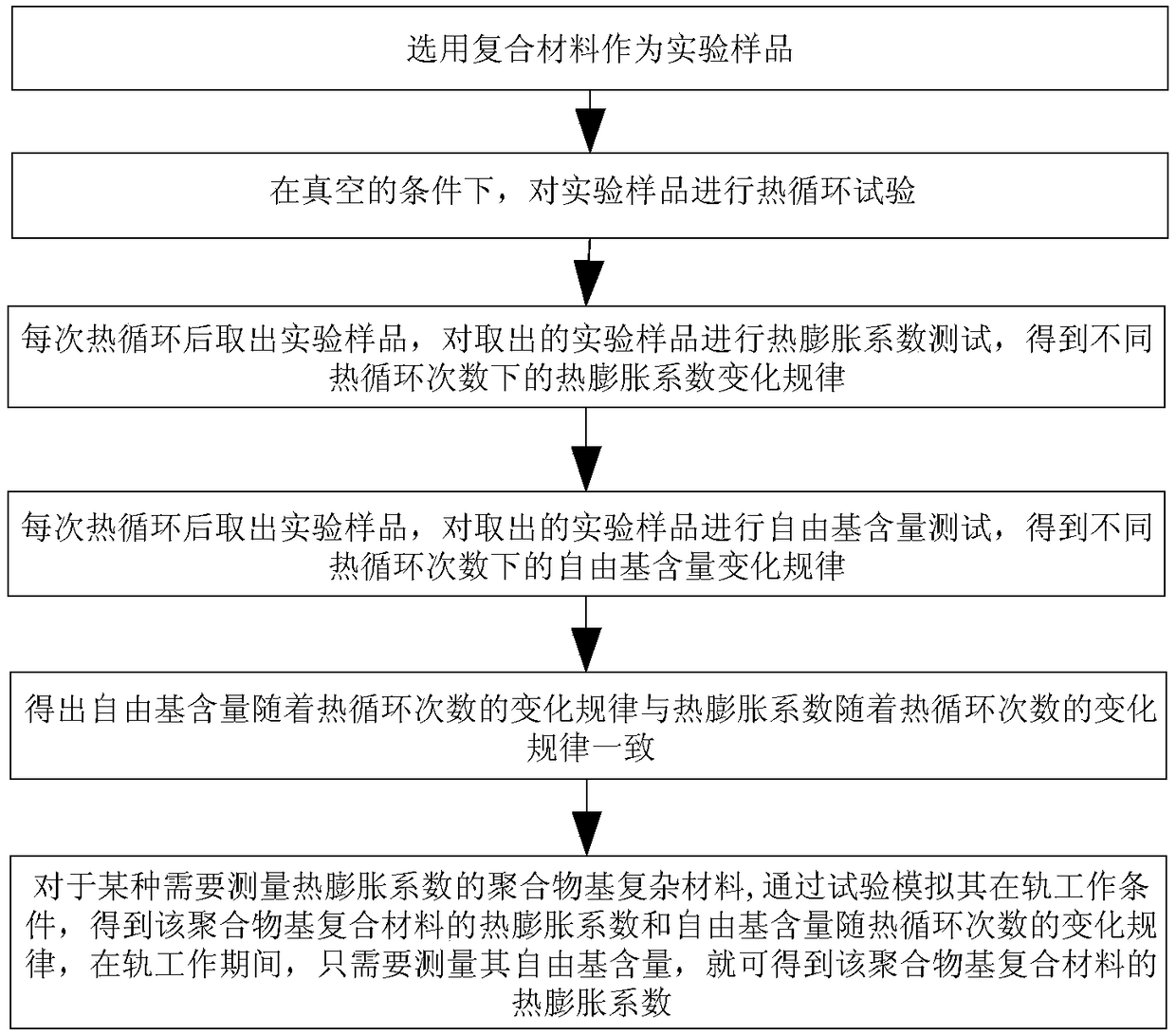
[0029] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 This embodiment will be described. A method for predicting the effect of thermal cycles on the thermal expansion coefficient of polymer-based composite materials based on the content of free radicals described in this embodiment, the specific steps of the method are:
[0030] Step 1. Select the polymer-based composite material as the experimental sample, and conduct a thermal cycle test on the selected experimental sample under the condition that the vacuum degree is less than 1Pa; set the number of thermal cycles for each thermal cycle test to not less than 200 times, The number of groups of thermal cycle test shall not be less than 3 groups;
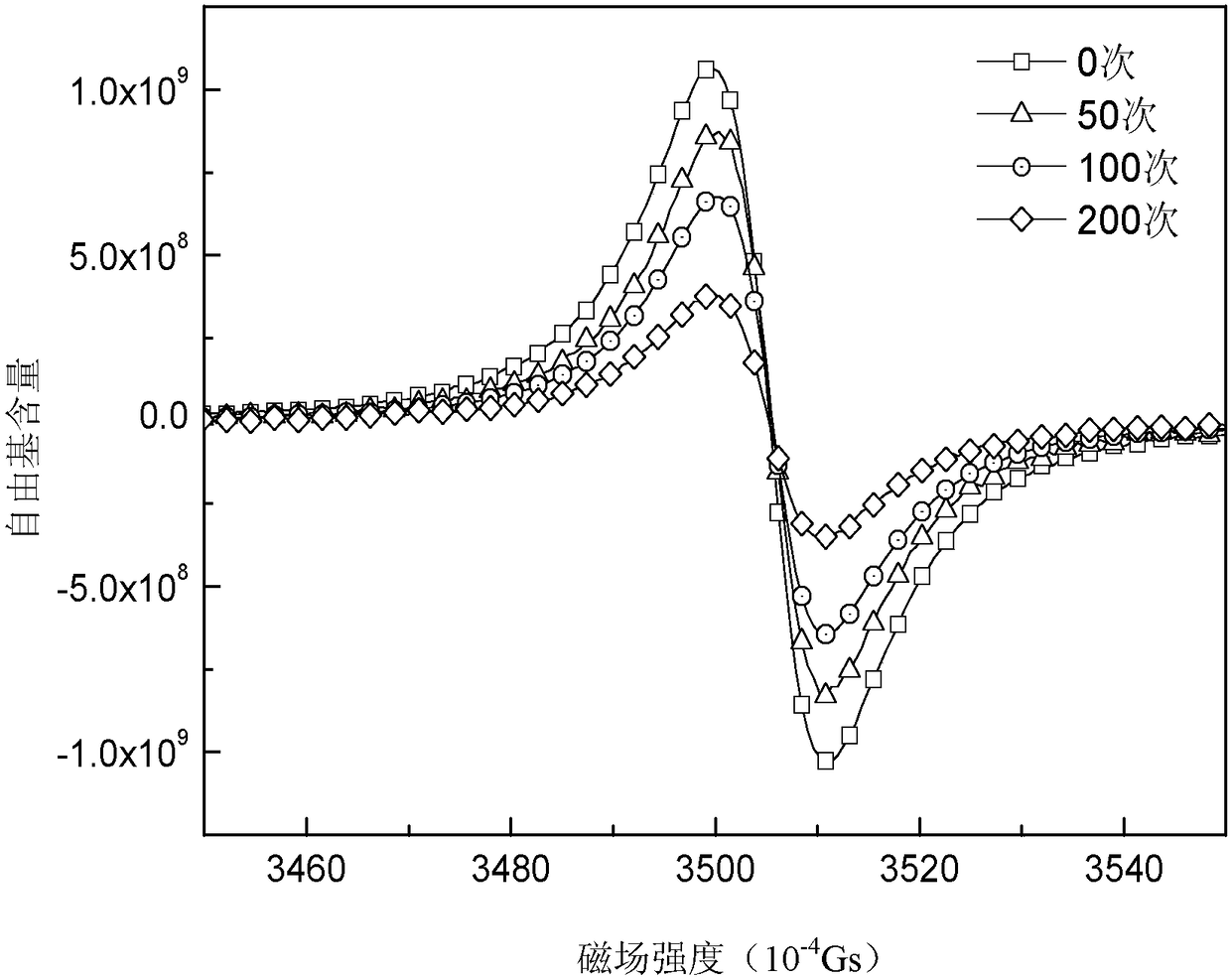
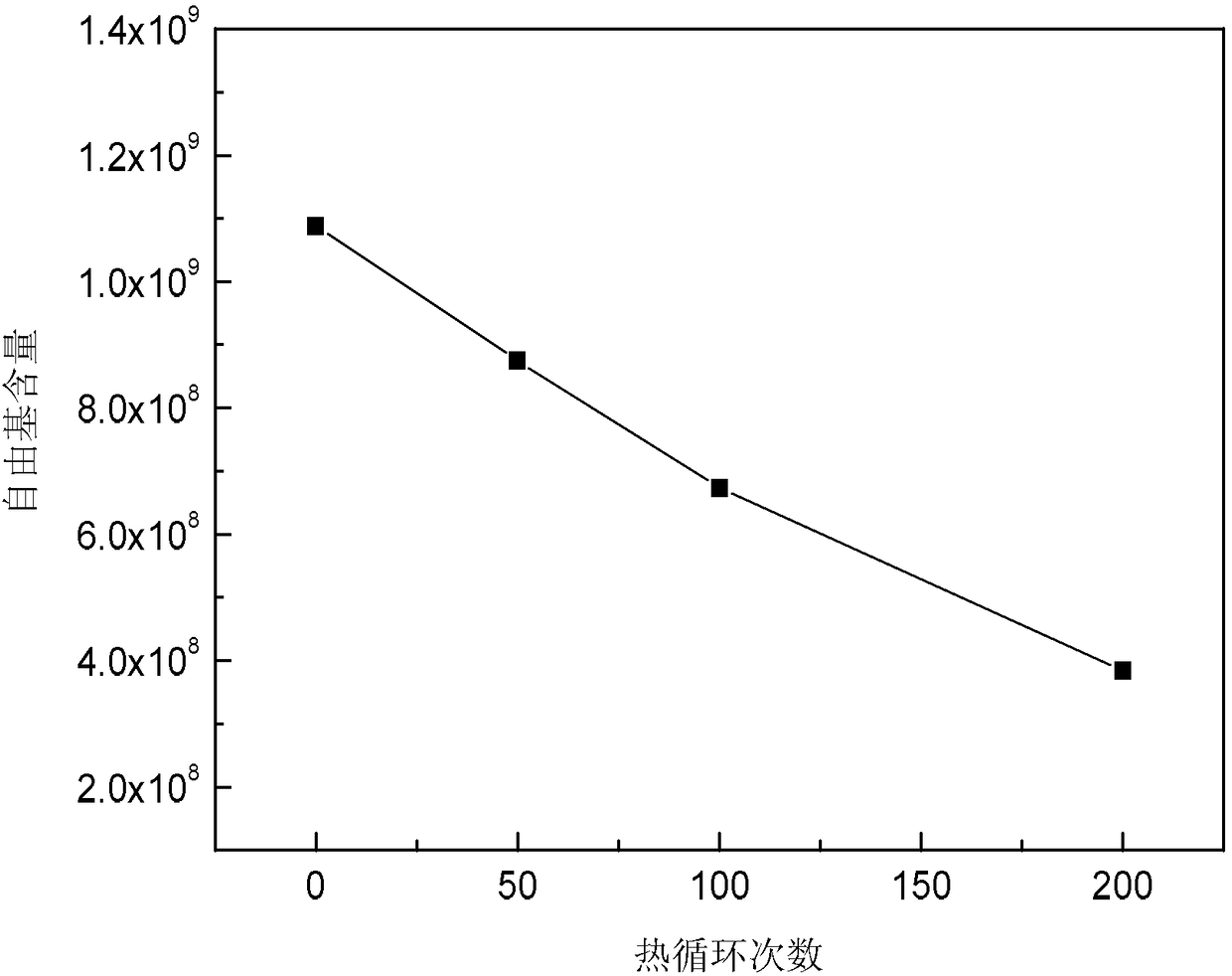
[0031] Step 2, take out the experimental sample after each thermal cycle, and test the thermal expansion coefficient of the experimental sample taken out; record the thermal expansion coefficient under the different thermal cycle times of each group of thermal cycle tests respe...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0039] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment further limits the method for estimating the effect of thermal cycles on the thermal expansion coefficient of polymer-based composite materials based on the content of free radicals described in Embodiment 1. In step 1 of this embodiment The size of the experimental sample is: length 20mm~25mm, width 5mm~6mm, thickness 1mm~3mm; set the temperature range of each thermal cycle to -150℃~150℃;
[0040] Set the ambient temperature around the experimental sample to gradually cool down from 150°C to -150°C, the cooling rate is x, and 0.2≥x>0, the unit is °C / min, and then gradually increase the ambient temperature from -150°C at the heating rate x to 150°C; when the ambient temperature around the experimental sample is from 150°C to -150°C, and then from -150°C to 150°C, it is a thermal cycle;
[0041] In this embodiment, the temperature range of each thermal cycle is set to be -150° C. to 150° C. to ensure that the test temperature of the...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment further limits the method for estimating the effect of thermal cycles on the thermal expansion coefficient of polymer-based composite materials based on the content of free radicals described in embodiment two, and the polymer-based composite material is carbon fiber composite material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com